Biology
advertisement

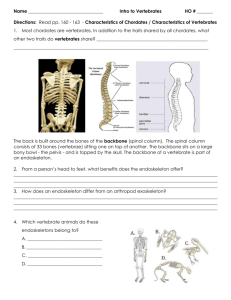
Subject: Biology Grade Level: pre-MYP Unit and time period Unit title Area of Interaction Context Significant concept Unit 1 – September to the end of November Life and its Diversity. Health & Social: Understanding how cells work, its function as "building blocks" of organisms and describe the requirements for cells to live. Basic requirements of Life. The cell theory. Pro-/ Eukaryotic cell Animal / Plant cell “Cell city analogy” Darwin’s theory of evolution. Advances of diversity in population for survival. Teacher: Dr. Compel Peter Possible assessment tasks 1. Quiz – “Charles Darwin.” MYP 3 Modified Objectives addressed (Students should be able to ...) - explain how cells function and describe the requirements for cells to live. - understand the Value of biodiversity in the context of Darwin’s theory of Evolution. Understanding basic unit of structure and function in living things. 2. End-of-unit test Understanding the process of Evolution as a main reason for today Diversity between living Organisms Unit 2 – December to the end of January Unit 3 – February to the April Earth - our Home. The Human –Earth interaction and coexistence in flow of the time. Community & Service: Understand the consequences of the Human – Earth interactions. Understand the changes on the Earth that led to the human evolution and understand the consequences of the human activities to the changes of the Earth. 1. Poster / PPT presentation” Earth – our Home” 2. Lab work: “Observe the life variability in micro-ecosystem of your home”. - read scientific text effectively in order to understand the most relevant information to understand and use scientific language. - understand and discuss the connection between the Human Evolution and Changes on the Earth. Environment: Ecology. Biosphere - levels of organization. Energy flow. Cycles of Matter (Vater, nutrient, Nitrogen…). How does environment effect the other ones? Understanding the interactions and interdependence among the organisms and between the organisms and their surroundings (environment). 1. End-of-unit test - understand the energy flow in the nature and recognize the internal connections within the food chain /food web. - discus the interdependence of organisms in different ecosystems. - recognize and recall scientific information relevant to the unit - explain and apply scientific information Unit 4 – May to the June Plant diversity ENV, H&S Can cyanobacteria be useful ? Which plants and their extracts have been used in medicine and why? What is my favorite plant and why is it good for me? What kind of herbal tea should I drink? Which parts of plants do we eat? Are there strangers among plants worth introducing? Should herbal remedies be regulated? Should humankind use technology to design flowers and highly nutritional plants? Through this AOI students will learn about the importance of plants for living organisms, medicine, diet and environment. The will find out about the adaptations of plants living in different environments. Students will find out what are some of the endangered species of Plants. Students will learn about the Plant structure, function and importance for medicine. They will learn the basic Classification of Plants – Seed plants, Flowering plants. Learning how the plants are important, understanding how the plant structure is related to its function. They will find out how the plants can be used in Medicine. Learning about the nutritional specialists – parasites and carnivorous plants. Understanding how the plants can defend themselves. 1. Lab work 1 “Comparing Mosses and Ferns” 2. Lab work 2 “What are the most common Seed plants found in Slovakia?” 3. Argumentative essay “Should herbal remedies be regulated?” 4. End-of-unit test - to understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit in written lab reports - to formulate a simple research question and hypothesis - to design a simple investigation, materials/equipment needed, describe a method, comment on it and suggest improvements - to carry out scientific investigation safely and skillfully and work effectively and responsibly as a member of a team - to draw conclusions, discuss and explain the results - to discuss the importance of plants for our health - to understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit clearly and effectively - to demonstrate honesty when handling the data, acknowledging sources as appropriate Subject: Biology Unit and time period Unit 1 – September to the end of October Unit title Unit 2 – November to the mid of January Multicelled organisms Unit 3 – Mid of January to the mid of March Single celled organisms. Prokaryotes. Eukaryotes. Invertebrates Sponges Cnidarians Worms Molluscs Echinoderms Grade Level: MYP 1 Area of Interaction Context Health & Social: How to protect from serious illnesses? Example malaria and sleeping sickness Significant concept Understanding the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms and between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. Community & Service: What can I do to protect coral reefs? How does environment effect the other one?. Understanding basic unit of structure and function in living things Enviroment: Understanding basic unit of structure and function in living things How does one animal effect the other one? Teacher: Dr. Compel Peter Possible assessment tasks End-of-unit test. - understand, that single-celled organisms are parasites , which cause many diseases 1. Lab work 1 Observe invertebrates that live in local environments. 