221 exam 1.doc
advertisement

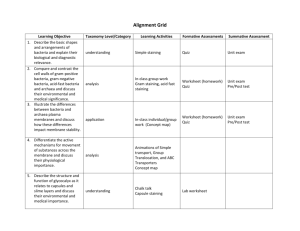
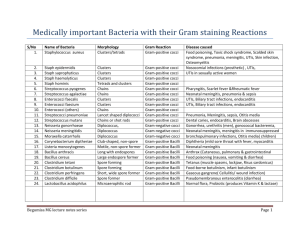
BioSc221/325 Exam 1 Name ______________________________ Multiple choice. (1 point each) Choose the one best answer to each of the following questions. ____ Which of the following are made up of eukaryotic cells? A. Bacteria and fungi B. Archaea and fungi C. Protozoa and animals D. Bacteria and archaea ____ In general, prokaryotic cells are __. A. larger than eukaryotic cells B. smaller than eukaryotic cells C. about the same size a eukaryotic cells D. not physiologically comparable to eukaryotic cells and therefore proaryotic and eukaryotic cell sizes should not be compared. ____ The periplasm is a(n) __. A. Part of the outer cell membrane of gram negative organisms. B. Part of the inner cell membrane of gram negative organisms. C. Space between the cytoplasmic membrane and the outer membrane layers. D. Alternate name for the inner cell membrane of any prokaryotic cell. ____ Enzyme found in saliva that cleaves the -1,4 linkage of the peptidoglycan layer. A. lysozyme B. murein C. penicillin D. vancomycin ____ Which of the following statements is false? A. The flagellar protein subunit is flagellin. B. In flagellar motion, the basal body acts as a motor. C. Flagella rotate at a constant speed and in a constant direction. D. The hook is the wider region between the basal body and the filament. _____ __ is found only in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. A. Lipoteichoic acid B. N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid C. Lipopolysaccharide D. Teichoic acid ____ Enzyme that protects bacteria from damage caused by hydrogen peroxide. A. catalase B. superoxide dismutase C. lysozyme D. hydrogenase ____ Which of the following does not accurately describe the conditions early in Earth’s life prior to the appearance of cyanobacteria? A. Absence of oxygen in the atmosphere B. Presence of an ozone layer. C. Cataclysmic bombardments and volcanic activity. D. Early appearance of prokaryotes. ____ Bacterial cell which has lost its peptidoglycan layer but remains intact is called a(n) A. lysozome B. protoplast C. periplasm D. osmoplast ____ Proteins that form channels in the outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. A. bactoprenols B. lipoproteins C. porins D. transport proteins ____ Fiber like structures on the surface of bacteria that aid in attachment to surfaces. A. bactoprenol B. flagella C. glycocalyx D. pili ____ Which of the following proteins is not found in the cytoplasmic membrane of a bacterial cell? A. Regulatory proteins B. Transport proteins C. Proteins for synthesis of peptidoglycan D. Proteins for energy generation E. Porins ____ Molecules found in halophiles that protect them from the low water activity of their environment. A. compatible solutes B. halites C. halogens D. isotoners _____ Which of the following used carbolic acid to disinfect surgical wounds and made surgery a much safer procedure due to the decrease in patients dying of infected surgical wounds. A. John Snow B. Robert Koch C. Joseph Lister D. Ignaz Semmelweis ____ Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is associated with __ . A. the outer membrane of Gram-positive bacteria. B. the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. C. the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-positive bacteria. D. the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. ____ Which of the following organisms are responsible for introducing molecular oxygen into the early Earth’s atmosphere? A. algae B. bryophytes C. cyanobacteria D. ferns E. protozoa ____ Which of the following does not describe the conditions for an enrichment culture for methanogenic archaea from the human colon? A. Use selective medium containing antibiotics to prevent overgrowth of archaea by bacteria. B. Provide an aerobic atmosphere by vigorous shaking. C. Supply H2 and CO2 at above atmospheric pressure to facilitate entry of gases into the liquid medium. D. Growth of methanogenic archaea is detected by the appearance of methane in the culture vessel. ____ Which of the following accurately describes the primary microbial composition of the colonic flora of a human living in the United