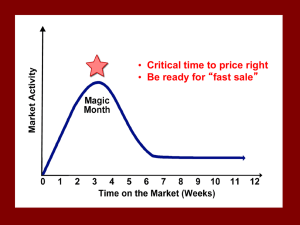
Marketing - Midterm Practice Exam
advertisement

Marketing - Midterm Practice Exam Created: 5:48:50 PM EST Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. Prospective customers for a waterproof marker that can be erased as simply as if it were a pencil would include: A. supermarkets that create and post hand-lettered signs weekly. B. students who are making signs for a bake sale. C. children who like to draw. D. delivery company employees who mark location zones on packages. E. all of the above. 2. Which of the following conditions is necessary for marketing to occur? A. a physical location for an exchange to occur B. a tangible exchange C. advertising to express unrealized needs D. two or more parties with unsatisfied needs E. all of the above 3. The first task of marketing is to discover consumer: A. diversity. B. ability to pay. C. objectives. D. needs. E. synergy. 4. The market for cosmetic dentistry (which can cost $15,000 for straightening and whitening) is: A. children with crooked teeth. B. all former smokers. C. any adult who has the time, the money, and the desire to undergo the procedures. D. anyone that has ever had any plastic surgery. E. adults who rely on making a good first impression for job success. 5. In marketing, the most common meaning of market is: A. a store that sells groceries. B. any place consumers can buy things. C. a particular line of products or specific line of merchandise for sale. D. a group of companies that have goods for sale. E. people with the desire and with the ability to buy a specific product. 6. Sound and Cinema is a company that will turn an ordinary basement into a home theater. It advertises in publications that are mailed to homeowners in subdivisions in which the least expensive home costs $475,000. These homeowners are the __________ for Sound and Cinema. A. mass market B. tangent market C. market aggregation D. target market E. promotional market 7. A local university offers business courses for a specific target market composed of people who are currently working who want to take refresher courses or work toward further degrees. Which of the following would be the most effective way to communicate with the target market, bearing in mind that communication must be both effective and economical? A. put announcements on campus bulletin boards. B. distribute promotional materials during classes. C. advertise on national television. D. E. advertise on local hip-hop radio shows. advertise in the local newspaper. 8. A marketing manager's controllable factors—product, price, promotion, and place—are the company's: A. environmental factors. B. marketing program. C. marketing mix factors. D. marketing concept. E. four utilities. 9. The ability to buy a soda from a vending machine demonstrates which element of the marketing mix? A. product B. price C. promotion D. place E. process 10. The element of the marketing mix demonstrated when an art gallery suggests a $2.00 donation at the door is: A. product. B. price. C. promotion. D. place. E. production. 11. The unique combination of benefits received by targeted buyers that include quality, price, convenience, ontime delivery, and both before-sale and after-sale service is called: A. target marketing. B. benefit segmentation. C. customer value. D. customer satisfaction. E. product dissonance. 12. After discovering consumers' needs, marketing's next task is to: A. create a target market mission statement. B. determine consumer demographics. C. translate information about consumer needs into products that satisfy them. D. design product prototypes. E. develop a value strategy. 13. What kinds of organizations engage in marketing? A. only those that can afford national advertising B. very large and established nonprofit organizations C. exclusively Fortune 1000 companies D. every organization markets E. virtually no organizations 14. Units such as manufacturers, retailers, or government agencies that buy for their own use or resale are collectively referred to as: A. intermediate buyers. B. purchasing agents. C. organizational buyers. D. professional buyers' organizations. E. manufacturing agents. 15. __________ is the money left over after a firm's total expenses are subtracted from its total revenues. A. Shareholders' equity B. C. D. E. Profit Inventory turnover Contribution margin Asset leverage 16. In terms of an organization's vision, railroads may have lost business because they: A. are too slow and cumbersome. B. defined their business too narrowly. C. defined their business too broadly. D. priced their services too high. E. are simply an outmoded form of transportation. 17. A new company projects that its sales will be greater than its expenses within the first year of operation. This is an example of which type of goal? A. profit B. sales revenue C. market share D. unit sales E. survival 18. The ratio of the sales revenue of the firm to the total sales revenue of all firms in the industry, including the firm itself, is known as: A. sales quality. B. market share. C. industry potential. D. contribution margin. E. marginal revenue. 19. DVD Overnight is a small company that rents DVD movies by mail using the Web. It jumped into an industry where there were no firm leaders but lots of competitors and established a loyal clientele by seizing the opportunity to provide a service that was not available through other companies that rented movies over the Internet—reliable overnight shipment. Its delivery system created its: A. viable mission. B. competitive advantage. C. tactical innovation. D. benchmarking-focus. E. sales-orientation. 20. The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) uses an approach to __________ that analyzes a firm's business units (called strategic business units, or SBUs) as though they were a collection of separate investments. A. target marketing B. business portfolio analysis C. marketing strategic planning D. market segmentation E. stock market investment 21. __________ are SBUs with a low share of low-growth markets—they may generate enough cash to sustain themselves, but they do not hold the promise of ever becoming real winners for the firm. A. Cash cows B. Stars C. Question marks D. Dogs E. Problem children 22. One of the strengths inherent in the use of the BCG portfolio analysis is the fact that it: A. is remarkably easy to locate an SBU on the BCG matrix. B. C. D. E. considers all factors that might impact an SBU's value to an organization. acts as a strong motivational tool for employees in SBUs that have been labeled dogs or problem children. forces firms to assess their SBUs in terms of relative market share and industry growth rate. does none of the above. 23. Which market-product strategy requires no change in the product but requires a company to seek out new customers in new markets? A. market penetration B. market development C. product development D. diversification E. all of the above 24. Gulfstream Aerospace Corp. engaged in a __________ strategy when it sold 3 Gulfstream V business jet aircraft to the Israeli Ministry of Defense for use as Special Electronic Mission Aircraft. This was Gulfstream's first sale to a Middle Eastern country. A. market penetration B. market development C. product development D. diversification E. product dissemination 25. Which market-product strategy requires no change in the product line but an increase in sales to existing customers through better advertising, more retail outlets, or lower prices, or more effective distribution? A. market development B. market penetration C. product development D. diversification E. product divestment 26. For several years, advertisements for Arm & Hammer baking soda have prompted consumers to place an opened box of the product in the refrigerator to lessen food odor and to replace that box monthly. The same ads advise customers to pour the used box down their kitchen sinks to freshen drains. Arm & Hammer employed a __________ strategy in its attempt to sell more baking soda. A. market penetration B. market development C. product development D. diversification E. product penetration 27. Which of the following actions best illustrates a product development strategy for McDonald's? A. opening the first McDonald's in China B. developing a line of McDonald's toys to be sold through Toys R Us stores C. adding a line of new deli sandwiches to the menu of existing McDonald's stores D. running a promotion based on the Monopoly game, whereby customers have a chance to win prizes with each purchase E. opening McDonald's restaurants in Six Flags theme parks 28. The first step in the strategic marketing process is: A. establishing the budget. B. developing advertising appeals. C. goal setting. D. marketing programming. E. situation analysis. 29. An effective technique a firm can use to appraise in detail its internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats is called: A. SWOT analysis. B. strategic management. C. market segmentation. D. market programming. E. marginal analysis. 30. __________ would be used to group consumers for soda on the basis of whether they wanted sugar-free and caffeine-free, caffeine-free but with sugar, or regular with sugar and caffeine. A. Aggregation marketing B. Market segmentation C. Market clustering D. Profiling E. Mass marketing 31. A cohesive marketing program concentrates on: A. product. B. price. C. promotion. D. place. E. all of the above 32. The __________ element of the marketing mix includes features, packaging, brand name and warranty. A. product B. pricing C. promotion D. placement E. budgeting 33. The __________ element of the marketing mix includes outlets, channels, coverage, transportation and stock level. A. product B. pricing C. promotion D. placement E. budgeting 34. A company engaged in environmental scanning is: A. taking into account the effect its marketing activities can have on plants and animals in our environment. B. continually acquiring information on events occurring outside the organization to identify and interpret potential trends. C. maintaining a time constant horizon in its strategic planning process. D. maintaining retail customer databases. E. requiring all employees to spend time outside the office to avoid the "ivory tower" syndrome. 35. Which of the following is a reason to track an environmental trend? A. to better understand the type of business likely to be influenced by the trend B. to help predict the future for a particular business C. to better understand consumer preferences D. to better compete in an industry E. All of the above are reasons to track an environmental trend. 36. Demographic characteristics of the population and its values are known as: A. ecology. B. C. D. E. macroeconomic conditions. regulatory forces. social forces. psychographics. 37. Baby boomers are an important target market because they: A. include most of the important business leaders in the United States. B. represent a small proportion of the population, but have large disposable incomes. C. have the longest life expectancies; therefore, they will remain active in the market place for the longest period of time. D. account for the majority of purchases of most consumer products and services. E. have the lowest income level. 