2. End-of-unit- test. 1. End-of-unit test. Where does a pearl come from? Unit 4 – Mid of March to the end of June Arthropods Arachnids Crustaceans Insect Human Ingenuity: Insects – friends or enemies? Learning how to write a good essay. students will discuss different examples of reports and will try to evaluate their quality MYP 3 Modified Objectives addressed (Students should be able to ...) - explain how cells "building blocks" of living organism. - recognize differences between a host and a parasite 1. Argumentative essay “Insects – friends or enemies?” 2. End-of-unit test -ability to read scientific text effectively in order to understand the most relevant information to understand and use scientific language - discuss the diversity of invertebrates. - recognize and recall scientific information relevant to the unit of mixtures - apply the knowledge to solve problems in familiar and, with guidance, in unfamiliar situations - describe different types of mollusks and their features. - describe different types of echinoderms and their features. - observe details of mollusks and echinoderm shells. - recognize and recall scientific information relevant to the unit - explain and apply scientific information to solve problems in familiar and, with guidance, unfamiliar situations - understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit in written essay. - describe, explain, discuss and support your ideas. - understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit clearly and effectively - to demonstrate honesty acknowledging sources as appropriate Subject: Biology Grade Level: MYP 2 Teacher: Dr. Compel Peter Unit and time period Unit title Area of Interaction Context Significant concept Possible assessment tasks Unit 1 – September to the end of November Chordates. General characteristics of Chordates, Vertebrates, Invertebrates. Classification of Chordates. () Human Ingenuity: How are scientific names a universal tool for communication between scientists? Distinguish between chordates & vertebrates. Understand the key concept of endothermic and exothermic animals. 1. End-of-unit test Community & Service: How we can help some endangered animals to survive? Understanding the evolutionary insight of the vertebrates’ development. Presentation: Chordates and their Evolution Environments: What kinds of coldblooded animals living in Slovakia are bio indicators? Discuss, why it is worth to keep our environment clean because of bio indicators Unit 2 - December to January Unit 3 –February to mid of April. Unit 4 – Mid of April to the end of June Evolution of Chordates. Cold-blooded vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles) Warm-blooded vertebrates. ( birds, mammals) Health & Social: Can be a pet vector for serious illnesses? How to protect from serious illnesses? Lab work: Observe vertebrates that live in local environments. Explain the adaptations that enable most birds to fly. Understand terms, herbivore, carnivore, and omnivore. Objectives addressed (Students should be able to ......) - learn the basic characteristics of vertebrates and chordates. - understand the difference between cold blooded and warm blooded animals, and between the chordates and vertebrates. - to apply the knowledge and understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit in written presentation and lab report. 1.Lab work - Investigating how reptiles regulate the temperature of their body 2. End-of-unit test - understand the way of reptile adaptation for Life on Land - identify amphibians as vertebrates that can live on land for part of their lives. 1.Lab work - Investigating what happens to a feather in oilHow can be oil spill fatal to ocean life 2. End-of-unit test - understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit in written lab reports Subject: Biology Grade Level: MYP 3 Teacher: Dr. Compel Peter Unit and time period Unit title Area of Interaction Context Significant concept Possible assessment tasks Unit 1 – September to the November Human body construction. Systems, organs, tissues and cells. The Skeletal system. Type of Bones. Type of joints. Structure of bones. When leg gets broken… Community & Service: How we can help people with disabilities? Students will become familiar with the bones of the human body. Students will discuss the importance of healthy diet for bone development. 1.End-of-unit test Unit 2 - December to January Muscular system. Type of muscles. Structure of muscles. Function of muscles. Human Ingenuity: How can I demonstrate how the power development? Students will learn about the movement complexity and understand how muscular and skeletal systems cooperate. 