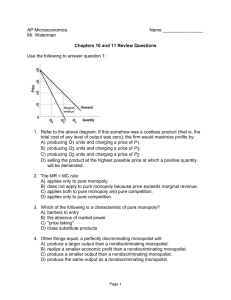
1 Which of the following is the best description of a
advertisement

1 Which of the following is the best description of a monopolistically competitive industry? A) An industry in which a large number of rival firms sell products that are close, but not perfect, substitutes. B) An industry in which a large number of rival firms sell products that are identical. C) An industry in which a small number of large firms sell products that are either close or perfect substitutes. D) substitutes. An industry in which there is only one supplier of a product with no close 2 Which of the following is the best definition of market power? A) The proportion of a firm's market share. B) The ability of a firm to earn accounting profit in the long-run. C) The ability of a firm to expand its output without losing profit. D) The ability of a firm to raise the price of a good without losing all of its sales. 3 If a firm is experiencing economies of scale, it means ______ are ______ as output increases. A) marginal costs; increasing. B) average total costs; increasing. C) total costs; increasing. D) average total costs; decreasing. 4 Which of the following firms is the most likely to exhibit economies of scale? A) One with large fixed costs and large marginal costs. B) One with large fixed costs and small marginal costs. C) One with small fixed costs and small marginal costs. D) One with small fixed costs and large marginal costs. 5 A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P=100 – 2Q. The equation for their marginal revenue curve is given by: A) MR = 100 – 4Q. B) MR = 200 – 2Q. C) MR = 100 – Q. D) MR = 200 – Q. 6 A monopolist's economic profit will be positive when: A) price exceeds average total cost. B) marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost. C) price is less than average total cost. D) a monopolist's profit will always be positive. 7 Use the following diagram representing a single price monopolist to answer the following question. The profit of the monopolist shown in the diagram above equals A) $1,000 B) $400 C) $600 D) cannot be determined from this graph 8 A monopolist produces a _____ equilibrium quantity and charges a _____ equilibrium price compared to a perfectly competitive industry. A) lower; higher. B) higher; lower. C) lower; lower. D) higher; higher. 9 Use the following diagram representing a single price monopolist to answer the following question: If the market shown above is a monopolist, the area of "deadweight loss" is represented by letter: A) A B) B C) C D) D 10 Of the following, the best example of price discrimination is when: A) a vending machine charges a different price for a bag of chips than for a candy B) a restaurant offers discounted prices to senior citizens. C) bars charge different prices for a soda than sports arenas. bar. 1-a D) two consumers pay different prices for a camera on e-bay. 2-d 3-d 4-b 5-a 6-a 7-d 8-a 9-c 10-b 1 Monopolistic competition differs from perfect competition primarily because: in monopolistic competition, firms can differentiate their products. in monopolistic competition, entry into the industry is blocked. in monopolistic competition, there are relatively few barriers to entry. in perfect competition, firms can differentiate their products. 2 In monopolistic competition, firms achieve some degree of market power: by producing differentiated products. by virtue of size alone. because of barriers to entry into the industry. because of barriers to exit from the industry. 3 A monopolistically competitive firm that is incurring a loss will produce as long as the price that the firm charges is sufficient to cover: marginal costs. fixed costs. variable costs. advertising costs. 4 A firm in a monopolistically competitive industry: must raise price to sell more output. must lower price to sell more output. can sell an infinite amount of output at the market-determined price. sells a fixed amount of output regardless of price. 5 The long-run equilibrium outcomes in monopolistic competition and perfect competition are similar because in both market structures: the efficient output level will be produced in the long run. firms will only earn a normal profit. firms realise all economies of scale. firms will be producing at minimum average cost. 6 Which of the following statements best describes the outcome under monopolistic competition? It is not efficient because too little output is produced, but is efficient in that the output produced is produced at minimum average total cost. It is not efficient because too little output is produced and the output that is produced is produced at a cost above minimum average total cost. It is efficient because entry is free and economic profits are eliminated in the long run. It is efficient because the right amount of output is produced, but not efficient in that the output produced is produced at a cost above minimum average total cost. 7 Which of the following statements best describes the outcome under monopolistic competition? In monopolistic competition, there is the correct number of firms and each firm produces a slightly different product at an optimal scale. In monopolistic competition, there are too many firms and each firm produces a slightly different product at a scale that is less than optimal. In monopolistic competition, there are too many firms and each firm produces a slightly different product at the optimal scale. In monopolistic competition, there are too few firms and each firm produces a slightly different product at a scale that is greater than optimal. 8 A form of industry structure characterised by a few firms, each large enough to influence market price is: perfect competition. monopolistic competition. monopoly. oligopoly. 9 When one firm in the breakfast cereal market started an advertising campaign that stressed the nutritional value of its cereals, all other cereal manufacturers started similar advertising campaigns. This suggests that the breakfast cereal market is: monopolistically competitive. indeterminate from this information. perfectly competitive. oligopolistic. 10 An industry that has a relatively small number of firms that dominate the market is called: a concentrated industry. a merged industry. a colluding industry. a natural monopoly. 1-a 2-a 3-c 4-b 5-b 6-b 7-b 8-d 9-d 10-a 1 Long-term capacity planning deals with which of the following factors? Overtime budgets Workforce size Inventories Investment in new facilities 2 Input measures of capacity are preferred when there is/are: flexible flow processes. service processes. high-volume processes. Low customization. 3 A measure of the reserve capacity a process has to handle in unexpected increases in demand is the: capacity constraint limit. capacity utilization rate. capacity cushion. capacity bottleneck. 4 In general, a less capital-intensive industry such as a hotel chain would do well with a utilization rate of: 60-70%. 100%. approximately 18%. 30-40%. 5 An expansionist capacity strategy is NOT indicated when: Expansion will lead to economies of scale. a preemptive marketing strategy is used. capacity expansion is consistently ahead of demand. Expansion is made in large increments. 6 Chang and Chang observe that the competition is increasing the size of its warehouses. They have decided to do the same. They are following a ____________ strategy. expansionist follow the leader wait-and-see Theory of Constraints 7 Jorge Ortega has been using a 10 percent capacity cushion, servicing 60 customers an hour. There is a good deal of customer contact, and customer service has been poor due to random fluctuations in demand. If he increases his capacity cushion to 20%, what will be the new capacity requirement? 80 75 67 60 8 When evaluating alternative capacity decisions, qualitative concerns exclude: competitive reaction. technology change. uncertainties about demand. cash flow. 9 Under ideal conditions, a picture frame manufacturing facility can produce 480 frames per day. Under normal conditions, the company schedules 135 frames per day. Current market conditions and production strategy have combined to limit production to 120 frames per day. What is the approximate utilization rate for current capacity? 75% 25% 112% 89% 10 Anna’s landscaping business has a capacity gap; which alternative can best be described as “simply to do nothing”? Wait-and-see strategy Expansionist strategy Follow-the leader strategy Base-case strategy 1-d 2-a 3-c 4-a 5-a 6-b 7-b 8-d 9-d 10-d