French Revolution Vocabulary
advertisement

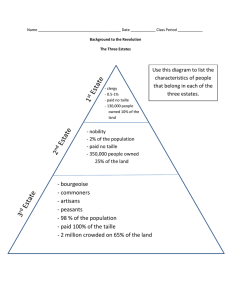
French Revolution Vocabulary Estate- One of the 3 distinct social classes in France in the 1700’s Estates General- meeting of the three estates to vote on new taxation laws Absolute Monarchy- king or queen with total power Louis XIV- Known as the sun king, he lived an extravagant lifestyle and waged many wars against Great Britain and Spain which depleted France’s treasury Louis XVI- King during French Revolution, he called the Estates General together. Palace of Versailles- Extravagant building that represented Louis XIV’s lifestyle. Tyranny- Unrestricted use of power. Taxation- When people are made to pay a certain amount that is put on income, property and sales. Marie Antoinette- Wife of Louis XVI Lack of Social Mobility- Inability to move out of your social class. Crop Failures- Unsuccessful crop growth. National Debt- The amount of money a government owes. Bastille- Prison is Paris that was overtaken by the third estate, symbol of royal tyranny. Robespierre- (Radical) Leader of Jacobins and Committee for Public Safety. Committee of Public Safety- Group who ruled France during the reign of terror and promoted radical ideas. National Assembly- The gathering of the third estate to set up a new constitution. Radical- Group favoring extreme changes in government policy. Moderate- Group open to minor changes in the government. Conservative- Group that favors maintaining the status quo. Guillotine- Device designed to behead people during the reign of terror. “Liberty, Equality, Fraternity”- Slogan of the radicals. Reign of Terror- Period in France during the revolution when opposition was killed. Directory- Council of 5 men who tried to restore order to France. 1 Girondins- Moderate group who felt the revolution had gone far enough. Jacobins- Extreme radicals in favor of the reign of terror. Declaration of the Rights of Men- Document created in 1789 stating all men are equal before the law. Today it is the French Constitution. Tennis Court Oath- Agreement among the third estate to keep meeting until a new constitution was formed. National Convention- Met from 1792-1795 and wrote the first democration constitution Constitution- Created in 1791 which kept a monarchy but limited loyal powers. Old Regime- French society before the revolution. Bourgeoisie- Top educated members of the third estate (middle class) 1789- Start of the French Revolution. Napoleon- French dictator at the end of the Revolution. Napoleonic Code- Unified law Made French law clear and concise. Coup d’etat- Overthrow of the government. Scorched Earth Policy- Burning everything of use when retreating, The Russians did this as they retreated from Napoleon. Nationalism- Pride in ones country. Plebiscite- Popular vote. Continental System- Napoleon ordered all European nations to stop trade with British, he wanted to use economic warfare against the British. Metternich- Chief Minister of Austria who wanted to restore Europe to Pre-Revolution status. Congress of Vienna- Powerful European aristocrats gathered to discuss way to prevent political and social unrest in Europe. Reactionary- Favors to return past/traditional policies. Status quo- The existing state or condition (the norm) Concert of Europe- The regular meetings held to settle international problems. Prussia- Originally one of Napoleon’s allies, but revolted after the Spaniards overthrew them. 2