1. Lab work: Power development by exercise. Students will distinguish between different types of blood cells and their function. Students will recognize that body is a dynamic system with many inputs and outputs To understand how is body regulated by senses, nervous and endocrinal system To know how to prevent from sexual diseases 1. End-of-unit test Integumentary system. Unit 3 – February to April Unit 4 - May to the end of June Transit in human body. Circulatory and Respiratory system. (Parts- blood, vessels, heart, how does it work) Digestive and Urinary system (parts, how does it work) Environments: How does air pollution affect living things? Nervous, Endocrine and Reproductive system. Human ontogenesis (parts, how does it work) Health & Social: Why is prevention the most important cure? 2. Poster presentation: Where the power comes from? 2. Lab work: Measuring your pulse rate and breathing rate. 1.End-of-unit test 2. Essay: Civilization diseases. Objectives addressed (Students should be able to ......) - understand the levels of the body construction. - describe the general structure of the bone and the functions of the skeletal system and its parts. - demonstrate the knowledge about the function of muscular system - explain and apply scientific information and ability to use scientific language clearly - understanding significant role of blood in our bodies - ability to use scientific language clearly - identifying problems – including deductive reasoning, solutions to problems Subject: Biology Grade Level: MYP 4 Teacher: Dr. Compel Peter Unit and time period Unit title Area of Interaction Context Significant concept Possible assessment tasks Unit 1 – September to November Fundamentals of the life. Characteristics of Living Things. Health & Social: Understanding a balanced diet necessity to keep our body healthy. Students will understand that all living organisms are composed of cells and what all living things have in common. They will learn distinguish between organic/ inorganic compounds, macromolecules/ polymeric molecules and understand which chemical compounds are necessary in order to maintain the life and why. They will learn the composition of the cell membrane and understand the mechanism of the movement of materials in and out of cells. Student will learn about the experimental background and important moments of the DNA function discovery. They will understand the connection between the structure and function of nucleic acids and their importance for life Students will learn about the different cell types and understanding the function of cell organelles. Learning about the basic processes of the cell energy flow - photosynthesis and respiration. Understanding the mechanisms of Mitosis and crucial importance of cell division for maintaining life of all living organisms and also impact of cell division defects. 1. End-of-unit test 2. Lab work: Using the light microscope. Chemistry of the life. What makes water so special for life? Why does a cell need proteins, carbohydrates and lipids? Transport across the membrane. How is transportation in cell secured? Unit 2 – December to January Nucleic acids –the key to inheritance and evolution. DNA, RNA structure – Same, but different. DNA replication. Gene Expression: Translation, Transcription. Unit 3 – February to April Life is cellular Why are the functions of cell organelles important for its survival? Cell cycle – Cell division. How do cells of gut, skin and blood get renewed? How is renovation (mitosis) of cells regulated and why is cancer relevant? Can a cell get tired? Human Ingenuity: Understand the Rosalind Franklin contribution to DNA structure & role discovery / importance of the academic honesty in the science. Community& Service: Significance of safe and responsible behavior of individuals within communities. Promotion of equality and equity within communities. Health & Social: Cell division dysfunction related diseases - cancer. MYP4 Modified Objectives addressed (Students should be able to ...) - to understand characteristics of living things - to understand characteristic of water and its importance for all living things - to understand the structure and function of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and their importance for cell - to understand homeostasis - to understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit. - to understand and explain how the molecules move in and out of the cell - to be able to demonstrate diffusion and osmosis and explain its importance in the aspects of everyday life. 1.Poster presentation “The story of DNA” - learn about the important moments of the inheritance key molecules and laws of heredity discovery - to understand the structure and function of nucleic acids and their importance for life 1. Lab work. Observing Plant and Animal Cell 2. Lab work 2 Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis. 