38. Components of a consumer's income include: A. inflation, recession, and recovery. B. salary, wages, commissions, and fees. C. gross, disposable, and discretionary incomes. D. taxes, perquisites, and salary. E. liquidity items, liabilities, and assets. 39. Emily had an excellent year as a saleswoman in 2005. She earned $97,000. She paid $17,000 for "necessities" such as mortgage, food, and clothing. She was given a six-week all expenses paid vacation by the company for her sales performance that had a value of $9,000. Her state and federal income taxes totaled $24,000. What was her discretionary income? A. $56,000 B. $73,000 C. $80,000 D. $88,000 E. There is not enough data provided to calculate her discretionary income. 40. The owner of your local KFC franchise has had a good year with rising revenues and reduced operating costs that resulted in a personal income of roughly $100,000. Approximately one-third of that was taken for local, state, and federal income taxes, and another third went to pay for mortgage, car payments, food, clothing, and other necessities. What is the remaining third called? A. Windfall B. Bonus C. Discretionary income D. Disposable income E. Franchiser fee 41. Competitive pressures among existing firms depend on: A. the rate of industry growth. B. low fixed costs in the industry. C. large numbers of competitors. D. high variable costs. E. low variable costs. 42. Consumer behavior includes: A. actions a person takes in purchasing services. B. actions a person takes in using services. C. actions a person takes in purchasing products. D. the mental and social processes that come before and after purchase and use. E. all of the above. 43. During the purchase decision process, an individual at the __________ stage will perceive differences between his or her ideal and actual situations big enough to trigger a decision. A. B. C. D. E. problem recognition alternative evaluation cognitive dissonance routine response behavior post purchase behavior 44. In which stage in the consumer purchase decision process would a consumer ask, "Is installation included in the price of this air conditioner?" A. problem recognition B. information search C. alternative evaluation D. purchase decision E. evaluation 45. When the elementary teacher needed to buy poster board for her class, she remembered that she had found some poster board at her local 99 Cents Only store, at Walgreen's, and at her Family Dollar Store. What term best describes the information search method used by the teacher? A. personal external source B. public external source C. market-dominated external source D. internal search E. market-dominated internal source 46. A(n) __________ in the consumer purchase decision process occurs when consumers scan their memory for previous experiences with products or brands. A. problem recognition B. internal search C. external search D. purchase task E. antecedent state 47. Keisha is buying a new car appropriate to her role as the newest vice president at her company. She was overheard telling a co-worker, "The Volvo has reclining bucket seats, but the Cadillac has front and back stereo speakers." In which stage of the purchase decision process is Keisha? A. problem recognition B. information search C. alternative evaluation D. purchase decision E. post purchase evaluation 48. The objective and subjective attributes of a brand consumers use to compare different products and brands are called: A. temporal states. B. antecedent states. C. information sources. D. evaluative criteria. E. the CONSIDERATION set. 49. The group of brands a consumer would consider acceptable from among all the brands in the product class of which he or she is aware is the: A. evaluative set. B. evolved set. C. consideration set. D. alternative selection group. E. aspiration group. 50. At the __________ of the purchase decision process, a consumer compares the product with his or her expectations and is either satisfied or dissatisfied. A. problem recognition stage B. information search stage C. alternative evaluation stage D. purchase decision stage E. postpurchase stage 51. Customer satisfaction is an important focus for marketers because: A. marketing research is an inexpensive process. B. the financial value of a retained customer can be significant. C. customer value is a non-quantifiable statistic. D. attracting new customers is easier than keeping old ones. E. a market development strategy is preferable to a market penetration strategy. 52. The feeling of postpurchase psychological tension or anxiety that a consumer often experiences is called: A. angst. B. the temporal state. C. the dissociative state. D. selective comprehension. E. cognitive dissonance. 53. Which problem solving variation would likely be used for clothing, sheets and towels, or electric can openers? A. routine response behavior B. limited problem solving C. extended problem solving D. simulated selection E. integrated problem solving 54. NetJets is a company that offers 1/16 or more ownership in a jet plane for a price beginning at $325,000. It gives the purchaser privacy, convenience and flexibility as well as saves them time since the plane is available with four hours notice. This is a high-involvement purchase for most people because: A. The item is inexpensive, can have serious personal consequences, or could reflect on one's social image. B. The item is inexpensive, has no serious personal consequences, but could reflect on one's social image. C. The item is expensive, has no serious personal consequences, but could reflect on one's social image. D. The item is expensive, can have serious personal consequences, or could reflect on one's social image. E. The item is inexpensive, has no serious personal consequences, or would not reflect on one's social image. 55. Those needs which are basic to survival and which must be satisfied first are: A. physiological needs. B. safety needs. C. social needs. D. personal needs. E. self actualization needs. 56. In the hierarchy of needs, a burglar alarm would satisfy a __________ need. A. physiological B. safety C. social D. personal E. self actualization 57. An ad for Conesco's life insurance asks the question, "How do you plan on supporting your family after you pass away?" The ad shows a tombstone with a sign that offers the face of the stone as ad space. The ad is intended to appeal to which of the needs in the hierarchy of needs? A. physiological needs B. safety needs C. social needs D. personal needs E. self actualization needs 58. Because the average consumer operates in a complex environment, the human brain attempts to organize and interpret information with a process called: A. selective retention. B. selective attention. C. selective exposure. D. selective perception. E. stimulus discrimination. 59. The tendency to pay attention to messages consistent with one's attitudes and beliefs and to ignore messages that are inconsistent is called: A. selective retention. B. selective comprehension. C. selective exposure. D. selective perception. E. stimulus discrimination. 60. Charlie needs to purchase an automobile to drive to his new job in the city center. He begins to notice ads for many cars he wasn't aware of previously. This is an example of: A. subliminal perception. B. selective exposure. C. retention. D. tuning out. E. behavioral learning. 61. An aspiration group is a group is one: A. to which a person belongs, including fraternities and social clubs. B. that a person wishes to be a member of or wishes to be identified with. C. that a person wishes to maintain a distance from because of differences in values or behaviors. D. that a person knows he or she can never really fit into because of basic cultural differences. E. that a person feels is excessively high above him or her socioeconomically. 62. Movie studios use tracking studies, in which prospective moviegoers are asked questions about an upcoming film release to help them forecast sales. This is an example of: A. advertising of the movie. B. marketing research. C. tactical support. D. cross-tabulations. E. social audits. 63. Attempting to identify and define both marketing problems and opportunities and to generate and improve marketing action is the role __________ performs. A. advertising B. sales promotion C. publicity D. E. marketing research tactical support 64. Grape-Nuts was one of the first cereals Post Cereal Company ever marketed. It scores well in brandawareness, but its sales have been steadily declining. Rather than assume the product was a dog, the marketing manager for this cereal decided Post Cereal Company should first: A. hire a consultant. B. engage in marketing research. C. spend more dollars on advertising. D. hire more salespeople. E. develop new cereals. 65. During the marketing research process, __________ are the goals the decision maker seeks to achieve in solving a problem. A. measures of success B. objectives C. marketing research plans D. decisions E. definitions 66. Which of the following is a typical marketing objective? A. Increase sales revenue and profit for Diet Coke. B. Discover whether consumers that buy Pampers are aware of gender-specific disposables. C. Find out why the new line of plus-size clothing is not selling well. D. Determine whether to offer a new & improved version of an existing product. E. All of the above are typical marketing objectives. 67. Secondary data are: A. facts and figures that are newly collected for the project at hand. B. facts and figures obtained by watching people mechanically rather than in person. C. facts and figures obtained by asking people questions. D. facts and figures that have already been recorded before the project. E. conclusions developed from information obtained from a representative sample of a population. 68. Two important advantages of secondary data are: A. they are inexpensive and up-to-date. B. they are up-to-date and supply all relevant categories of information. C. they are usually inexpensive and save time. D. they are tailor-made to your specifications and relatively inexpensive. E. none of the above. 69. The best way to find information that precisely addresses the problem at hand is to: A. collect primary data. B. collect internal secondary data. C. collect external secondary data. D. perform a sensitivity analysis. E. use probability sampling. 70. Observational data are: A. facts and figures newly collected for the project at hand. B. facts and figures obtained by watching people mechanically or in person. C. facts and figures obtained by asking people questions. D. facts and figures that have already been recorded before the project. E. conclusions developed from information obtained from a representative sample of a population. 71. A marketing research approach that uses a discussion leader to interview 6 to 10 past, present, or prospective customers is called: A. a depth (or individual) interview. B. an experiment. C. a focus group. D. small group dynamics. E. secondary data collection. 