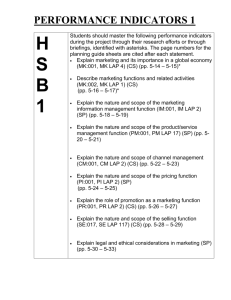
2007 Regionals EMDM
advertisement

2007 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 926 E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 1 1. A hacker who manipulates an online business's software program and deletes information or changes information is involved in A. computer-based fraud. C. web-site vandalism. B. sending e-mail viruses. D. denying Internet access. 2. After her seventh month in business, Martha realized that her new online venture was paying off, and she would be earning a $1,000 profit for the month. Finally, she could reap the financial rewards of being the boss. This is an advantage of what type of business ownership? A. Merger C. Corporation B. Partnership D. Sole proprietorship 3. Why is it important for the home office of an Internet-based company to comply with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration's (OSHA) workplace regulations? A. To avoid paying penalties C. To prevent on-site inspections B. To monitor work-related accidents D. To eliminate all complaints 4. An online retailer whose goal is to make sure the company's products are at the right place in time for purchase by consumers should focus on the marketing function of A. utility. C. distribution. B. selling. D. packaging. 5. Intermediaries buy large quantities of goods from producers and sell smaller quantities to other intermediaries or to consumers. The result is that intermediaries __________ the per-unit cost of a good. A. control C. reduce B. increase D. stabilize 6. How has the use of the Internet impacted the distribution process? A. It has enabled end users to negotiate product terms and pricing with each member of the supply chain. B. It has created a need for concentrated shipment destinations and warehousing accommodations. C. It has changed the shipment types from smaller diverse lots to larger bulk lots. D. It has shifted the supply chain from a predictable ordering schedule to one that is more flexible. 7. The dealers who are authorized by manufacturers to distribute the manufacturers' products are the ones who usually are negatively affected by A. personal selling. C. volume buying. B. gray marketing. D. sale pricing. 8. Why is it important for Internet-based businesses to coordinate distribution with other marketing activities? A. To provide customer service C. To plan warehouse space B. To arrange transportation D. To manage inventory levels 9. Which of the following often is the goal of online retailers that use the channel strategy of intensive distribution: A. Create an upscale image C. Target a specific area B. Saturate the market D. Eliminate the middleman 10. E-businesses regularly meet with channel members to discuss problems and improve performance in order to develop A. cost-effective inventories. C. transportation systems. B. long-term partnerships. D. routine buying procedures. 11. One of the purposes of staff communication is for Internet-based business managers to provide A. customers with product information. C. stockholders with financial reports. B. employees with access to the grapevine. D. employees with guidance and direction. 12. When participating in staff meetings, an Internet-based company's employees should be prepared to A. remain silent. C. comment on every detail. B. join in the discussion. D. argue. Test 926 2007 DECA Ontario Regionals E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 2 13. When giving job instructions to employees, an Internet-based company's managers should take into consideration the employees' level of A. professionalism. C. authority. B. income. D. experience. 14. Why should you summarize your online customers' problems when responding to their e-mail messages? A. To thank customers for their business B. To show that you fully understand the problem C. To decide how the problem can be resolved D. To apologize for any inconvenience 15. What do managers often develop to create positive relations with their online customers? A. Operating procedures C. Sales strategies B. Service policies D. Marketing tactics 16. Which of the following provides an e-tailer with the most control over fulfillment processes: A. Outsourcing all of the processes to a fulfillment house B. Keeping inventory on hand until customer orders are received C. Contracting with a drop-shipper to deliver products to customers D. Purchasing products from a local distributor after customer orders are received 17. Bart, a receiving clerk with GoodProducts.com, usually counts each item in a shipment and marks it off the purchase order in order to A. warehouse excess goods. C. distribute stock. B. label merchandise. D. identify discrepancies. 18. Calculate the least expensive way to combine and ship eight 10-pound packages if the parcel post rate is $4.55 for a 10-pound package, $5.90 for a 20-pound package, $7.05 for a 30-pound package, and $8.35 for a 40-pound package. A. Three 20-pound packages and two 10-pound packages B. Eight 10-pound packages C. Two 30-pound packages and one 20-pound package D. Two 40-pound packages 19. Visual control of inventory often involves the use of __________ to rotate stock. A. tickler control C. color coding B. reorder control D. check-out scanner 20. E-tailers develop real time inventory systems in order to A. know if products listed for sale on their web sites are actually in stock. B. keep track of the items that visitors put in their online shopping carts. C. prevent hackers from deleting products from the business's web site. D. send out e-mail messages to customers when back-ordered items appear in stock. 