3. End-of-unit- test 4. Poster presentation - to recognize, understand and use scientific knowledge relevant to the unit Cells in written lab reports - to formulate a simple hypothesis and explain it - to identify variables, materials /equipment needed, describe a method, comment on it and suggest improvements - to collect and record the data and organize them into a table or a graph and analyze them Unit 4 – April to the end of June Invisible yet dangerous What are viruses and bacteria? Can we fully grasp role of microorganisms in our environment? How did Louis Pasteur save Russian kids in Paris? Should mass vaccination be required? How do bacteria develop resistance and why is it relevant? How to prevent spread of HIV? How to protect ourselves in season of flu? Epidemiologist - a carrier path for me? H&S, HI Through this AOI Students will focus their learning on vaccination, its history and stimulation of immune system to fight subsequent invasion by the same microbes. They will learn about viral diseases that damage immune system. Based on the gain knowledge students will discuss the ways how to protect against viruses and bacteria. Students will also find out about epidemiology as a carrier path. Students will find out how the viruses and bacteria may infect animals, plants and humans and interfere with normal life functions. Understanding how are bacteria and viruses affecting our immune system. They will learn about vaccination and all understand how can we fight against some diseases. Students will learn that understanding the structure and function of microbes is very important for finding the right treatment. Students will learn about the career in Epidemiology 1.Argumentative essay “Should mass vaccination be required?” 2. End-of-unit test - to give example and discuss positive and negative effects of vaccination - to understand the function and structure of bacteria and viruses - to provide scientific information in an argumentative essay - to understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit - to demonstrate honesty when handling the data, acknowledging sources as appropriate - to recognize and recall scientific information relevant to the unit - to explain and apply scientific information to solve problems in familiar and, with guidance, unfamiliar situations Subject: Biology Unit and time period Unit 1 – September to the mid of November Unit title Grade Level: MYP 5 Area of Interaction Context Unicellular versus Multicultural Importance of organization for structure and function of a whole organism. Evolution and Diversity of species Ch. Darwin and Neodarwinism. Natural selection Are there any rules of evolution? Where does it go? Environments: Unit 2 – November to the end of January Finding Order in Diversity How are animals organized? History of Taxonomy Why to classify? Binomial Nomenclature. Understand the evolutionary insights of the modern taxonomy. Unit 3 – February to April Unicellular organisms How useful and dangerous can single cells be? Why scientists pay close attention to Ciliata? Porifera, Cnidaria and Worms What are Sponges? How does a jellyfish hunt? How coral reefs grow and Human Ingenuity: The key persons and the taxonomy milestones. (Confucius, Aristotle, Carolus Linnaeus,). Understand the importance of Binomial nomenclature in context of scientific communication around the world. H&S Knowledge of selfprotection, prevention and life cycle of contagious infections caused by single celled organisms. Self-protection, prevention and life cycle of diseases caused by parasitic Flatworms and Roundworms. Environment. Students will understand the relationship between evolutionary processes and diversity of species. Milestones of Evolution towards the Humans. Diversity – Advantage or Disadvantage? Teacher: Dr. Compel Peter Significant concept Possible assessment tasks MYP4 Modified Objectives addressed (Students should be able to ...) Understanding the important levels of organization for structure and function of an organism. Recognizing the process of Evolution as a process of continuous and gradual change under the pressure of natural selection. Learning about the Darwin’s Evolution theory with impact to today world. 1. Lab work “Use of Microscope” - to understand the organization of living things - to understand the Darwin’s theory of Evolution and diversity of species in meaning of new evidences from modern scientific disciplines (molecular biology, genetics, geology, etc.) - to understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit in written lab reports Students will learn to understand the modern classification system in context of the historical background. They will understand how the organisms are classified and will know how to use classification tools. 1.PPT Presentation “Finding Order in Diversity. 