Text Notes Guide Questions Modern Biology Text Chapter 9
advertisement

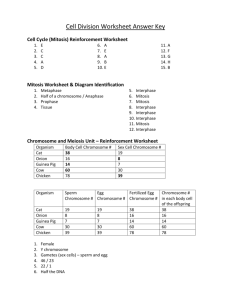
Text Notes Guide Questions Modern Biology Text Chapter 9 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis For pages 129 to 130 – what is cell division for? – what is the difference in the division for unicellular and multicellular organisms? – what is chromatin composed of and how does it exits? – what makes a chromosome visible? Also, what is a Histones? – Copy the diagram of a chromosome from your teacher. (Should be on the board, if not, ask her to put it up.) – on the chromosome label the centromere and chromatids – what is the function of the centromere – do each species of life have the same number of chromosomes? – define homologous chromosomes, then explain in your own words what this term means. – draw a picture of 2 different homologous chromosomes – define diploid and what is its mathematical notation? – define haploid and what is its mathematical notation? – you have two types of cells in your body, somatic cells and sex cells, look up these terms to find what they mean. – for the somatic cells and sex cells which are haploid and which are diploid? – If an organism has a diploid number of 246, what is its haploid number, show your work. – if an organism haploid number is 86, what is its diploid number? Chromosomes, Mitosis and Meiosis Text Notes Guide Questions Chapter 9 Modern Biology Text Section 2.0 Mitosis pages 131 to 135 – define mitosis – define somatic cells. – What triggers the process of Mitosis? – define cell cycle. – What are the 3 main phases of the cell cycle? – define interphase. – define mitosis again. – define cytokinesis. – List and describe the 3 phases of Interphase – which part of the cell cycle is the largest? – do all cells continuous go through the cell cycle? Explain your answer. – What does mitosis produces? Teacher will go over the stages of Mitosis, but you should have vocab in your notes. – list the stages of mitosis in the order they occur. – define centrioles, polar fibers, kinetochore fibers, and asters. – Define cytokinesis again. – explain the process in a plant cell and an animal cell.