21. One way that an online business's customer-service department can facilitate the distribution process is to make sure the customer A. tells others about the product. C. pays full price for the product. B. accepts delivery of the product. D. receives the correct product. 22. Cash-register tapes and shipping forms used by an online business would be classified as industrial A. supplies. C. parts. B. equipment. D. materials. 23. In market economies, which of the following is the most critical factor in deciding how products will be produced: A. Competition C. Tradition B. Government D. Distribution Test 926 2007 DECA Ontario Regionals E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 3 24. When a rival's product on the market reduces sales of your online company's product, your online company is experiencing economic risk caused by A. shifts in consumer demand. C. product obsolescence. B. the efforts of competitors. D. government intervention. 25. An e-commerce business's market structure in an industry can be described as A. a tool for measuring economic activity. C. a way for suppliers and demanders to interact. B. a method of categorizing goods and services. D. a means of gauging a business's financial success. 26. What does price level measure in a given year? A. What prices may look like in the future B. How fast prices rose last month C. How high or low prices are D. How fast prices have dropped in the last decade 27. What often happens to an economy during a mildly inflationary period? A. Increased growth C. Decreased profits B. Decreased prosperity D. Increased unemployment 28. An online business's employee is trying to reduce the level of stress s/he is experiencing by focusing on a peaceful beach scene and trying to imagine the sights and sounds of the scene. This is an example of which stress management and relaxation technique? A. Muscular relaxation C. Positive self-talk B. Deep breathing D. Visualization 29. The way in which e-tail supervisors guide the work of employees depends upon their A. desire for success. C. management style. B. technical skills. D. level of education. 30. Which of the following is a guideline for giving effective recognition: A. Limit compliments C. Exaggerate praise B. Be general D. Be timely 31. A credit account in which the purchaser usually makes a down payment and signs a contract to make a series of scheduled payments and finance charges describes which of the following: A. Open account B. Installment credit C. Revolving credit D. Layaway plan 32. Which of the following is a reason why Internet-based businesses should evaluate speculative risks: A. To estimate the level of property damage C. To reduce the possibility of theft B. To obtain adequate insurance coverage D. To determine the potential for loss 33. Joe is the owner of Newgoods.com. His employees plugged the electrical cord for display lights into an old, worn, extension cord. Joe instructed them to get a new, heavy-duty cord. Joe is implementing __________ measures. A. expense-control C. employee-control B. loss-prevention D. security-precaution 34. Which of the following are the categories that web-based companies use to summarize information on their balance sheets: A. Liabilities, equipment and sales C. Assets, liabilities, and equity B. Equity, budget, and cash D. Cash, budget, and credit 35. On an e-tailer's income statement, the difference between the cost of goods sold and net sales is A. gross sales. B. net profit. C. gross margin. D. net expenses. 36. If an online business sells an item for $26.75 and has costs and expenses of $22.25 per item, what is the business's return on investment for each item? A. 22% B. 20% C. 24% D. 26% Test 926 2007 DECA Ontario Regionals E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 4 37. When determining its hiring needs, an e-business must first consider its financial status and its __________ needs. A. uniform B. secondary C. productivity D. temporary 38. When concluding an interview with a job applicant, the interviewer should explain the A. next step in the process. C. performance evaluation system. B. requirements of the position. D. problems in the business. 39. An e-tailer's current employees often assist with the orientation process by helping the new employees to A. negotiate contracts. C. develop work skills. B. ask questions. D. learn their jobs. 40. Since not all of an e-tailer's training and development needs are as important as others, the e-tailer needs to prioritize its needs according to the A. trainees' personal needs. C. population to be served. B. implementation checklist. D. training offered by competitors. 41. Which function of a marketing-information management system involves collecting data from internal and external sources on an ongoing basis: A. Information processing C. Sales forecasts B. Information gathering D. Information reporting 42. What technological tool allows marketers to find valuable information in remote locations? A. Cookies B. E-mail C. Internet D. Cell phones 43. CarlsCandy.com needs more information in order to define the reason for its research and to decide which direction to take. What type of marketing research would CarlsCandy.com use? A. Causal B. Descriptive C. Predictive D. Exploratory 44. As a result of tracking how often customers visit a web site and what they buy, an e-business might use that information to A. prepare an online privacy statement. C. negotiate with a key supplier. B. decide which products to feature. D. collect primary research data. 45. The sale of goods and services on the Internet is having a negative effect on many salespeople by A. reducing the need for product knowledge. C. increasing commission rates. B. decreasing job opportunities. D. promoting additional customer contact. 