2. End-of-unit- test - to understand the levels of Classification and difference between the natural/artificial taxonomical categories. - to be able to use classification tools and to construct them - to be able to read scientific text effectively in order to understand the most relevant information Understanding the impact of parasitic Sarcomastigophora on their host. Understanding the sleeping sickness, malaria etc. and the lifecycles of parasites. Discussing the prevention and treatment of malaria, toxoplasosmosis, giardiasis etc. Understanding the development of Invertebrates and the milestones in their evolution 1. Lab work “Comparing and contrasting Flatworm and Roundworm” - to understand the body structure and function of protists - to discuss the life cycle of parasitic protozoans - to understand the symptoms, prevention and treatment of malaria, sleeping sickness etc. - to formulate a simple hypothesis and explain it - to collect and record the data and organize them into a table or a graph and analyze them 2. End-of-unit test 3.Quiz “Evolution and diversity of species.” 2. PPT / Poster presentation “Parasitic Worms” 3.Lab work what is threatening them? Do Nematoda affect our health? Molusca, Annelida and Arthropoda Can a delicacy be deadly? How do pearls get formed? What are the wonders of octopus? Earthworm as a pioneer. Diversity of Arthropda. Mysteries of social insect Protection of endangered invertebrates. Realizing that Corals are living organisms and underlining the importance of their protection. Understand how the marine invertebrates are adapted to their environment and how the Annelids can be useful for Ecosystem. They will learn about the life and organization of social insect. Students will focus their learning on the important features of arthropods and their importance in Ecosystem. (germ layers, body symmetry, cephalization etc.). Learning about the body organization, function and ecology of Porifera and Cnidaria (Sponges). Understanding the life cycle of parasitic worms (Tapeworms and Roundworms), the diseases they cause and learn about treatment and prevention. Describing the features, characteristics and ecology of Annelids Learning about the benefit of Leeches Learning about the features of Mollusks, its form and function and ecology Finding out the connection between bivalves and pollution Identifying the features of arthropods, explaining their development and the important trends in their evolution. “How are Insects adapted for feeding?” 4. End-of-unit test - to recognize and recall scientific information relevant to the unit of Porifera, Cnidaria and Worms - to apply the knowledge to solve problems in familiar and, with guidance, in unfamiliar situations - to compare and contrast the defining features of Annelids, Mollusks and Arthropods - to understand the usefulness of Bivalvia for people. - to explain the benefit of leeches- to understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit - to demonstrate honesty when handling the data, acknowledging sources as appropriate - to recognize and recall scientific information relevant to the unit - to explain and apply scientific information to solve problems in familiar and, with guidance, unfamiliar situations Unit 4 – May to June Chordates. H&S Milestones of evolution towards humans. Introducing remarkable sharks. Chimera and bit of mythology. Why shark is not a fish? Inconsistent frogs not as delicacy. Temperature matters for crocodiles, turtles and snakes. Conquerors of air. Is milk only commonality for mammals? Through this AOI students will learn what the Chordates are They will understand the Milestones of evolution towards humans. The will learn about how fishes are adapted for life in water Students will learn about the adaptation of aquatic animals to terrestrial life. They will understand the essential functions of mammals. Learning the phylogeny and development, body structure, life function and adaptation of Echinodermata, They will understand the characteristics of Chordates and explain what vertebrates are. They will focus on difference in structure, function and adaptation between aquatic and terrestrial chordates; Tunicata, Cephalochordata, Cyclostomata, Chondroichtyes, Osteichtyes, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, Learning about the Endangered species Students will understand the relationship between climate change and adaptation of reptiles. Understand the characteristic, evolution and life functions of Mammals. Discuss and understand the diversity of Mammals. 1. Poster presentation “Diversity of Reptiles” 2. Lab work 2 “How do birds breath?” 3. Argumentative essay “What are the ecological consequences of distinction of animal species.?” 4. End-of-unit test - to understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit in written lab reports - to formulate a simple research question and hypothesis - to carry out scientific investigation safely and skillfully and work effectively and responsibly as a member of a team - to draw conclusions, discuss and explain the results - to discuss the evolution and adaptation of Vertebrates - to understand and use scientific language relevant to the unit clearly and effectively - to demonstrate honesty when handling the data, acknowledging sources as appropriate