Resources - geographylwc.org.uk
advertisement

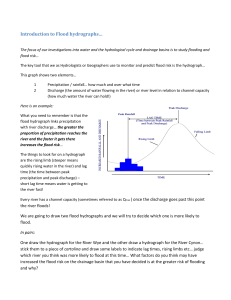
grs03/03/16 Rivers, physical. Aims: To identify the main features of the drainage basin. To understand how the storm hydrograph operates and identify the human impact on the hydrograph. To identify how the geomorphological features change within the drainage basin. Rivers, floods and management The drainage basin hydrological cycle: the water balance. Factors affecting river discharge: the storm hydrograph. The long profile – changing processes: types of erosion, transportation and deposition, types of load; the Hjulstrom curve. Valley profiles – long profile and changing cross profile downstream, graded profile, potential and kinetic energy. Changing channel characteristics – cross profile, wetted perimeter, hydraulic radius, roughness, efficiency, and links to velocity and discharge. Landforms of fluvial erosion and deposition –potholes, rapids, waterfalls, gorges, meanders, braiding, levees, flood plains and deltas. Process and impact of rejuvenation – knick points, waterfalls, river terraces and incised meanders. Magnitude-frequency analysis of flood risk. Physical and human causes of flooding – two case studies of recent flooding events should be undertaken from contrasting areas of the world. Impact of flooding – two case studies of recent flooding events should be undertaken from contrasting areas of the world. Flood management strategies – to include hard engineering – dams, straightening, building up of levees, diversion spillways, and soft engineering – forecasts and warnings, land use management on floodplain, wetland and river bank conservation and river restoration. River DVD grs03/03/16 Key Questions Suggested Pupil activities/methods What is meant by the drainage basin? How can it be represented by a system approach? Draw basin run off system and def terms. interception, stemflow, dripflow, overland, through, infiltration, percolation, groundwater. Draw the flow diagram for the drainage basin What is the significance of the hydrograph? How is discharge measured? What are the controlling factors that affect the hydrograph? Water budget, ex on website Ex on P 11 PPT, as a summary Hydrological flows Draw the flood hydrograph. PPT to explain how Ex to draw hydro Discuss ‘shape’ of hydrograph as storm progresses Examples of calculation Go through examples from Wye or other data Discuss the factors that control the shape of the hydrograph including effect of man. Resources Text 8 DVD 12 11 14 6 Misc Red 2,3,4 Nagle 58 ++ GIAA P50 Knapp Ex1 Bishop Ex 18,19 GeoR 7,3, Ross 224 Landmark 14 Red 4 Landmark 25 Waugh 53 Red 5-7 Ex of figs for discharge Figs for storm hydro Carter 1 GeoFact 83 Geofile 87 GeoFile 16,316, Catchment area (Drainage basin) studies Geofile 25, 542 Hyrographs and physical/human impacts GeoR 4,5 Bishop, Water CH 3 Ex of figs GIAA P55 GeoR 3,2 Ross 229 Waugh 53 Hordern 5 Landmark 14 Geo Fact 189 Red 4 Landmark 25 Sugg and skills Comparing graphs grs03/03/16 What are the main methods of erosion? What are the main methods of transportation? What are the main measurements of a channel? How do all these relate to field work? Discuss hydraulic action, abrasion, solution and 19 attrition. Also consider vertical, lateral and headwater erosion. Define suspension, solution, saltation and 19 traction. How is velocity linked to transportation? (Hjulstrom). Discuss competence and capacity. Discuss wp, HR, w/d ratio and their influence on efficiency. Intro. Mannings(?) Roughness and link to velocity and discharge Use diagram Ross 241 Bradshaw Cross section ex Ppt of HR HR exercise Eg data for HR Case study R Derwent Also 9 Red 7 Red 9 Ross 240 Waugh 65 Horndern 27 Nagle 95 Red 17 Waugh 63 Ross 242 Nagle 81 Clowes 102 