72. Aggregating prospective buyers into groups that have common needs and will respond similarly to a marketing action is called: A. consumer differentiation. B. psychographics. C. market segmentation. D. market delineation. E. aggregation marketing. 73. Market segmentation involves aggregating prospective buyers into groups that have common needs and will: A. pay attention to marketing messages. B. respond similarly to a marketing action. C. be responsive to marketing research. D. use the same payment methods. E. go shopping on a regular basis. 74. To be identified as a market segment, its members must: A. represent a large share of the entire market and have critical buying power. B. have common needs and respond similarly to market actions. C. have different needs and have potential for future growth. D. have different needs and respond similarly to market actions. E. have potential for future growth and have potential for increased profit or ROI. 75. The phrase "relatively homogeneous collections of prospective buyers" is most descriptive of: A. market segments. B. demographic clusters. C. organizational buyers. D. ultimate consumers. E. qualified prospects. 76. The process of segmenting a market and selecting specific segments as targets is the link between __________ and the organization's marketing program. A. self-regulatory industry standards B. government regulations C. top-level management D. market needs E. controllable environmental factors 77. Marketers use market segmentation to: A. link market needs to an organization's marketing program. B. develop specific marketing actions related to product or price. C. develop specific marketing actions related to advertising. D. increase overall sales, profits and/or other organizational goals. E. do all of the above. 78. The first step in segmenting and targeting markets is to: A. recognize a need. B. group prospective buyers into segments. C. D. E. create product groupings. estimate size of the overall market. develop a market-product grid 79. There are five steps involved in segmenting and targeting a market. What should a marketer do once he or she has selected a target market and grouped products to be sold into categories? A. create product groupings B. develop a market-product grid and estimate size of market C. identify market needs D. take marketing actions to reach that target market E. form prospective buyers into market segments 80. The best segmentation approach is the one that: A. makes it easiest to reach the segment. B. recognizes different needs of buyers among different segments. C. recognizes similarities of needs of potential buyers within a segment. D. is simplest and least costly in assigning potential buyers to segments. E. maximizes the opportunity for future profit and ROI. 81. More than half of all U.S. households are made up of only one or two persons, so Campbell's packages meals with only one or two servings--from Great Starts breakfasts to L'Orient dinners. Campbell's is using __________ to segment its market. A. usage rates. B. usage patterns. C. buyer situations. D. demographic characteristics. E. psychographic characteristics. 82. Magnavox sells many different types of TVs from flat screens to a 20" combination TV/DVD. The larger sets can be outfitted with surround sound at a higher price than the small set. The small set is much less expensive and allows the viewer to watch a DVD without extra equipment. Magnavox is using which buying situation segmentation variable in this example? A. benefits sought B. psychographic C. demographic D. socioeconomic E. behavior 83. Airlines have developed frequent-flier programs to encourage passengers to use the same airline repeatedly. This segmentation technique focuses on: A. benefits sought B. usage rate C. product awareness D. buyer intentions E. buying condition 84. Todd Harris and Associates, a New York sales promotion agency, discovered from analysis of its files that one-fifth of its clients accounted for more than three-quarters of its fees and commissions. This is an example of what classic concept? A. the law of inverse proportions B. the 80/20 rule C. the survival of the fittest D. the law of eminent domain E. the primogeniture rule 85. In developing a marketing strategy for Hallmark you decide that what it is really selling is memory keeping, and not photo albums, scrapbooks, and related supplies. This is an example of: A. target market selection. B. product grouping. C. market-product grid development. D. taking marketing actions to reach target markets. E. market segmentation of prospects. 86. Determining the size of specific markets using a market-product grid is helpful in determining which target market segments to select and __________. A. how to implement the 80-20 rule. B. which products to be sold into groups. C. how to implement a harvesting strategy. D. which product groupings to offer. E. which products to reposition. 87. Which of the following is a criterion used for selecting a target segment? A. size of the market B. expected growth C. cost of reaching the segment D. compatibility with the selling company's objectives E. all of the above 88. In developing a marketing strategy for the recently released Nike Air Jordan XVII with a price tag of $200, Nike decided to concentrate on affluent teens rather than members of high school basketball teams. This is an example of: A. selecting target market segments to reach. B. forming products to be sold into groups. C. developing a market-product grid and estimating size of markets. D. taking marketing actions to reach target markets. E. forming prospective buyers into segments. 89. Doris Lewis owns Lewis Edibles, Inc., a company that makes Tongue Tinglin' B.B.Q. Sauce. She wants to target local people who like the special blend of flavors found only in North Carolina barbecue sauce. In developing a marketing strategy to sell the sauce, Lewis decided to join Goodness Grows in North Carolina, a specialty food association that advertises local products and distributes them to local supermarkets and gourmet shops. Lewis has just: A. selected target market segments to reach. B. formed products to be sold into groups. C. developed a market-product grid and estimating size of markets. D. taken marketing actions to reach target markets. E. formed prospective buyers into segments. 90. What does the term product positioning refer to? A. a careful analysis of cross tabulations B. shelf locations in major chain, grocery, and department stores C. geographic segmentation, often within major metropolitan areas D. the place a product offering occupies in consumers' minds on important attributes E. an old and outdated concept no longer worthy of consideration in marketing planning 91. Changing the place an offering occupies in consumers' minds is called: A. perceptual mapping. B. product positioning. C. product differentiation. D. repositioning. E. psychographics. 92. Recently, U.S. dairies, struggling to increase milk sales, tried to change the way adults thought about milk. The dairies wanted to __________ milk in the minds of the consumer. A. segment B. differentiate C. reposition D. explain E. represent 93. A graph displaying consumers' perceptions of product attributes across two or more dimensions is a: A. payoff table. B. growth matrix. C. market-product grid. D. perceptual map. E. consumer preference matrix. 94. The maximum total sales of a product by all firms to a segment under specified environmental conditions and marketing efforts of the firms is called: A. top-down forecast. B. market potential. C. growth potential. D. sales forecast. E. Delphi forecast. 95. Superba Cravats is a major marketer of men's bow ties. It estimates there are 20 million buyers of bow ties each year, that the average wearer of bow ties purchases 4 ties per year, and that the average price per bow tie is $10. Superba Cravats has a market share of 20 percent. The market (or industry) potential for bow ties is: A. $200 million. B. $80 million. C. $400 million. D. $800 million. E. $160 million. 96. By dividing its market into categories, which it labels Basic, Expression, Classic, Fashion, Premium, and Communicator, Nokia is using: A. consumer differentiation. B. behavioral segmentation variables. C. market delineation. D. market segmentation. E. aggregation marketing. 97. By developing and introducing a communication device which includes a built-in stopwatch, a thermometer, downloaded game packs, a personalized logo, a personal information manager and a cellular phone, Nokia is implementing a __________ strategy. A. product sampling B. product extrapolation C. product differentiation D. usage segmentation. E. market differentiation 98. The stage of the product life cycle when a product is first commercialized to its intended target market is called the __________ stage. A. growth B. commercialization C. D. E. launch introduction awareness-trial 99. Lack of profit in the introductory stage of the product life cycle is very often the result of: A. insufficient allocation of resources to the marketing mix. B. poor selection of distribution channels. C. high taxes. D. large investment costs in product development. E. ineffective execution of the marketing program. 100. A few years ago Who Wants to Be a Millionaire premiered as the first nighttime game show in a couple of decades. The marketing for the show was intent on making television viewers aware of its existence and excited enough about the show that we would watch the first episode. Which of the following statements about televised game shows is true? A. Who Wants to Be a Millionaire was in the introduction stage of the product life cycle of televised nighttime game shows when it premiered. B. Because television has been around for many years, all programs fall naturally into the maturity stage. C. Televised programs are either in the introduction stage or the growth stage and are discontinued when they move into the maturity stage. D. All televised programming uses a three-stage product life cycle--growth, maturity, and decline. E. The product life cycle is totally inapplicable to any television genre. 101. During the introduction stage of the product life cycle, __________ is used. This pricing strategy charges a high price to recoup the costs of product development. A. penetration pricing B. cost-plus pricing C. ROI pricing. D. market-oriented pricing E. skimming pricing 102. 3M is a master of __________ strategy. According to a 3M manager, "We hit fast, price high, and get the heck out when the me-too products pour in." A. penetration pricing B. cost-plus pricing C. ROI pricing. D. market-oriented pricing E. skimming pricing 103. Which stage in the product life cycle is characterized by a rapid increase in sales and the appearance of competitors? A. introduction B. growth C. maturity D. decline E. profit 104. Which stage in the product life cycle is characterized by a leveling off of industry sales? A. introduction B. growth C. maturity D. decline E. comparability 105. During the maturity stage of the product life cycle, profit declines because: A. there are fewer and fewer competitors in the market. B. better products are only in the growth stage. C. production costs increase the more a firm has to manufacture the same product. D. there is fierce price competition among sellers. E. all of the above. 