46. Marketing strategies are designed and implemented for the overall purpose of A. changing the image of an e-business. C. achieving planned goals. B. improving management techniques. D. increasing an e-tailer's profits immediately. 47. One way e-businesses segment their markets is by studying A. human relations. C. their employees. B. mass marketing. D. consumers' characteristics. 48. When an e-business selects a target market, the most useful or desirable market segments to the business are those that are measurable and A. inflexible. B. undifferentiated. C. concentrated. D. accessible. 49. Why is it important for e-businesses to regularly analyze the external environment in which they operate? A. To be socially responsible C. To behave ethically B. To understand change D. To calculate profit 50. Which of the following is an internal strength that an e-business might identify during a SWOT analysis: A. Financial resources C. Increased expenses B. Extensive regulations D. Limited competition Test 926 2007 DECA Ontario Regionals E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 5 51. Which of the following is a global trend that Internet-based businesses might identify as being an opportunity: A. Increased language barrier C. Decreased population growth B. Increased political unrest D. Decreased trade regulation 52. A manufacturer expects product sales to decrease during the coming year. How does this information affect the production of goods? A. Production should remain the same. C. Production should increase. B. Production should decrease. D. Production should not be affected. 53. Jackie wants to start her own web-based business and is beginning to develop her business plan. What are the three major sections of a well-organized business plan? A. Marketing plan, financial plan, and business situation analysis B. Financial plan, manufacturing plan, and market segment analysis C. Projected income report, marketing plan, and SWOT analysis D. Business situation analysis, SWOT analysis, and trading area analysis 54. Which of the following is an adjustment that an e-tailer might make to its marketing plan after conducting a profitability analysis: A. Increase compensation and benefit package B. Reduce the number of employees in the accounting department C. Buy more equipment for the warehouse D. Eliminate certain items from the product mix 55. Which of the following is a characteristic of a search engine that uses web spiders to obtain information: A. Can return a large number of hits C. Only retrieves data from secure locations B. Usually has a high rate of repetitive hits D. Requires users to provide meta tags 56. When creating web pages, an online business should be sure to include a __________ the home page. A. summary of B. picture on C. link to D. reason for 57. How must a web page be formatted, so that it can be viewed on a computer screen? A. Hypertext transport protocol (HTTP) C. Internet service provider (ISP) B. Hypertext markup language (HTML) D. Secure sockets layer (SSL) 58. Online businesses should organize their records in a systematic manner so that information can be A. available to everyone. C. distributed freely. B. accessed when needed. D. published in newsletters. 59. As a result of conducting an environmental scan, an e-tailer might find that the rate of unemployment is slowly increasing, which is an example of a(n) __________ factor. A. economic B. geographic C. political D. cultural 60. Darla is concerned about the security of customers' transactions on her online company's web site. Which of the following methods can Darla use to protect her online business and her customers: A. Use encryption algorithms B. Hire a professional to try to break into the system C. Have an 800 number for customers to call and charge purchases D. Transfer the user to a page that explains transaction security 61. DeluxeProducts.com routinely has employees take office supplies for personal use. This is an example of A. shoplifting. B. pilferage. C. burglary. D. robbery. 62. In relation to production activities, a shirt, a car, and a computer are examples of A. raw materials. B. inputs. C. outputs. D. robotics. Test 926 2007 DECA Ontario Regionals E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 6 63. Calculate an e-business's gross profit if it had sales of $370,500, fixed costs of $115,200, $500 in charitable donations, and spent $135,750 on cost of goods sold. A. $226,600 B. $255,300 C. $241,250 D. $234,750 64. Why does an e-business conduct a break-even analysis? A. To determine the approximate consumer demand levels B. So it can receive a tax break from the government C. So it can evaluate product sales from the previous year D. To determine a product's possible range of profit 65. Which of the following would help an Internet-based business to control payroll expenses: A. Hiring part-time employees C. Scheduling overtime shifts B. Monitoring operating costs D. Changing purchasing policies 66. An e-tailer budgets a 6% increase in sales next month and expects a 4% increase in expenses which usually are 52% of sales. If current sales are $68,500, what amount will the e-tailer spend on expenses next month? A. $37,757.70 B. $40,661.60 C. $40,023.40 D. $35,520.50 67. A skill that e-tail employees often need to be able to move up the career ladder is the ability to A. assign blame. C. ignore personal rights. B. dominate others. D. delegate responsibility. 