States. A. Gram-positive cocci, Gram-negative rods, methanogenic archaea B. Gram-positive cocci, Gram-positive rods, Gram-negative rods C. Gram-positive cocci, Gram-positive rods, protozoa D. Gram-positive rods, Gram-negative rods, Gram-negative cocci E. Gram-positive cocci, Gram-positive rods, halophilic archaea ____ Which of the following cell wall components elicits an inflammatory response in the human body? A. pili B. porins C. peptidoglycan D. capsule E. lipoteichoic acid ____ Which of the following important enzymes is found in the cytoplasm of a bacterial cell? A. Enzymes of the electron transport chain B. ATP synthase C. Bactoprenol D. Sensor proteins E. Ribosomes ____ Amino acid found in the pentapeptide of the peptidoglycan of gram-negative bacteria. A. diaminopimelic acid B. dipicolinic acid C. L-lysine D. teichoic acid ____ When doing a colony count __. A. It is assumed that each colony arose from only one organism. B. Only viable cells are counted C. The medium must be suitable for colonial growth D. All of the above Matching. (1 point each) Match the definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. Note, not all terms will be used. ____ The cell wall of some archaea consists of ___. ____ Molecule found in the cell wall of Gram-positive but not Gram-negative bacteria. ____ Bacteria in which the flagella are distributed as tufts at one end of the cell. ____ A component of pseudomurein ____ Associated child-bed fever with medical students not washing their hands after surgery. ____ The first to use an epidemiological approach to solving a disease outbreak (cholera). ____ Identified the causative agents of the deadly diseases anthrax and tuberculosis ____ Cocci arranged in "grape-like" clusters. ____ A culture technique in which conditions favor the growth of the desired type of organism. ____ A device for enumerating microorganisms by microscope instead of cultivation. ____ Bacteria that remain blue after completion of the Gram stain procedure. ____ Technique that makes it possible to separate genome size DNA fragments on a gel. A. Amphitrichous B. Enrichment C. Gram-negative D. Gram-positive E. Koch, Robert F. Lipoteichoic acid G. Lophotrichous H. Murein I. N-acetylmuramic acid J. N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid K. Pasteur, Louis L. Peptidoglycan M. Peritrichous N. Petroff-Hauser counter O. Pseudopeptidoglycan P. Pulsed-field Gel Electrophoresis Q. Sarcina R. Semmelweis, Ignaz S. Snow, John T. Staphylococci U. Streaking V. Streptococci W. Tyndal, John Short answer. (1 point each) Penicillin can kill bacteria because it interferes with ______________________. A bacterium that has an optimal growth temperature of 37oC but still grows at 4oC is described as ______________________. A bacterium that has an optimal growth temperature of 30 oC would be described as a ___________________________. Two forms of oxygen that are toxic to living organisms: __________________________ ___________________________. An organism that requires a pH of 9.5 for optimal growth would be called a(n)___________________________. An organism requiring many growth factors and only grows on rich medium is described as ___________________________. An organism that is killed by the presence of oxygen is described as a(n) ___________________________. (be precise) Give one reason why microbiologists have failed to cultivate many of the microbes in the environment. Short Essay Questions. Please answer 3 of the following 4 short essay questions (6 points each - 6 bonus points possible for answering all 4 questions) Explain how penicillin and vancomycin kill bacteria. Describe how resistance to these antibiotics can arise. Describe how 16S rRNA sequence information is used to track the evolutionary relationship between different organisms. What three things have we learned from analysis of 16S rRNA sequence data? Describe the structure of the outer membrane of a Gram-negative bacterium in as much detail as possible. Include a description of any key components of the outer membrane. A labeled picture is OK. Describe the process of peptidoglycan synthesis beginning with the first precursor molecule inside the cell. (It is OK to use abbreviations for the monomeric components of the cell wall)