106. The marketing objective of a firm whose product is in the maturity stage of the product life cycle is to: A. actively search out new first time users. B. maintain existing buyers since new ones are hard to find. C. actively reinforce competitors' marketing efforts. D. maintain existing distributors and actively seek out new ones. E. shift to a skimming price strategy. 107. Promotional expenses at the maturity stage of the product life cycle are often designed to: A. allow a price increase. B. remind repeat purchasers. C. create primary demand. D. gain new distributors. E. eliminate distribution channels. 108. To handle products in the decline stage of the product life cycle, companies often use either: A. diversification or harvesting. B. diversification orcontracting. C. deletion or harvesting. D. deletion or diversification. E. building or contracting. 109. A number of years ago Pokémon was the hottest name in toys, but as other more high-tech toys appeared on the market, the popularity of Pokémon waned as did its sales. Some toy experts predict Pokémon will soon be only a memory for toy retailers. Pokémon is in the __________ stage of its product life cycle. A. decay B. uncommercialization C. decline D. maturity E. harvested 110. __________ refers to the entire product category or industry, such as video games. A. Product form B. Product class C. Product line D. Product family E. Product brand 111. Televisions are an example of a __________, and flat screen TVs are an example of a __________. A. product line; product class B. product family; product line C. product brand; product line D. product form; product class E. product class; product form 112. Snickers candy bar was repositioned from a candy bar to a snack food through commercials that showed the busy people satisfying their hunger with a Snickers bar. Mars, Inc., used this strategy with its Snickers bar to: A. react to a competitor's position. B. reach a new market. C. D. E. catch a rising trend. change the value offered. do none of the above. 113. When consumers think of Harley-Davidson, the image of a masculine, non-conformist is the likely associated with that brand name. With the Vespa motorscooters, the image is more likely to be a brainy environmentalist that wears polyester and socks that don't match. Both Vespa and Harley-Davidson: A. have brand personalities. B. have created brand mannerisms. C. are symbolic brands. D. use brand personification. E. use product personification. 114. Brand equity is: A. the resources invested to create a name, phrase, design, symbol, or combination of these to identify a firm's products and distinguish them from those of its competitors. B. adding customer value to the product brand through additional features or higher-quality materials, or reducing its price. C. increasing the content contained within the brand's package without changing its size or increasing its price. D. the net present value of the royalties the firm receives as a result of licensing its brand to other firms to manufacture and/or market. E. the added customer value a given brand name gives to a product beyond the functional benefits provided. Marketing - Midterm Practice Exam KEY Created: 5:48:50 PM EST 1. (p. 8) Prospective customers for a waterproof marker that can be erased as simply as if it were a pencil would include: a. supermarkets that create and post hand-lettered signs weekly. b. students who are making signs for a bake sale. c. children who like to draw. d. delivery company employees who mark location zones on packages. E all of the above. Prospective customers include anyone who could benefit from owning a product. 2. (p. 9) Which of the following conditions is necessary for marketing to occur? a. a physical location for an exchange to occur b. a tangible exchange c. advertising to express unrealized needs D two or more parties with unsatisfied needs e. all of the above For marketing to occur, at least four factors are required: (1) two or more parties (individuals or organizations) with unsatisfied needs, (2) a desire and ability on their part to be satisfied, (3) a way for the parties to communicate, and (4) something to exchange. 3. (p. 10) The first task of marketing is to discover consumer: a. diversity. b. ability to pay. c. objectives. D needs. e. synergy. The first objective in marketing is discovering the needs of prospective consumers. See also Figure 1-4. 4. (p. 13) The market for cosmetic dentistry (which can cost $15,000 for straightening and whitening) is: a. children with crooked teeth. b. all former smokers. C any adult who has the time, the money, and the desire to undergo the procedures. d. anyone that has ever had any plastic surgery. e. adults who rely on making a good first impression for job success. Potential customers make up a market, which is (1) people (2) with the desire, and (3) the ability to buy a specific product. 5. (p. 13) In marketing, the most common meaning of market is: a. a store that sells groceries. b. any place consumers can buy things. c. a particular line of products or specific line of merchandise for sale. d. a group of companies that have goods for sale. E people with the desire and with the ability to buy a specific product. Key term definition—market 6. (p. 14) Sound and Cinema is a company that will turn an ordinary basement into a home theater. It advertises in publications that are mailed to homeowners in subdivisions in which the least expensive home costs $475,000. These homeowners are the __________ for Sound and Cinema. a. mass market b. tangent market c. market aggregation D target market e. promotional market A target market is a specific group of potential consumers toward which an organization directs its marketing program. 7. (p. 14) A local university offers business courses for a specific target market composed of people who are currently working who want to take refresher courses or work toward further degrees. Which of the following would be the most effective way to communicate with the target market, bearing in mind that communication must be both effective and economical? a. put announcements on campus bulletin boards. b. distribute promotional materials during classes. c. advertise on national television. d. advertise on local hip-hop radio shows. E advertise in the local newspaper. Alternatives A, B, and D would miss the target market. Alternative C would reach a lot of nopotential people and is too costly. Alternative E is the most effective and economical of the alternatives. 8. (p. 14) A marketing manager's controllable factors—product, price, promotion, and place—are the company's: a. environmental factors. b. marketing program. C marketing mix factors. d. marketing concept. e. four utilities. Key term definition—marketing mix 9. (p. 14) The ability to buy a soda from a vending machine demonstrates which element of the marketing mix? a. product b. price c. promotion D place e. process Place refers to the means of getting the product into the consumer's hands. 10. (p. 14) The element of the marketing mix demonstrated when an art gallery suggests a $2.00 donation at the door is: a. product. B price. c. promotion. d. place. e. production. Price is what is exchanged for the product—in this case, access to an art gallery. 11. (p. 15) The unique combination of benefits received by targeted buyers that include quality, price, convenience, on-time delivery, and both before-sale and after-sale service is called: a. target marketing. b. benefit segmentation. C customer value. d. customer satisfaction. e. product dissonance. Key term definition--customer value 12. (p. 16) After discovering consumers' needs, marketing's next task is to: a. create a target market mission statement. b. determine consumer demographics. C translate information about consumer needs into products that satisfy them. d. design product prototypes. e. develop a value strategy. A marketing program is defined as a plan that integrates the marketing mix to provide a good, service, or idea to prospective buyers. Consumer needs trigger product concepts that are translated into actual products that stimulate further discovery of consumer needs. 13. (p. 21-What kinds of organizations engage in marketing? 22) a. b. c. D e. only those that can afford national advertising very large and established nonprofit organizations exclusively Fortune 1000 companies every organization markets virtually no organizations Every organization markets, because in some way it is important for it to encourage people either to engage in exchanges with it, or perhaps just to think or behave in a particular way—as in the case of many non-profits such as the American Cancer Society or government agencies such as the U.S. Department of Transportation. 14. (p. 22) Units such as manufacturers, retailers, or government agencies that buy for their own use or resale are collectively referred to as: a. intermediate buyers. b. purchasing agents. C organizational buyers. d. professional buyers' organizations. e. manufacturing agents. Key term definition--organizational buyers 15. (p. 30) __________ is the money left over after a firm's total expenses are subtracted from its total revenues. a. Shareholders' equity B Profit c. Inventory turnover d. Contribution margin e. Asset leverage Key term definition--profit 16. (p. 32) In terms of an organization's vision, railroads may have lost business because they: a. are too slow and cumbersome. B defined their business too narrowly. c. defined their business too broadly. d. priced their services too high. e. are simply an outmoded form of transportation. Railroads may have let other forms of transportation take business away from them because they perceived themselves in the railroad business instead of the transportation business. This definition was too limited and it hurt railroads because they failed to design effective marketing strategies to compete with trucks, buses, airlines, and automobiles. 17. (p. 34) A new company projects that its sales will be greater than its expenses within the first year of operation. This is an example of which type of goal? A profit b. sales revenue c. market share d. unit sales e. survival Classic economic theory assumes a firm seeks to maximize long-run profit, achieving as high a financial return on investment as possible. Profit is sales minus expenses. 18. (p. 34) The ratio of the sales revenue of the firm to the total sales revenue of all firms in the industry, including the firm itself, is known as: a. sales quality. B market share. c. industry potential. d. contribution margin. e. marginal revenue. Key term definition--market share 19. (p. 36) DVD Overnight is a small company that rents DVD movies by mail using the Web. It jumped into an industry where there were no firm leaders but lots of competitors and established a loyal clientele by seizing the opportunity to provide a service that was not available through other companies that rented movies over the Internet—reliable overnight shipment. Its delivery system created its: a. viable mission. B competitive advantage. c. tactical innovation. d. benchmarking-focus. e. sales-orientation. Competitive advantage is a unique strength relative to competitors, often based on quality, time, cost, or innovation. 