Chapter 1 Cells Lesson 1 “What Are the Parts of a Cell?” Cell Theory
advertisement

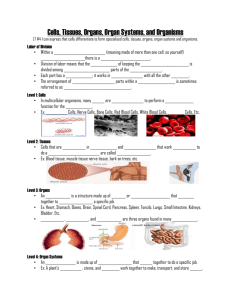
Chapter 1 Cells Lesson 1 “What Are the Parts of a Cell?” Cell Theory (YOU WILL BE TESTED ON THIS) All living things are made up of cells The cell is the smallest unit of an organism Cells come from other cells Basic Needs of Living Things Make food(plants) or take in food (animals), which is a source of energy A way to support and protect their bodies Get rid of wastes Grow Reproduce Cell Parts Nucleus- “The Brain” of the cell. Directs all activities, stores a molecule of DNA (genetic material). Cell Membrane- Thin, flexible covering that surrounds all types of cells. Allows food, water, and gases to enter the cell, and wastes to leave. Cell Wall-In plant cells, the rigid outer layer that surrounds the cell membrane. Helps plant stay upright. Pores in cell wall allows materials to pass in and out. Cytoplasm-Gel-like material between the nucleus and cell membrane. Organelles float in the gel. Ribosomes-tiny and scattered throughout the cell. Help assemble proteins which are necessary for growth and repair. Lysosomes-Small, ball-shapes organelles. Help cell break down nutrients and old cell parts. Common in animal cells, rare in plant cells. Vacuoles-membrane-bound sacs filled with fluid. Store water, food, waste, and other substances the cell processes. Animal cells may have several vacuoles. Plant cells often have one large central vacuole. Golgi Apparatus-receives proteins and processes them for “shipment” outside the cell. Chloroplasts- Found only in plants and some protists. Contain pigments that absorb sunlight. They use the energy to make food. Mitochondria-“Power plants” of the cell. Inside them sugars break apart as they react with oxygen. This process releases carbon dioxide, water, and LOTS of energy. Endoplasmic Reticulum-System of membranes and tubes. The membranes twist and turn through the cell, providing passages through which materials can pass. Endoplasmic reticulum can be rough or smooth. Rough ER helps cells secrete proteins. Smooth ER helps cells break down toxic chemicals. Organelles-structures that perform specific functions in the cell. Animal Cells and Plant Cells-have many of the same organelles, but some are different such as, cell walls and LARGE vacuoles which exist in plant cells ONLY. Lesson 2 “How Do Cells make and Use Energy?” Glucose and oxygen are broken down in a process called cellular respiration, which releases energy in the form of ATP. Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide and water. Breathing supplies the oxygen required for cellular respiration and also eliminates the carbon dioxide produced as a waste product. Making proteins, movement, cell division, and transport of materials are examples of the life functions that require energy. Not all organisms have the same need for energy. Some large animals are endangered because humans now occupy many spaces where the animals found food. The amount of energy available often determines how organisms grow and reproduce. Lesson 3 “How Are Cells Organized?” In multicellular organisms, similar cells form tissues and similar tissues form organs. Organs work together in organ systems to support the whole organism. Complex organisms have more than one kind of tissue to be able to perform all the functions of life. Organs are organized into organ systems: a group of related organs that work together to perform a specific function. Plants have organs and organ systems, such as leaves.