Pre/Post Test Electricity & Magnetism
advertisement

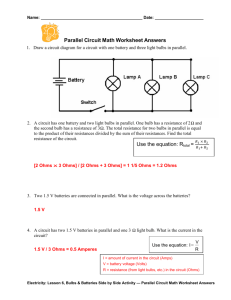
How is Electricity a System? Pre/Post Test 1) The attraction or repulsion between electric charges is called the electric__________ a. Force b. Discharge c. Field D. current 2) Clothes in a dryer acquire static cling by A. friction b. Conduction c. Induction D. static discharge 3) Materials that allow the charges of an electric current to move freely through them are called A. insulators b. Conductors c. Resistors D. magnets 4) What causes charges to move in a circuit? A. voltage B. energy C. electricity d. Magnetism 5) An electric current will always follow A. the path of least resistance. b. a path toward the North Pole. c. a path toward the South Pole. d. the path that leads through insulators. 6) According to Ohm’s Law, resistance is equal to voltage divided by a. time b. conduction c. current d. Potential 1 How Is Electricity a System? 7) According to Ohm’s Law, what is the resistance of a light if the voltage is 9.0 volts and the current is 0.30 amps? a. 0.033 ohms b. 2.7 ohms c. 30 ohms d. 8.7 ohms 8) In a series circuit with three bulbs, adding another bulb a. makes the nearest bulb brighter b. makes some of the bulbs dimmer. c. makes all the bulbs brighter d. makes all the bulbs dimmer Circuit Diagram: 9) What will be the explanation why the above circuit diagram best describes a parallel circuit? a. There is more than one bulb in the circuit. b. The bulbs are located on the same branch. c. There is only one path for current to take. d. There is more than one path for current to take. 10) A connection that allows current to take the path of least resistance is called a a. short circuit b. series circuit c. Parallel circuit d. Grounded circuit 11) What effect would a current of greater than 0.2 amps have on your body? a. It would be almost unnoticeable. b. It might cause an irregular heartbeat and disrupt the flow of blood. c. It could cause burns and stop your heart. d. It would feel like a shock you get from touching a doorknob. 2 How Is Electricity a System? 12) The interaction of magnetic and electric forces result in the production of a (n) a. current. b. Electromagnetism. c. solenoid. d. voltage. 13) You can increase the strength of an electromagnet’s field by a. decreasing the current in the solenoid. b. decreasing the number of loops in the solenoid. c. using a stronger ferromagnetic material for the core. d. winding the coils more loosely. 14) What is used to turn the pointer of a galvanometer? a. a crank b. an electric current c. a bar magnet d. a battery 15) What device transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy? a. an electromagnet b. an electric motor c. a generator d. a solenoid 3 How Is Electricity a System? How is Electricity a System? Pre/Post Test Answer key 1) A 2) A 3) B 4) A 5) A 6) C 7) C 8) D 9) D 10) A 11) C 12) B 13) C 14) B 15) B 4 How Is Electricity a System?