20. (p. 38) The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) uses an approach to __________ that analyzes a firm's business units (called strategic business units, or SBUs) as though they were a collection of separate investments. a. target marketing B c. d. e. business portfolio analysis marketing strategic planning market segmentation stock market investment Text term definition--business portfolio analysis 21. (p. 38) __________ are SBUs with a low share of low-growth markets—they may generate enough cash to sustain themselves, but they do not hold the promise of ever becoming real winners for the firm. a. Cash cows b. Stars c. Question marks D Dogs e. Problem children Dropping SBUs in the dog quadrant from a business portfolio is generally advocated except when relationships with other SBUs, competitive considerations, or potential strategic alliances exist. Also see Fig. 3. 22. (p. 40) One of the strengths inherent in the use of the BCG portfolio analysis is the fact that it: a. is remarkably easy to locate an SBU on the BCG matrix. b. considers all factors that might impact an SBU's value to an organization. c. acts as a strong motivational tool for employees in SBUs that have been labeled dogs or problem children. D forces firms to assess their SBUs in terms of relative market share and industry growth rate. e. does none of the above. The primary strength of business portfolio analysis lies in forcing a firm to place each of its SBUs in the growth-share matrix, which in turn suggests which SBUs will be cash producers and cash users in the future. 23. (p. 40) Which market-product strategy requires no change in the product but requires a company to seek out new customers in new markets? a. market penetration B market development c. product development d. diversification e. all of the above Text term definition--market development 24. (p. 40) Gulfstream Aerospace Corp. engaged in a __________ strategy when it sold 3 Gulfstream V business jet aircraft to the Israeli Ministry of Defense for use as Special Electronic Mission Aircraft. This was Gulfstream's first sale to a Middle Eastern country. a. market penetration B market development c. product development d. diversification e. product dissemination Market development is the process of taking present products to new markets. 25. (p. 40) Which market-product strategy requires no change in the product line but an increase in sales to existing customers through better advertising, more retail outlets, or lower prices, or more effective distribution? a. market development B market penetration c. product development d. diversification e. product divestment Text term definition--market penetration 26. (p. 40) For several years, advertisements for Arm & Hammer baking soda have prompted consumers to place an opened box of the product in the refrigerator to lessen food odor and to replace that box monthly. The same ads advise customers to pour the used box down their kitchen sinks to freshen drains. Arm & Hammer employed a __________ strategy in its attempt to sell more baking soda. A market penetration b. market development c. product development d. diversification e. product penetration Arm & Hammer is attempting to sell more of their present product in current markets. The company is not creating new products nor are they seeking new markets for their product. They are attempting to create new uses for their product within existing markets. 27. (p. 41) Which of the following actions best illustrates a product development strategy for McDonald's? a. opening the first McDonald's in China b. developing a line of McDonald's toys to be sold through Toys R Us stores C adding a line of new deli sandwiches to the menu of existing McDonald's stores d. running a promotion based on the Monopoly game, whereby customers have a chance to win prizes with each purchase e. opening McDonald's restaurants in Six Flags theme parks The deli sandwiches (a new product) involve a new product for present restaurant customers, a product development strategy. (A secondary, minor effect might be to attract new customers.) 28. (p. 43) The first step in the strategic marketing process is: a. establishing the budget. b. developing advertising appeals. c. goal setting. d. marketing programming. E situation analysis. Although marketing consultants often want to establish the budget first, and many people think it is fun to do advertising, the planning for a strategic marketing program should always begin with the situation analysis. 29. (p. 43) An effective technique a firm can use to appraise in detail its internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats is called: A SWOT analysis. b. strategic management. c. market segmentation. d. e. market programming. marginal analysis. Key term definition--SWOT analysis 30. (p. 44) __________ would be used to group consumers for soda on the basis of whether they wanted sugar-free and caffeine-free, caffeine-free but with sugar, or regular with sugar and caffeine. a. Aggregation marketing B Market segmentation c. Market clustering d. Profiling e. Mass marketing Market segmentation is the terms for aggregating prospective buyers into groups that have common needs and will respond similarly to a marketing action. 31. (p. 46;A cohesive marketing program concentrates on: Fig. 6) a. b. c. d. E product. price. promotion. place. all of the above A cohesive marketing program is composed of all of the 4 Ps, also known as "the marketing mix." 32. (p. 46;The __________ element of the marketing mix includes features, packaging, brand name and warranty. Fig. 7) A b. c. d. e. product pricing promotion placement budgeting The product element of the marketing mix includes features, packaging, brand name and warranty. 33. (p. 46;The __________ element of the marketing mix includes outlets, channels, coverage, transportation and Fig. 7) stock level. a. product b. pricing c. promotion D placement e. budgeting 34. (p. 72) A company engaged in environmental scanning is: a. taking into account the effect its marketing activities can have on plants and animals in our environment. B continually acquiring information on events occurring outside the organization to identify and interpret potential trends. c. maintaining a time constant horizon in its strategic planning process. d. maintaining retail customer databases. e. requiring all employees to spend time outside the office to avoid the "ivory tower" syndrome. Key term definition--environmental scanning 35. (p. 73) Which of the following is a reason to track an environmental trend? a. to better understand the type of business likely to be influenced by the trend b. to help predict the future for a particular business c. to better understand consumer preferences d. to better compete in an industry E All of the above are reasons to track an environmental trend. Environmental trends affect the marketing activities of a firm in numerous ways including competitive analysis: what types of businesses are likely to be influenced by the trend, industry analysis: future industry predictions, and market analysis: an explanation of consumer behavior 36. (p. 74) Demographic characteristics of the population and its values are known as: a. ecology. b. macroeconomic conditions. c. regulatory forces. D social forces. e. psychographics. Key term definition--social forces 37. (p. 75) Baby boomers are an important target market because they: a. include most of the important business leaders in the United States. b. represent a small proportion of the population, but have large disposable incomes. c. have the longest life expectancies; therefore, they will remain active in the market place for the longest period of time. D account for the majority of purchases of most consumer products and services. e. have the lowest income level. As the 78 million baby boomers have aged, their participation in the work force and their earnings have increased, making them an important consumer market. It has been estimated that this group accounts for 56 to 58 percent of the purchases in most consumer product and service categories. 38. (p. 81) Components of a consumer's income include: a. inflation, recession, and recovery. b. salary, wages, commissions, and fees. C gross, disposable, and discretionary incomes. d. taxes, perquisites, and salary. e. liquidity items, liabilities, and assets. A consumer's ability to buy is related to actual income, which consists of gross, disposable, and discretionary components. 39. (p. 83) Emily had an excellent year as a saleswoman in 2005. She earned $97,000. She paid $17,000 for "necessities" such as mortgage, food, and clothing. She was given a six-week all expenses paid vacation by the company for her sales performance that had a value of $9,000. Her state and federal income taxes totaled $24,000. What was her discretionary income? A $56,000 b. c. d. e. $73,000 $80,000 $88,000 There is not enough data provided to calculate her discretionary income. Discretionary income is the money that remains after paying for taxes and necessities. Therefore, $97,000=gross income less 17,000 for necessities less 24,000 for taxes equals $56,000 for discretionary income. 40. (p. 83) The owner of your local KFC franchise has had a good year with rising revenues and reduced operating costs that resulted in a personal income of roughly $100,000. Approximately one-third of that was taken for local, state, and federal income taxes, and another third went to pay for mortgage, car payments, food, clothing, and other necessities. What is the remaining third called? a. Windfall b. Bonus C Discretionary income d. Disposable income e. Franchiser fee Since discretionary income is the money that remains after paying taxes and necessities from gross income, $100,000 less one third for taxes and one third for necessities, leaves one third for discretionary income. 41. (p. 87) Competitive pressures among existing firms depend on: A the rate of industry growth. b. low fixed costs in the industry. c. large numbers of competitors. d. high variable costs. e. low variable costs. Competitive pressures among existing firms depend on the rate of industry growth. In slowgrowth settings, competition is more heated for any possible gains in market share. High fixed costs also create competitive pressures for firms to fill production capacity. Large numbers of competitors do not automatically increase competitive pressures—especially when the competitors are small. Variable costs have no relationship to competitive pressures as they are solely dependent on the amount of product sold. 42. (p. 120) Consumer behavior includes: a. actions a person takes in purchasing services. b. actions a person takes in using services. c. actions a person takes in purchasing products. d. the mental and social processes that come before and after purchase and use. E all of the above. Key term definition--consumer behavior 43. (p. 120) During the purchase decision process, an individual at the __________ stage will perceive differences between his or her ideal and actual situations big enough to trigger a decision. A problem recognition b. alternative evaluation c. cognitive dissonance d. routine response behavior e. post purchase behavior Text term definition--problem recognition 44. (p. 121) In which stage in the consumer purchase decision process would a consumer ask, "Is installation included in the price of this air conditioner?" a. problem recognition B information search c. alternative evaluation d. purchase decision e. evaluation The information search stage clarifies the problem for the consumer by suggesting criteria to use for the purchase, yields brand names that might meet the criteria, and develops consumer value perceptions. 