Monopolistic Competition
advertisement

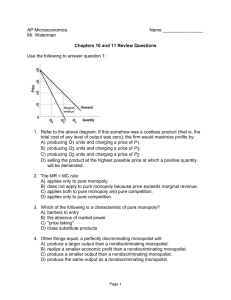
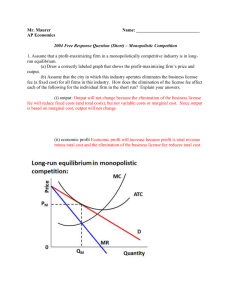
Monopolistic Competition True or false : 1) Monopolistic competitors have some control over the price of their products. 2) Brand names and packaging are forms of product differentiation under monopolistic competition. 3) The demand curve faced by a monopolistically competitive firm is more elastic than the monopolist's demand curve. 4) If a monopolistically competitive firm's optimal level of output occurs where P < AVC, it will shut down. 5) In the long run, typical firms that are monopolistically competitive earn economic profits. 6) In long-run equilibrium, a monopolistically competitive firm achieves optimal productive efficiency but not optimal allocative efficiency. 7) Pure competition results in a lower price but identical output level compared to those in monopolistic competition. 8) The demand curve of the monopolistic competitor is likely to be more elastic than the demand curve of the pure monopolist. Essay questions : “Pure competition or pure monopoly industries will tend to be oneprice industries. Monopolistic competition, however, is a multiprice industry.” Explain. Compare pure competition, pure monopoly, and monopolistic competition on each of the following points: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) Nature of the product. Ability to manipulate price. Expenditures on advertising and sales promotion. Equilibrium condition. Relationship between price and marginal revenue. Long run economic profits. Efficiency in allocation of resources. Multiple choice : (1) Which is a characteristic of monopolistic competition ? A) standardized product B) a relatively small number of firms C) absence of nonprice competition D) relatively easy entry (2) A feature of monopolistic competition is : A) many (thousands) of buyers and sellers . B) homogeneous or standardized products . C) considerable control over price . D) nonprice competition. (3) One difference between monopolistic competition and pure competition is that : A) products can be standardized or differentiated in pure competition . B) there is some control over price in monopolistic competition . C) monopolistic competition has significant barriers to entry . D) firms differentiate their products in pure competition. (4) Monopolistically competitive firms have a : A) B) C) D) horizontal demand curve . perfectly inelastic demand curve . perfectly elastic demand curve . downward-sloping demand curve. (5) Demand and marginal revenue curves are downward sloping for monopolistically competitive firms because : A) there is free entry and exit . B) product differentiation allows each firm some degree of monopoly power . C) there are a few large firms in the industry and they each act as a monopolist . D) mutual interdependence among all firms in the industry leads to collusion. (6) A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output level in the short run where average total cost is kd 4.50, price is kd 4.00, marginal revenue is kd 2.50, and marginal cost is kd 2.50. This firm is operating : A) with a profit in the short run . B) with a loss in the short run . C) at the break-even level of output in the short run . D) at an efficient level of output in the short run. (7) Refer to the graph. In the short run, this monopolistically competitive firm will set price at: A) B) C) D) kd 65 and produce 45 units of output. kd 65 and produce 35 units of output. kd 50 and produce 35 units of output. kd 50 and produce 50 units of output. (8) Refer to the above graph. This monopolistically competitive firm is : A) making economic profit in the long run . B) making economic profit in the short run . C) earning only normal profit in the long run . D) earning only normal profit in the short run. (9) In the long run, a representative firm in a monopolistically competitive industry will typically: A) have an elasticity of demand that will be less than it was in the short run. B) have a larger number of competitors than it will in the short run. C) produce a level of output at which marginal cost and price are equal. D) earn a normal profit, but not an economic profit. (10) In the short run, the monopolistically competitive firm will experience: A) an economic profit, and also one in the long run. B) a normal profit, but in the long run only an economic profit. C) economic profits and losses, but in the long run only a normal profit. D) economic profits and losses, but in the long run only an economic profit. (11) In long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive industry : A) P = minimum AC . B) P > minimum AC . C) P = MC . D) P < MC. (12) Monopolistic competitive firms are productively inefficient because production occurs where : A) marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue . B) marginal cost is less than marginal revenue . C) D) average total cost is greater than the minimum average total cost . average total cost is less than the difference between average total cost and average variable cost. (13) In monopolistic competition, there is: A) allocative efficiency. B) productive efficiency. C) both allocative and productive efficiency. D) neither allocative nor productive efficiency. (14) Compared to a purely competitive firm in long-run equilibrium, the monopolistic competitor has a : A) lower price and lower output . B) higher price and lower output . C) higher price and higher output . D) price and output that may be higher or lower. ** Answer the next question(s) based on the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistic competitor given in the table below. Price Quantity TC Output kd Demanded kd 20 1 10 1 18 2 20 2 16 3 29 3 14 4 36 4 12 5 40 5 10 6 42 6 (15) Refer to the above table. What output will the profit-maximizing monopolistic competitor produce ? A) 3 B) 4 C) 5 D) 6 (16) Refer to the above table. What will be the economic profit or loss for this monopolistic competitor at the profit-maximizing level of output ? A) - kd 15 B) + kd 10 C) + kd 20 D) + kd 27 Problems : (1) A monopolistically competitive firm is producing 50 units of output in the short run where marginal cost is kd 3.00, average total costs are kd 5.00, price is kd 4.50, average variable cost is kd 4.00, and marginal revenue is kd 3.00. How much profit is the firm making? What output recommendation would you make for the firm? (2) In the short run, a monopolistically competitive firm calculates that marginal cost is kd 6.00, average total costs are kd 4.00, and marginal revenue is kd 3.00. The firm is charging a price of kd 6.00 and producing 200 units of output. How much profit is the firm making? What output recommendation would you make as the company economist? ( 3 ) Assume that the short-run cost and demand data given in the table below confront a monopolistic competitor selling a given product and engaged in a given amount of product promotion. Compute the marginal cost and marginal revenue of each unit of output and enter these figures in the table. Total Marginal Output cost cost 0 kd 75 1 120 kd_____ 2 135 _____ 3 165 _____ 4 210 _____ 5 270 _____ 6 345 _____ 7 435 _____ 8 540 _____ 9 660 _____ 10 795 _____ Quantity demanded Price 0 kd 180 1 165 2 150 3 135 4 120 5 105 6 90 7 75 8 60 9 45 10 30 Marginal revenue kd_____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ (a) At what output level and at what price will the firm produce in the short run? What will be the total profit? (b) What will happen to demand, price, and profit in the long run?