68. Julie, a newly promoted e-tail manager, doesn't have time to prepare the employees' work schedules and assigns this duty to the assistant manager. Which of the following time management techniques is Julie using: A. Setting objectives C. Standardizing tasks B. Delegati D. 69. Which of the following statements about pricing is true: A. The cost of the product determines its selling price. B. The selling price can never be set too low. C. The price must satisfy both buyers and sellers. D. Once prices are set, e-tailers should not adjust them. 70. Evidence exists that two online businesses have communicated and decided to charge consumers the same prices for similar products. In some countries, this is an illegal practice referred to as price A. coercion. B. discrimination. C. fixing. D. altering. 71. An e-tailer that uses sales-oriented pricing objectives wants to increase the A. cost of its marketing efforts. C. amount of promotion it uses. B. total amount of its income from sales. D. inefficiency of its human resources. 72. Online businesses use different marketing strategies from one stage of the product's __________ to another. A. feasibility analysis C. test-marketing B. research studies D. life cycle 73. During which stage of a product life cycle do sales and profit usually increase even though competition is intense? A. Existing B. Introduction C. Universal D. Maturity 74. One way online businesses use computer technology to obtain information to improve their product/service mix is by A. preparing interactive software programs. C. compiling detailed databases. B. mailing questionnaires to customers' homes. D. tracking visitors to their web sites. 75. When using synectics to develop unique product ideas for an existing market, an entrepreneur might generate ideas by focusing on A. positive attributes. C. general needs. B. personal wants. D. specific details. Test 926 2007 DECA Ontario Regionals E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 7 76. A feasible product idea should provide the target market with a good or service that offers A. attributes. B. value. C. depth. D. standards. 77. What type of standard is an e-business setting when it requires all invoices to be free of pricing errors? A. Quantity B. Industry C. Quality D. Activity 78. Why is it important for Internet businesses to update the information and appearance of their web site? A. So they can reach Internet surfers who are connected to different networks B. So that additional promotional activities can be eliminated C. To reduce the expenses associated with maintenance outsourcing D. To encourage repeat business and to attract new customers 79. An online office supply store that sells ink pens claims that no other pen on the market uses a type of ink that changes color when exposed to light. The store is positioning its product according to what strategy? A. Price and quality C. Unique characteristics B. Features and benefits D. Relation to other products in a line 80. A distinctive symbol, design, or group of letters that cannot be spoken is known as a A. trade name. B. brand mark. C. brand. D. trade character. 81. A primary reason for an e-tailer to provide customer service is to increase A. employee responsibility. C. sales volume. B. the number of salespeople. D. the use of facilities. 82. Emotional connections with customers are frequently strengthened by A. an e-business owner's personality. B. a brand's personality. C. pleasing colors and textures on the company's web site. D. changing a brand's core values to meet customers' changing needs. 83. Part of planning purchases is determining open-to-buy, which refers to the A. planned purchases minus goods on order. C. ratio of sales to stock on hand. B. percentage of markup on goods. D. number of items to be ordered. 84. When developing content for a web site, it is most important to make sure that the information is accurate and A. complex. B. in-depth. C. timely. D. bilingual. 85. When is an e-tailer most likely to increase its inventory level? A. Prior to peak selling season C. During peak selling season B. After physical stock counts D. Before physical stock counts 86. An online business that decides when to buy based on the supplier's lead time is considering A. the number of steps in the receiving process. C. how long it takes to order and receive goods. B. how quickly the merchandise turns over. D. the location of shipping and delivery companies. 87. Promotion is thought of as being at the heart of Internet-based marketing because it allows sellers to A. bypass middlemen such as manufacturers. C. create new products. B. distribute online products carefully. D. communicate the benefits of products to online buyers. 