45. (p. 120) When the elementary teacher needed to buy poster board for her class, she remembered that she had found some poster board at her local 99 Cents Only store, at Walgreen's, and at her Family Dollar Store. What term best describes the information search method used by the teacher? a. personal external source b. public external source c. market-dominated external source D internal search e. market-dominated internal source When you scan your memory for previous purchase experiences, you are engaged in an internal search. 46. (p. 120) A(n) __________ in the consumer purchase decision process occurs when consumers scan their memory for previous experiences with products or brands. a. problem recognition B internal search c. external search d. purchase task e. antecedent state Text term definition--internal search 47. (p. 121) Keisha is buying a new car appropriate to her role as the newest vice president at her company. She was overheard telling a co-worker, "The Volvo has reclining bucket seats, but the Cadillac has front and back stereo speakers." In which stage of the purchase decision process is Keisha? a. problem recognition b. information search C alternative evaluation d. purchase decision e. post purchase evaluation The problem recognition stage prompted the need for transportation; the information stage clarified the problem for the consumer by suggesting methods of satisfying the need by means of an automobile, bike, etc. The alternative evaluation stage provides evaluative criteria by which to make a decision from an CONSIDERATION set. In this case the purchase will be a car, but is it more important to have bucket seats or an exceptional stereo? 48. (p. 121) The objective and subjective attributes of a brand consumers use to compare different products and brands are called: a. temporal states. b. antecedent states. c. information sources. D evaluative criteria. e. the CONSIDERATION set. Key term definition--evaluative criteria 49. (p. 122) The group of brands a consumer would consider acceptable from among all the brands in the product class of which he or she is aware is the: a. evaluative set. b. evolved set. C consideration set. d. alternative selection group. e. aspiration group. Key term definition--consideration set 50. (p. 122) At the __________ of the purchase decision process, a consumer compares the product with his or her expectations and is either satisfied or dissatisfied. a. problem recognition stage b. information search stage c. alternative evaluation stage d. purchase decision stage E postpurchase stage After buying a product a consumer compares it with his or her expectations and is either satisfied or dissatisfied. The consumer may attempt to reduce cognitive dissonance by reinforcing the belief that he or she made the right choice. This occurs at the postpurchase stage. 51. (p. 122-Customer satisfaction is an important focus for marketers because: 3) a. B c. d. e. marketing research is an inexpensive process. the financial value of a retained customer can be significant. customer value is a non-quantifiable statistic. attracting new customers is easier than keeping old ones. a market development strategy is preferable to a market penetration strategy. Various marketers have calculated the value of customer retention over time and found it to be very profitable. Customers continue to buy from a specific marketer because that marketer provided them with satisfaction. 52. (p. 123) The feeling of postpurchase psychological tension or anxiety that a consumer often experiences is called: a. angst. b. the temporal state. c. the dissociative state. d. selective comprehension. E cognitive dissonance. Key term definition--cognitive dissonance 53. (p. 124) Which problem solving variation would likely be used for clothing, sheets and towels, or electric can openers? a. routine response behavior B limited problem solving c. extended problem solving d. simulated selection e. integrated problem solving In limited problem solving, consumers typically seek some information or rely on a friend to help them evaluate alternatives. There is little time or effort used in these situations 54. (p. 124) NetJets is a company that offers 1/16 or more ownership in a jet plane for a price beginning at $325,000. It gives the purchaser privacy, convenience and flexibility as well as saves them time since the plane is available with four hours notice. This is a high-involvement purchase for most people because: a. The item is inexpensive, can have serious personal consequences, or could reflect on one's social image. b. The item is inexpensive, has no serious personal consequences, but could reflect on one's social image. c. The item is expensive, has no serious personal consequences, but could reflect on one's social image. D The item is expensive, can have serious personal consequences, or could reflect on one's social image. e. The item is inexpensive, has no serious personal consequences, or would not reflect on one's social image. High-involvement purchase occasions typically have at least one of three characteristics: The item to be purchased (1) is expensive, (2) can have serious personal consequences, or (3) could reflect on one's social image. 55. (p. 126) Those needs which are basic to survival and which must be satisfied first are: A physiological needs. b. safety needs. c. social needs. d. personal needs. e. self actualization needs. Text term definition--physiological needs 56. (p. 127) In the hierarchy of needs, a burglar alarm would satisfy a __________ need. a. physiological B safety c. social d. personal e. self actualization Safety needs involve self-preservation and physical well-being. 57. (p. 127) An ad for Conesco's life insurance asks the question, "How do you plan on supporting your family after you pass away?" The ad shows a tombstone with a sign that offers the face of the stone as ad space. The ad is intended to appeal to which of the needs in the hierarchy of needs? a. physiological needs B safety needs c. social needs d. personal needs e. self actualization needs Safety needs involve self-preservation and physical well being. Providing financial security for one's family would help to satisfy that need. 58. (p. 128) Because the average consumer operates in a complex environment, the human brain attempts to organize and interpret information with a process called: a. selective retention. b. selective attention. c. selective exposure. D selective perception. e. stimulus discrimination. Text term definition--selective perception 59. (p. 128) The tendency to pay attention to messages consistent with one's attitudes and beliefs and to ignore messages that are inconsistent is called: a. selective retention. b. selective comprehension. C selective exposure. d. selective perception. e. stimulus discrimination. Text term definition--selective exposure 60. (p. 128) Charlie needs to purchase an automobile to drive to his new job in the city center. He begins to notice ads for many cars he wasn't aware of previously. This is an example of: a. subliminal perception. B selective exposure. c. retention. d. tuning out. e. behavioral learning. Selective exposure occurs when people pay attention to messages that are consistent with their attitudes and beliefs or when a need exists. 61. (p. 136) An aspiration group is a group is one: a. to which a person belongs, including fraternities and social clubs. B that a person wishes to be a member of or wishes to be identified with. c. that a person wishes to maintain a distance from because of differences in values or behaviors. d. that a person knows he or she can never really fit into because of basic cultural differences. e. that a person feels is excessively high above him or her socioeconomically. Text term definition--aspiration group 62. (p. 205) Movie studios use tracking studies, in which prospective moviegoers are asked questions about an upcoming film release to help them forecast sales. This is an example of: a. advertising of the movie. B marketing research. c. tactical support. d. cross-tabulations. e. social audits. The survey helps the movie studio research the prospective audience awareness and interest in the movie. If necessary, the studio will run last minute ads to increase awareness and interest. 63. (p. 205) Attempting to identify and define both marketing problems and opportunities and to generate and improve marketing action is the role __________ performs. a. advertising b. sales promotion c. publicity D marketing research e. tactical support Key term definition--marketing research 64. (p. 205) Grape-Nuts was one of the first cereals Post Cereal Company ever marketed. It scores well in brandawareness, but its sales have been steadily declining. Rather than assume the product was a dog, the marketing manager for this cereal decided Post Cereal Company should first: a. hire a consultant. B engage in marketing research. c. spend more dollars on advertising. d. hire more salespeople. e. develop new cereals. Post Cereals recognized a serious marketing problem existed--sales were declining. However, it didn't know what the factors causing the decline. It needed more information to learn the cause of the sales decline and how to reverse the trends. 65. (p. 207) During the marketing research process, __________ are the goals the decision maker seeks to achieve in solving a problem. a. measures of success B objectives c. marketing research plans d. decisions e. definitions Objectives are specific, measurable goals the decision maker seeks to achieve in solving a problem. 66. (p. 207-Which of the following is a typical marketing objective? 