Horndern 22 Ross 243 Nagle 103 Data from sheets Triangle graph of bedload size Dispersion and scatter graph Spearman’s Mean median and mode grs03/03/16 How does the long profile of a river change? What are the landforms associated with fluvial erosion? What are the landforms associated with deposition? What are the physical causes of floods? Draw a simple long profile and then using an OS map draw an actual one; try one on Arran 2003(?) Discuss effect of rejuvenation and mark knick points on profile, note landforms e.g. waterfalls, rapids and incised meanders, terraces. Also impact of humans e.g. dams Note impact of climate change on this Consider how the valley cross profile changes downstream The importance of potential and kinetic energy Rejuvenation 16 Discuss formation of: V shaped valleys, potholes Rapids, Waterfalls e.g. High Force Gorges Emphasize processes here Consider: braiding Meanders, and ox bows Flood plains and levees, link above with sediment deposition across valley floor. deltas 17 Go through the physical causes of floods Go through recurrence intervals, frequency 24 Red 13, 23 Data in Clowes P 133 Waugh 69, 74 Horndern 13 19 Nagle 101 Memory map to show section(?) Red 14 Red 16 GeoFile 621 19 12 34 Red 18 Waugh 69 Ross 245 Nagle 87 Ross 246 Landmark 15, 16 GeoAct 330 Red 19 Ross 248 Waugh 71 Nagle 93, 96 Carter 3 Geofile 26 563 Landmark 23 Red 26 Carter 2 Red 27 WW 14,1,1 Annotated sketches grs03/03/16 What are the human causes of floods? Discuss what have humans done to increase the likelihood of a flood event, link to flood hydrograph Compare LEDC and MEDC either Boscastle, Carlisle and Bangladesh 2004 Just causes here and impact How can the flood hazard be managed? Go through hard and soft strategies Hard: dams, straightening, levees, diversion spillways, Soft: channelization and naturalisation Case study of Windsor flood relief channel Conway valley flood 2004 Hi tech 21st century flood warnings Case study Carlisle and Bangladesh for cost benefit Revision http://www.geographypods.com/2-drainagebasins-and-flooding.html A range of physical taboo words for the Rivers and Coasts topics. Taboo is played in teams each player has 1 minute to describe as many bold words as possible without 26 28, 41 30 36 Red 27 11 48 63 Red 26,31 Geoactive 17341 19394 WW 16,3,8 GeoFact 45, 189, 233 Red 33 Ross 254, 259 Horndern 46 Geofile 14 268 16, 330 19 399, WW 9.3,4 GeoFact G206 Landmark 20 38, 41 Geog R 19,1,30, Flood hazard in the Conwy Valley Geog R 20,1,24 Hi Tech flood warnings GeoFact 45 grs03/03/16 Rivers: flooding and flood management Key Questions What are the physical causes of floods? Suggested Pupil activities/methods Go through the physical causes of floods Go through recurrence intervals, frequency Resources Text 24 DVD 12 34 Misc Red 26 Carter 2 Red 27 WW 14,1,1 Sugg grs03/03/16 What are the human causes of floods? Discuss what have humans done to increase the likelihood of a flood event, link to flood hydrograph 26 Compare LEDC and MEDC either Boscastle and Bangladesh 2004 Just causes here and impact 28, 41 Red 27 11 48 63 Red 26,31 Geoactive 17341 19394 WW 16,3,8 GeoFact 45, 189, 233 Case study of Cockermouth flood Nov 2009 North Pakistan July 2010 Cockermouth resource Powerpoint of flood Briefing note on cause of flood grs03/03/16 How can the flood hazard be managed? Go through hard and soft strategies Hard: dams, straightening, levees, diversion spillways, Soft: channelization and naturalisation Case study of Windsor flood relief channel Conway valley flood 2004 Hi tech 21st century flood warnings Case study Carlisle and Bangladesh for cost benefit 30 36 Red 33 Ross 254, 259 Horndern 46 Geofile 14 268 16, 330 19 399, WW 9.3,4 GeoFact G206 Landmark 20 38, 41 Geog R 19,1,30 20,1,24 GeoFact 45