88. Which of the following statements is true about regulating promotional activities: A. Businesses must submit all promotional materials to the International Ad Coalition for approval. B. A business must understand that the laws governing promotional activities vary by country. C. Governments bear the sole responsibility of monitoring promotional materials and regulations. D. Most countries have a system of checks and balances to verify that promotion regulations are fair. Test 926 2007 DECA Ontario Regionals E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 8 89. When an online business wants to notify preferred customers of a special offer, the most efficient and promotional medium to use is A. opt-in e-mail. B. online newspaper. C. compulsory e-mail. D. closed-circuit television. 90. When an e-business decides to create an infomercial to advertise its new product, it can maximize its customer response rate by requesting a call to action __________ the infomercial. A. at the beginning of C. several times during B. at the end of D. in the middle of 91. What do many businesses do in order to increase the number of people who receive their e-mails? A. Purchase lists from providers C. Send questionnaires to customers B. Rent space on web sites D. Use information in telephone directories 92. Which of the following is an example of an objective that businesses consider when planning their web sites: A. To design components C. To create systems B. To develop policies D. To support customers 93. Which of the following is an online promotional activity that should be coordinated with a business's advertising: A. Trade shows B. Special orders C. Printable coupons D. Target markets 94. Which of the following is the most cost-effective method of providing online customer support for Internet-based businesses: A. Using e-mail to communicate with customers B. Including helpful information on the business's web site C. Hiring employees to chat with customers online D. Establishing a customer call center 95. Which of the following is a benefit to the online business of building a clientele: A. Increased sales volume C. Increased knowledge B. Increased selling costs D. Personal satisfaction 96. On which of the following products would you expect to find safety information: A. Knitting yarn B. Apparel C. Paper D. Spray paint 97. A salesperson should obtain information about competitors' products because buyers tend to comparison shop when they are purchasing A. high-priced products. C. value-priced items. B. staple goods. D. novelty items. 98. Which of the following is not a reason for using brand names in selling: A. Customers are usually familiar with established brand names. B. Customers may feel an established brand offers good quality. C. Brand-name items are generally cheaper for customers to buy. D. Many brand-name items have a reputation for good performance. 99. Why is it important for businesses to evaluate online prospects? A. To control the number of customers who make daily purchases B. To identify customers who visit the sites of competitors C. To prevent unauthorized customers from viewing a web site D. To avoid spending time and money on customers who will not buy 100. Which of the following brings together the resources that are needed in the production of goods or services: A. Research C. Management B. Economizing D. Marketing 2007 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 926 E-Commerce Management Decision Making EMDM 9 1. C Web-site vandalism. Web sites, both big and small, are sometimes altered or destroyed by vandalism. Vandalism occurs when a hacker manipulates the web pages' HTML code and changes the prices of items or deletes those items from the web site. Other vandalism occurrences include the insertion of offensive material onto the web page. A hacker who manipulates an online business's software program is not involved in sending e-mail viruses, computer-based fraud, or denying Internet access. SOURCE: BA:211 SOURCE: BA LAP 4—Issues in E-Commerce 2. D Sole proprietorship. This is a form of business ownership in which the business is owned by only one person, and that person receives any profits made by the business. A merger is the absorption of one company by another rather than a type of business ownership. A partnership is owned by two or more people, and profits would be split between them. A corporation is owned by people who own stock in the business, and they split the profits. SOURCE: BL:003 SOURCE: BA LAP 7—Own It Your Way 3. A To avoid paying penalties. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a federal governmental agency that writes and enforces safety and health standards for businesses (e.g., Internet-based companies' home offices). OSHA has the authority to impose financial penalties on businesses that are in violation of OSHA regulations. These penalties may be significant depending on the type of violation. Also, OSHA may give a business a certain amount of time to correct the violation and impose additional penalties if the problem is not corrected by then. OSHA has the authority to make on-site inspections at any time. Businesses comply with OSHA regulations to prevent workrelated accidents rather than to monitor the number of accidents. Complying with OSHA will not eliminate all complaints but will make the workplace safer for employees. SOURCE: BL:008 SOURCE: Dessler, G. (2000). Human resource management (8th ed.) [pp. 564-568]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 4. C Distribution. Distribution is all the activities involved in moving, storing, locating