208) a. b. c. d. E Increase sales revenue and profit for Diet Coke. Discover whether consumers that buy Pampers are aware of gender-specific disposables. Find out why the new line of plus-size clothing is not selling well. Determine whether to offer a new & improved version of an existing product. All of the above are typical marketing objectives. Objectives are specific, measurable goals the decision maker seeks to achieve in solving a problem. Typical marketing objectives are increasing sales and profits, discovering what consumers are aware of and want, and finding out why a product isn't selling well. 67. (p. 210) Secondary data are: a. facts and figures that are newly collected for the project at hand. b. facts and figures obtained by watching people mechanically rather than in person. c. facts and figures obtained by asking people questions. D facts and figures that have already been recorded before the project. e. conclusions developed from information obtained from a representative sample of a population. Key term definition--secondary data 68. (p. 212) Two important advantages of secondary data are: a. they are inexpensive and up-to-date. b. they are up-to-date and supply all relevant categories of information. C they are usually inexpensive and save time. d. they are tailor-made to your specifications and relatively inexpensive. e. none of the above. Two important advantages of secondary data are (1) the tremendous time savings if the data have already been collected; and (2) the low cost (for example, most census reports are available for only a few dollars each). 69. (p. 221) The best way to find information that precisely addresses the problem at hand is to: A collect primary data. b. collect internal secondary data. c. collect external secondary data. d. perform a sensitivity analysis. e. use probability sampling. Primary data are those facts and figures, which are new and are collected for the first time for the project at hand. 70. (p. 213) Observational data are: a. facts and figures newly collected for the project at hand. B facts and figures obtained by watching people mechanically or in person. c. facts and figures obtained by asking people questions. d. facts and figures that have already been recorded before the project. e. conclusions developed from information obtained from a representative sample of a population. Key term definition--observational data 71. (p. 216) A marketing research approach that uses a discussion leader to interview 6 to 10 past, present, or prospective customers is called: a. a depth (or individual) interview. b. an experiment. C a focus group. d. small group dynamics. e. secondary data collection. Text term definition--focus groups 72. (p. 233) Aggregating prospective buyers into groups that have common needs and will respond similarly to a marketing action is called: a. consumer differentiation. b. psychographics. C market segmentation. d. market delineation. e. aggregation marketing. Key term definition--market segmentation 73. (p. 233) Market segmentation involves aggregating prospective buyers into groups that have common needs and will: a. pay attention to marketing messages. B respond similarly to a marketing action. c. be responsive to marketing research. d. use the same payment methods. e. go shopping on a regular basis. Key term definition--market segmentation 74. (p. 233) To be identified as a market segment, its members must: a. represent a large share of the entire market and have critical buying power. B have common needs and respond similarly to market actions. c. have different needs and have potential for future growth. d. have different needs and respond similarly to market actions. e. have potential for future growth and have potential for increased profit or ROI. An organization develops its segments by aggregating prospective buyers on the basis of common needs and similar response to a marketing action. 75. (p. 233) The phrase "relatively homogeneous collections of prospective buyers" is most descriptive of: A market segments. b. demographic clusters. c. organizational buyers. d. ultimate consumers. e. qualified prospects. Key term definition--market segments 76. (p. 233;The process of segmenting a market and selecting specific segments as targets is the link between Fig. 9-1) __________ and the organization's marketing program. a. self-regulatory industry standards b. government regulations c. top-level management D market needs e. controllable environmental factors Figure 9-1 illustrates how the process of segmenting and targeting markets links market needs to marketing programs. 77. (p. 233) Marketers use market segmentation to: a. link market needs to an organization's marketing program. b. develop specific marketing actions related to product or price. c. develop specific marketing actions related to advertising. d. increase overall sales, profits and/or other organizational goals. E do all of the above. Market segmentation is used to link needs to marketing needs to marketing programs, to develop marketing actions including those related to all of the 4Ps, and to increase sales and profitability. 78. (p. 238;The first step in segmenting and targeting markets is to: Fig. 9-3) a. B c. d. e. recognize a need. group prospective buyers into segments. create product groupings. estimate size of the overall market. develop a market-product grid The steps in segmenting and targeting markets include: (1)group potential buyers into segments; (2)group products to be sold into categories; (3)develop a market-product grid and estimate size of markets; (4) select target markets; (5) take marketing actions to reach target markets. 79. (p. 238;There are five steps involved in segmenting and targeting a market. What should a marketer do once he Fig. 9-3) or she has selected a target market and grouped products to be sold into categories? a. create product groupings B develop a market-product grid and estimate size of market c. identify market needs d. take marketing actions to reach that target market e. form prospective buyers into market segments The steps in segmenting and targeting markets include: (1)group potential buyers into segments; (2)group products to be sold into categories; (3)develop a market-product grid and estimate size of markets; (4) select target markets; (5) take marketing actions to reach target markets. 80. (p. 238) The best segmentation approach is the one that: a. makes it easiest to reach the segment. b. recognizes different needs of buyers among different segments. c. recognizes similarities of needs of potential buyers within a segment. d. is simplest and least costly in assigning potential buyers to segments. E maximizes the opportunity for future profit and ROI. One of the best criteria to use in forming segments is the opportunity for increased profits and ROI. 81. (p. 239) More than half of all U.S. households are made up of only one or two persons, so Campbell's packages meals with only one or two servings--from Great Starts breakfasts to L'Orient dinners. Campbell's is using __________ to segment its market. a. usage rates. b. usage patterns. c. buyer situations. D demographic characteristics. e. psychographic characteristics. The number of people in a household is a demographic characteristic that Campbell's uses to segment the market. 82. (p. 240) Magnavox sells many different types of TVs from flat screens to a 20" combination TV/DVD. The larger sets can be outfitted with surround sound at a higher price than the small set. The small set is much less expensive and allows the viewer to watch a DVD without extra equipment. Magnavox is using which buying situation segmentation variable in this example? A benefits sought b. psychographic c. demographic d. socioeconomic e. behavior Benefits sought includes product features and customer needs. Customers for the 20" TV would like the smaller size and the built in DVD player. 83. (p. 239) Airlines have developed frequent-flier programs to encourage passengers to use the same airline repeatedly. This segmentation technique focuses on: a. benefits sought B usage rate c. product awareness d. buyer intentions e. buying condition Of the buying situation variables noted as possible answers, the airlines have focused on usage rate. 84. (p. 241) Todd Harris and Associates, a New York sales promotion agency, discovered from analysis of its files that one-fifth of its clients accounted for more than three-quarters of its fees and commissions. This is an example of what classic concept? a. the law of inverse proportions B the 80/20 rule c. the survival of the fittest d. the law of eminent domain e. the primogeniture rule The 80/20 rule is a concept that suggests 80 percent of a firm's sales are obtained from 20 percent of its customers. 85. (p. 244) In developing a marketing strategy for Hallmark you decide that what it is really selling is memory keeping, and not photo albums, scrapbooks, and related supplies. This is an example of: a. target market selection. B product grouping. c. market-product grid development. d. taking marketing actions to reach target markets. e. market segmentation of prospects. "what it is really selling" is an example product grouping so that buyers can relate to the products. 86. (p. 244) Determining the size of specific markets using a market-product grid is helpful in determining which target market segments to select and __________. a. b. c. D e. how to implement the 80-20 rule. which products to be sold into groups. how to implement a harvesting strategy. which product groupings to offer. which products to reposition. Even "guesstimates" of the size of specific markets using a market-product grid are helpful in determining which target market segments to select and which product groupings to offer. 87. (p. 245) Which of the following is a criterion used for selecting a target segment? a. size of the market b. expected growth c. cost of reaching the segment d. compatibility with the selling company's objectives E all of the above There are five criteria used for selecting a target segment--the four listed in a, b, c, and d, and competitive position. 88. (p. 244) In developing a marketing strategy for the recently released Nike Air Jordan XVII with a price tag of $200, Nike decided to concentrate on affluent teens rather than members of high school basketball teams. This is an example of: A selecting target market segments to reach. b. forming products to be sold into groups. c. developing a market-product grid and estimating size of markets. d. taking marketing actions to reach target markets. e. forming prospective buyers into segments. A decision to concentrate on affluent teenagers is the selection of a target market segment. 89. (p. 246) Doris Lewis owns Lewis Edibles, Inc., a company that makes Tongue Tinglin' B.B.Q. Sauce. She wants to target local people who like the special blend of flavors found only in North Carolina barbecue sauce. In developing a marketing strategy to sell the sauce, Lewis decided to join Goodness Grows in North Carolina, a specialty food association that advertises local products and distributes them to local supermarkets and gourmet shops. Lewis has just: a. selected target market segments to reach. b. formed products to be sold into groups. c. developed a market-product grid and estimating size of markets. D taken marketing actions to reach target markets. e. formed prospective buyers into segments. Alternative d is the final result in the process of segmenting and targeting markets. 