Worksheet - Cambridge Essentials

5 End-of-chapter test
1 a Explain the difference between i autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition ii photoautotrophic and chemoautotrophic nutrition. b Name a type of bacterium that uses chemoautotrophic nutrition, and briefly describe the reaction that this bacterium uses to gain its energy.
2 The diagram below shows the structure of a chloroplast, as seen using an electron microscope.
[2]
[2]
[2] a Identify structures A, B and C. b Photosystems I and II (PSI and PSII) are the clusters of chlorophyll molecules involved in is green. d The real length of the chloroplast shown in the diagram is 5 μm.
[3] photosynthesis. Where exactly are these photosystems located in a chloroplast? c Sketch an absorption spectrum of chlorophyll, and use your sketch to explain why chlorophyll
[2]
[4]
Calculate the magnification of the diagram. Show your working. [3]
3 The table below compares features of the light-dependent and light-independent stages of photosynthesis. Copy the table. If a statement is correct, put a tick (
) in the second or third column. If it is incorrect, put a cross (
) in the second or third column.
Statement produces ATP occurs on thylakoid membranes uses reduced NADP
Light-dependent stage Light-independent stage fixes carbon dioxide produces oxygen
4 The photosynthetic pigments present in a leaf were separated using paper chromatography. The chromatogram is shown here.
The R f
value for a pigment is calculated using the formula: distance moved by pigment
R f
= distance moved by solvent front a Calculate the R f
value of pigment X on the chromatogram. Show your working.
[5]
[2]
COAS Biology 2 Teacher Resources
Original material © Cambridge University Press 2009
1
5 End-of-chapter test
[1] b Identify pigment X using the information in the table below.
Pigment carotene phaeophytin xanthophyll chlorophyll a chlorophyll b
R f
value
0.95
0.81
0.71
0.65
0.45 c Describe how the pigment that you have identified is involved in photosynthesis. d Carotene is known as an accessory pigment. What is the role of an accessory pigment?
5 The diagram below shows some of the stages which occur in the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
[3]
[2] a Name the 5-carbon compound that combines with carbon dioxide (CO
2
). b Name enzyme R, which catalyses this reaction. c Identify the compounds X and Y. d Some of the triose phosphate is recycled to regenerate the 5-carbon compound.
What is the name given to this cycle? e Six turns of the cycle are needed to produce one molecule of glucose.
What fraction of the triose phosphate is used to regenerate the 5-carbon compound? f A plant can convert triose phosphate into a number of other organic compounds apart from glucose. What ion is required by the plant to convert triose phosphate into amino acids?
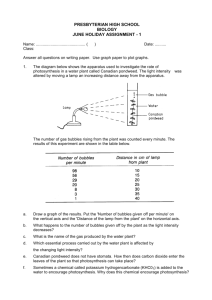
6 A piece of Canadian pondweed ( Elodea canadiensis ) was placed upside down in a test tube of water. The pondweed was illuminated by a 60 W lamp. After a few minutes, bubbles of gas were produced by the cut end of the weed. The distance of the lamp from the weed was varied, and the numbers of bubbles produced per minute were counted. The results are shown in the following table.
Distance of lamp, D/m
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
Numbers of bubbles per minute
132
91
67
41
32
18
15
11
[1]
[1]
[2]
[1]
[1]
[1]
COAS Biology 2 Teacher Resources
Original material © Cambridge University Press 2009
2
5 End-of-chapter test
The light intensity at different distances from a lamp is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the lamp. Therefore, if we calculate
1
D
2
, this value should be proportional to the light intensity. The number of bubbles of gas per minute is assumed to be proportional to the rate of photosynthesis.
1 a Calculate
D
2
. Copy and complete the table below.
Distance of lamp, D/m
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
1
D
2
/m
–2
400
100
44
25
0.35
0.40 b Plot a graph of the rate of photosynthesis (bubbles per minute) against the light intensity (
1
D
2
). c Describe the relationship between the light intensity and the rate of photosynthesis. d What environmental factor is limiting the rate of photosynthesis in this experiment?
The 60 W lamp was replaced with a 100 W lamp placed 0.05 m from the test tube.
After 5 minutes, the rate of bubbling was 130 bubbles per minute. e Explain why there was no increase in the rate of photosynthesis when the 100 W lamp was used. f Suggest three experimental limitations of the method used.
[1]
[5]
[2]
[1]
[2]
[3]
Grade boundaries: 80% A, 70% B, 60% C, 50% D, 40% E
Total:
52
Score: %
COAS Biology 2 Teacher Resources
Original material © Cambridge University Press 2009
3