Forms of Government - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement

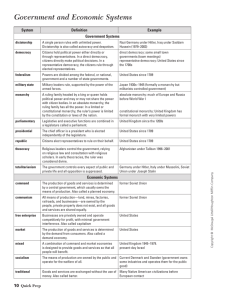
Forms of Government Identify the following terms (10 bolded words are required, others optional for extra credit) To identify, explain or define the term and give examples of when and where the form of government has existed or currently exists. In addition explain or describe how this form of government would work and the process involved in establishing the government in a classroom using a teacher and students as an example. Be creative in use of people and props. Forms of Government: 1. Government 2. Selfdetermination 3. Federal 4. Monarchy 5. Presidential 6. Feudalism 7. Military State 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Theocracy Totalitarianism Autocracy Aristocracy Democracy Direct democracy 14. Indirect (representative) democracy 15. Parliamentary 16. Oligarchy 17. Republic 18. Constitutional monarchy Examples: Government refers to a political system that directs, organizes, regulates, or controls a group of people to establish order. Different levels of government typically have different responsibilities (e.g. local, regional, and national governments). Most governments exercise legislative (make laws), executive (enforce laws), and judicial (judge actions) powers and split or combine them in various ways. Autocracy, democracy, republic, fascism, monarchy, oligarchy, plutocracy (government by the wealthy), theocracy, and totalitarianism, are all examples of types of government. Governments are practiced everywhere. For example, all classrooms have a form of government that is used to create order and organization. Generally teachers make rules, enforce rules, and judge student actions based on some sort of guideline and expectations for behavior. Without some rules, organization, and/or structure, classrooms would not be able to function and work together as a coherent system. Self-determination occurs when individuals control themselves and make their own choices and decisions in government. This requires individuals to be self-motivated. For example, American revolutionists fought for independence so they would be able to make their own choices in government and not be controlled by the king of Great Britain. For self-determination to be practiced in a classroom, students would have to be self-motivated to want to learn. Students that were self-motivated may establish their own guidelines and behavioral expectations. For example, if you walked into a class of self-determining students, they would probably all be working to understand the concepts and skills necessary for survival in a complex world. Federal government systems divide power among the federal or national government and a number of independent states. This form of government exists today in the United States because we have a national government and individual state governments. This helps balance power and also allows the national government to delegate authority to the state government. For example, each individual state is responsible for its own educational funding. The national government does not provide money for education of a people within a state unless there is an extreme emergency, etc. In a classroom, the federal system might break the students up into four groups with delegates from each group selected to represent their group. The teacher would then rule over and provide instruction (protection) to all four groups but each group might be responsible for grading their own assignments before turning them in. Match the form of government with the definition: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) Totalitarianism Military State Aristocracy Parliamentary Theocracy Republic Monarchy h) i) j) k) l) m) n) Presidential Democracy Federal Feudalism Autocracy Oligarchy Direct democracy o) Representative democracy p) Constitutional monarchy q) Constitution 1) A king allows nobles to use land in exchange for their loyalty, military service, and protection of the people who live on the land. 2) Powers are divided among the federal, or national government and a number of state governments. 3) Religious leaders control the government relying on religious law and consultation with religious scholars. 4) Rule by a few people or a small group. 5) A single person rules with unlimited power. 6) Citizens hold political power either directly or through representatives. 7) The government controls every aspect of public and private life and all opposition is suppressed. 8) Power is in the hands of a hereditary ruling class or nobility. 9) Legislative and executive functions are combined in a legislature called a parliament. 10) Citizens elect representatives to rule on their behalf. 11) The chief officer is a president who is elected independently of the legislature. 12) Military leaders rule; supported by the power of the armed forces. 13) Ruling family headed by a king or queen that holds political power and may not share power with citizen bodies. 14) A form of democracy in which the people as a whole make direct decisions, rather than have those decisions made for them by elected representatives. 15) A type of democracy in which the citizens delegate authority to elected representatives 16) A monarchy in which the powers of the ruler are restricted to those granted under the constitution and laws of the nation. 17) A document that embodies the fundamental principles according to which a nation, state, corporation, or the like, is governed.







![“The Progress of invention is really a threat [to monarchy]. Whenever](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005328855_1-dcf2226918c1b7efad661cb19485529d-300x300.png)