90. (p. 249) What does the term product positioning refer to? a. a careful analysis of cross tabulations b. shelf locations in major chain, grocery, and department stores c. geographic segmentation, often within major metropolitan areas D the place a product offering occupies in consumers' minds on important attributes e. an old and outdated concept no longer worthy of consideration in marketing planning Key term definition--product positioning 91. (p. 249) Changing the place an offering occupies in consumers' minds is called: a. perceptual mapping. b. product positioning. c. product differentiation. D repositioning. e. psychographics. Key term definition--repositioning 92. (p. 251) Recently, U.S. dairies, struggling to increase milk sales, tried to change the way adults thought about milk. The dairies wanted to __________ milk in the minds of the consumer. a. segment b. differentiate C reposition d. explain e. represent Changing the place an offering occupies in consumers' minds is called repositioning. The dairy industry tried to reposition milk in the minds of adult consumers. 93. (p. 250) A graph displaying consumers' perceptions of product attributes across two or more dimensions is a: a. payoff table. b. growth matrix. c. market-product grid. D perceptual map. e. consumer preference matrix. Using product attribute dimensions, a perceptual map shows the positions of the consumer's perception of the ideal product as well as all competing products in that market. 94. (p. 252) The maximum total sales of a product by all firms to a segment under specified environmental conditions and marketing efforts of the firms is called: a. top-down forecast. B market potential. c. growth potential. d. sales forecast. e. Delphi forecast. Key term definition--market or industry potential 95. (p. 252) Superba Cravats is a major marketer of men's bow ties. It estimates there are 20 million buyers of bow ties each year, that the average wearer of bow ties purchases 4 ties per year, and that the average price per bow tie is $10. Superba Cravats has a market share of 20 percent. The market (or industry) potential for bow ties is: a. $200 million. b. $80 million. c. $400 million. D $800 million. e. $160 million. Market potential equals the total buyers (20 million) times the number of ties bought per person (4) times the average purchase price ($10). So, 20 million x 4 x $10 = $800 million. Superba Cravats 20 percent market share is not relevant to the market (industry) potential question. 96. (p. 256) By dividing its market into categories, which it labels Basic, Expression, Classic, Fashion, Premium, and Communicator, Nokia is using: a. consumer differentiation. b. behavioral segmentation variables. c. market delineation. D market segmentation. e. aggregation marketing. Market segmentation helps Nokia best service different consumers' needs. 97. (p. 233) By developing and introducing a communication device which includes a built-in stopwatch, a thermometer, downloaded game packs, a personalized logo, a personal information manager and a cellular phone, Nokia is implementing a __________ strategy. a. product sampling b. product extrapolation C product differentiation d. usage segmentation. e. market differentiation Having a variety of products available allows consumers in each segment to select the phone best suited to their usage needs. 98. (p. 288) The stage of the product life cycle when a product is first commercialized to its intended target market is called the __________ stage. a. growth b. commercialization c. launch D introduction e. awareness-trial Commercialization is not a stage in the PLC. 99. (p. 288) Lack of profit in the introductory stage of the product life cycle is very often the result of: a. insufficient allocation of resources to the marketing mix. b. poor selection of distribution channels. c. high taxes. D large investment costs in product development. e. ineffective execution of the marketing program. The lack of profit is often a result of the large costs of product development. 100. (p. 288) A few years ago Who Wants to Be a Millionaire premiered as the first nighttime game show in a couple of decades. The marketing for the show was intent on making television viewers aware of its existence and excited enough about the show that we would watch the first episode. Which of the following statements about televised game shows is true? A Who Wants to Be a Millionaire was in the introduction stage of the product life cycle of televised nighttime game shows when it premiered. b. c. d. e. Because television has been around for many years, all programs fall naturally into the maturity stage. Televised programs are either in the introduction stage or the growth stage and are discontinued when they move into the maturity stage. All televised programming uses a three-stage product life cycle--growth, maturity, and decline. The product life cycle is totally inapplicable to any television genre. The televised game show was a new product category on television and as such was in the introduction stage. Because producers are always trying to gain and keep audiences, program types move in and out of favor, which means new products are introduced and others go into decline. There are program types today that can be said to be in their maturity such as news programs like Meet the Press. The four-stage product life cycle is applicable to television genres. 101. (p. 290) During the introduction stage of the product life cycle, __________ is used. This pricing strategy charges a high price to recoup the costs of product development. a. penetration pricing b. cost-plus pricing c. ROI pricing. d. market-oriented pricing E skimming pricing Text term definition--skimming 102. (p. 290) 3M is a master of __________ strategy. According to a 3M manager, "We hit fast, price high, and get the heck out when the me-too products pour in." a. penetration pricing b. cost-plus pricing c. ROI pricing. d. market-oriented pricing E skimming pricing Skimming pricing strategy charges a high price to recoup the costs of product development. 103. (p. 290) Which stage in the product life cycle is characterized by a rapid increase in sales and the appearance of competitors? a. introduction B growth c. maturity d. decline e. profit The second stage of the product life cycle, growth, is characterized by rapid increases in sales, and it is in this stage that competitors appear. 104. (p. 292) Which stage in the product life cycle is characterized by a leveling off of industry sales? a. introduction b. growth C maturity d. decline e. comparability The third stage, maturity, is characterized by a leveling off of total industry sales revenue. Most consumers who would buy the product are either repeat purchasers of the product or have tried and abandoned it. 105. (p. 292) During the maturity stage of the product life cycle, profit declines because: a. there are fewer and fewer competitors in the market. b. better products are only in the growth stage. c. production costs increase the more a firm has to manufacture the same product. D there is fierce price competition among sellers. e. all of the above. Profit declines because there is fierce price competition among many sellers and the cost of gaining each new buyer at this stage is greater. 106. (p. 292) The marketing objective of a firm whose product is in the maturity stage of the product life cycle is to: a. actively search out new first time users. B maintain existing buyers since new ones are hard to find. c. actively reinforce competitors' marketing efforts. d. maintain existing distributors and actively seek out new ones. e. shift to a skimming price strategy. The marketing objective for a company is to maintain its existing buyers because few new customers are available to replace any who are lost. 107. (p. 292) Promotional expenses at the maturity stage of the product life cycle are often designed to: a. allow a price increase. B remind repeat purchasers. c. create primary demand. d. gain new distributors. e. eliminate distribution channels. Promotional expenses in the maturity stage often are directed towards contests or games to keep people using the product and price competition continues through cents-off coupons. 108. (p. 292) To handle products in the decline stage of the product life cycle, companies often use either: a. diversification or harvesting. b. diversification orcontracting. C deletion or harvesting. d. deletion or diversification. e. building or contracting. To handle a declining product, a company often follows one of two strategies. Deletion is dropping the product from the line; harvesting is retaining the product but reducing support costs. 109. (p. 292) A number of years ago Pokémon was the hottest name in toys, but as other more high-tech toys appeared on the market, the popularity of Pokémon waned as did its sales. Some toy experts predict Pokémon will soon be only a memory for toy retailers. Pokémon is in the __________ stage of its product life cycle. a. decay b. uncommercialization C d. e. decline maturity harvested The market has abandoned Pokémon. 110. (p. 294) __________ refers to the entire product category or industry, such as video games. a. Product form B Product class c. Product line d. Product family e. Product brand Key term definition--product class 111. (p. 294) Televisions are an example of a __________, and flat screen TVs are an example of a __________. a. product line; product class b. product family; product line c. product brand; product line d. product form; product class E product class; product form Product class refers to the entire product category or industry; product form pertains to variations within the class. 112. (p. 298) Snickers candy bar was repositioned from a candy bar to a snack food through commercials that showed the busy people satisfying their hunger with a Snickers bar. Mars, Inc., used this strategy with its Snickers bar to: a. react to a competitor's position. B reach a new market. c. catch a rising trend. d. change the value offered. e. do none of the above. Mars, Inc., makers of Snickers, saw that time pressures meant more consumers were looking for a quick snack. By positioning the peanut filled candy bar as an energy-filled snack, it was able to reach a much larger market. 113. (p. 300) When consumers think of Harley-Davidson, the image of a masculine, non-conformist is the likely associated with that brand name. With the Vespa motorscooters, the image is more likely to be a brainy environmentalist that wears polyester and socks that don't match. Both Vespa and HarleyDavidson: A have brand personalities. b. have created brand mannerisms. c. are symbolic brands. d. use brand personification. e. use product personification. Brand personality is a set of human characteristics associated with a brand name. 114. (p. 300) Brand equity is: a. b. c. d. E the resources invested to create a name, phrase, design, symbol, or combination of these to identify a firm's products and distinguish them from those of its competitors. adding customer value to the product brand through additional features or higher-quality materials, or reducing its price. increasing the content contained within the brand's package without changing its size or increasing its price. the net present value of the royalties the firm receives as a result of licensing its brand to other firms to manufacture and/or market. the added customer value a given brand name gives to a product beyond the functional benefits provided. Key term definition--brand equity