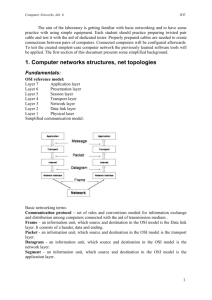
CSC 469/569 HOMEWORK 1
advertisement

CSC 469/569 HOMEWORK 1 Karthik Chandrasekaran 1. Part 1 Answer the following problems from page 67 of the class text : R1, R4, R5, R8, R9, R11, R12. R1. Host system is any networked computer that provides services to other systems or users. These services may include but are not limited to printer, web or database access. Computers that are connected to the Internet are sometimes referred to as End Systems. They are labeled end systems because they sit at the edge of the Internet. The end user always interacts with the end systems. R4. R5. HFC transmission rate is shared among users as the signal is broadcasted in HFC transmission. Collisions are not possible in downstream transmissions because each signal used different bandwidth frequency. R8. Unshielded twisted pairs and fiber optics are the two commonly used physical medium for ethernet. R9. Dial-up – 56 kbps DSL - 256 kilobits per second (kbit/s) to 24,000 kbit/s HFC – Cable modem speeds vary widely. While cable modem technology can theoretically support up to about 30 Mbps, most providers offer service with between 1 Mbps and 6 Mbps bandwidth for downloads, and bandwidth between 128 Kbps and 768 Kbps for uploads. R11. Circuit-switching is more reliable than packet-switching. When you have a circuit dedicated for a session, you are sure to get all information across. When you use a circuit which is open for other services, then there is a big possibility of congestion (which is for a network what a traffic jam is for the road), and hence the delays or even packet loss. R12. On demand sharing of resources for data transmission that does not have a fixed pattern is referred as statistical multiplexing. 2. Part 2 1. Other than conventional computers, (i.e. computers such as laptops, personal computers, minicomputers and mainframes and supercomputers), what other types of devices can appear as nodes in a computer network? (Name at least three). Printers, Smartphone’s, PDA’s and embedded computers in autos like GPS and in home security systems can be part of computer networks other than the conventional computers. 2. Explain what it means for a communication link to fall into the unguided media category, and list two types of unguided media links. Unguided transmission media are those media which can make a transmission without any physical medium on other word Unguided Transmission Media consists of a means for the data signals to travel but nothing to guide them along a specific path ,like satellite signals, wireless network routers, blueooth etc. 3. List the three different types of guided media that are commonly employed as to implement links in computer networks. Guided Transmission Media uses cables that guide the data signals along a specific path. The data signals are bound by the "cabling" system. Guided Media is also known as Bound Media. Three commonly used guided media types in computer networks are: 1. 2. 3. Twisted Pair Coaxial Cable Optical Fibers 4. Define the notions of simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex transmission. Simplex is a type of data transmission where data travels in only one direction. Half-Duplex is a type of data transmission where data travels in both directions, but the transmission is only one way at a time. Full-Duplex Duplex is a type of data transmission where data travels in both directions at the same time over one line. 5. Twisted pairs are used a lot in both data and voice communications. (1) Why does it require a pair of wires to carry a signal from a sender to a receiver? Signal transmission in data and voice communications requires 2 wires to complete a circuit of positive and negative signals. (2) Why are the two wires that carry the signal twisted together? In a duplex channel the circuits can produce Electro Magnetic Interference. Twisting the wires greatly reduces the EMI in a circuit from external sources. (3) If you pull the telephone wire out of a telephone handset and examine the connector, you will see 4 contacts, suggesting that the cable to the telephone consists of 4 wires, that is, two twisted pairs. Why are there two twisted pairs instead of only one? A telephone transmits data in both directions in duplex channel. So it requires 2 pairs of wires to form 2 circuits one for transmitting and other for receiving. (4) The telephone wiring in residential homes is made up of four pairs of twisted pair, even though a telephone uses only two of those pairs? What are the two extra twisted pairs for? The telephone wiring in residential homes are made up of four pairs. 2 pairs are used for voice transmission and the other 2 pairs are used for supporting data transmission via DSL technology for a computer network. 6. What is the difference between RJ 11 and RJ 45 cable? RJ-11 is the standard physical connector interface most often used for telephone wire terminals. The RJ-45 connector is the standard physical connector for Ethernet, ISDN, T1, and modern digital telephone systems. RJ-11 is 2-pair (4-wire) connector wiring which comes in two standard varieties- untwisted and Unshielded Twisted Pair. RJ-45 is a 4-pair (8-wire) Unshielded Twisted Pair cable. 7. Expand the following networking acronyms, and state briefly how the concepts denoted by the acronyms differ from each other. (1) LAN – Local Area Network (2) WAN – Wide Area Network (3) MAN – Metropolitan Area Network (4) PAN – Personal Area Network Personal Area Network (PAN) Personal area network PAN is a computer network used for communication among computer devices close to one person. Some examples of devices that are used in a PAN are printers, fax machines, telephones, PDAs and scanners. The reach of a PAN is typically about 20-30 feet (approximately 6-9 meters). Local Area Network (LAN) Local Area Network A Local Area Network (LAN) is a computer network covering a small physical area, like a home, office, or small group of buildings, such as a school, or an airport. Current LANs are most likely to be based on Ethernet technology. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Metropolitan Area Network A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a network that connects two or more LAN’s together within the city/town limit. Routers, switches and hubs are connected to create a Metropolitan Area Network. Wide Area Network (WAN) Wide Area Network A WAN is a data communications network that covers a relatively larger geographic area (i.e. one city to another and one country to another country) and that often uses transmission facilities provided by carriers such as telephone lines, fiber optic lines etc. 8. Explain what Bluetooth is. Bluetooth is a wireless protocol technology used for exchanging data over short distances from fixed and mobile devices. Bluetooth creates Personal Area Network. Bluetooth technology helps to connect and exchange information between devices such as mobile phones, telephones, laptops, personal computers, printers, Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers, digital cameras, and video game consoles through short-range radio frequency bandwidth. 9. Explain the concept of a network topology, and list the four topologies most frequently used in computer networks. Topology refers to the shape of a network's layout. In a network, how the nodes are connected to each other and how they communicate with each other is determined by the network's topology. Four commonly used topologies are : 1. Mesh Topology 2. Start Topology 3. Bus Topology 4. Ring Topology 10. Explain what is meant when we say that a link is point-to-point. Point-to-Point topology connects two nodes directly together. For example, a dial-up connection to an Internet Service Provider (ISP) uses a point-to-point protocol (PPP) connection. There is a modem at the customer end and one at the the provider points which are linked directly. 11. How does a computer network differ from an internetwork? A computer network is a group of interconnected computers. The network allows computers to communicate with each other and share resources and information. An Internetwork involves connecting two or more distinct computer networks or network segments via a common routing technology. The result is called an internetwork (often shortened to internet). 12. What do we mean when we say that a machine is multi-homed? Multi-homed computer is a host connected to two or more networks or having two or more network addresses. For example, a network server may be connected to a serial line and a LAN or to multiple LANs.