and/or transferring the ownership of goods or services. Packaging is enclosing products in appropriate wrappings or containers. Selling is a marketing function that involves responding to consumer needs and wants through planned, personalized communications intended to influence purchase decisions and enhance future business opportunities. Utility is a product's usefulness or ability to satisfy wants and needs. SOURCE: CM:001 SOURCE: DS LAP 1—Distribution 5. C Reduce. When intermediaries buy large quantities of goods from producers, large-scale production enables the producers to reduce the per-unit cost of the items. Intermediaries do not have the power to stabilize or control prices. SOURCE: CM:003 SOURCE: MB LAP 3—Channels of Distribution Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 10 6. D It has shifted the supply chain from a predictable ordering schedule to one that is more flexible. The inception of the Internet has altered the dynamics of product distribution. Because of technological advancement, customers demand faster delivery and service as well as product customization. To stay competitive, businesses are accommodating these demands. As a result, the distribution process has changed dramatically, including the way businesses order products. Businesses previously ordered products on a set or predictable schedule. Technological advancements such as the Internet have made the ordering process more sporadic and flexible. Since the ordering process is sporadic, businesses are generally shipping smaller lots of some products instead of the larger bulk lots. Because of increased order flexibility and small shipments, shipment destinations are more dispersed, or spread out, over a large area. Drop shipping products directly to customers is becoming more common. When orders are processed in bulk, concentrated destinations such as large, regional warehousing facilities are generally used. Technological advancements have not encouraged end users to negotiate terms and pricing with all channel members. SOURCE: CM:004 SOURCE: Coyle, J., Bardi, E. & Langley, C. (2003). The management of business logistics: A supply chain perspective (7th ed.) [p. 458]. South-Western. 7. B Gray marketing. Gray market goods are foreign-made products that are imported into countries by suppliers that are not authorized by the manufacturers. The distribution of gray market goods bypasses the authorized distribution channels, which enables them to sell the goods at low prices. Businesses that buy gray market goods for resale often charge discounted prices. This practice has a negative effect on authorized dealers that purchased the same goods from the manufacturers and are not able to offer large discounts. Sale pricing is pricing items at low levels and promoting them for a limited period of time. Personal selling is the form of promotion that determines client needs and wants and responds through planned, personalized communication that influences purchase decisions and enhances future business opportunities. Volume buying involves buying in large quantities, which often results in receiving a discount. SOURCE: CM:006 SOURCE: Boone, L.E., & Kurtz, D.L. (2004). Contemporary marketing (11th ed.) [pp. 446-447]. Mason, OH: Thomson/South-Western. 8. A To provide customer service. Distribution and marketing activities are closely related because goods must be available when and where customers want them. If Internet-based businesses do not have the goods in stock, customers cannot buy. Internet-based businesses are only able to serve customers when they have the advertised items on hand and at the right price. Arranging transportation, planning warehouse space, and managing inventory levels are types of distribution activities that should be coordinated with marketing activities to provide customer service. SOURCE: CM:007 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (pp. 16-17, 464-465). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 9. B Saturate the market. An intensive distribution strategy involves making a product available in all possible locations to make it easy for customers to buy. Products that most consumers buy on a regular basis usually are available everywhere because the goal is to saturate the market with the products. By saturating the market, the retailer business often increases sales because products are always accessible. Exclusive distribution may create an upscale image and may target a specific area. Intensive distribution is not intended to eliminate the middleman. SOURCE: CM:009 SOURCE: Boone, L.E., & Kurtz, D.L. (2002). Contemporary marketing (pp. 398-400). Mason, OH: South-Western. 10. B Long-term partnerships. Most e-businesses want to develop long-term partnerships with channel members because it is more cost effective to maintain a relationship with an existing member than to locate new channel members. To accomplish this, businesses often meet regularly with channel members to discuss problems and evaluate performance. This gives both the business and the channel members an opportunity to discuss problems and decide on a mutually satisfactory solution. By working together, the business and the channel members can improve performance and develop a long-term partnership. Businesses and channel members do not meet regularly to develop transportation systems, cost-effective inventories, or routine buying procedures. SOURCE: CM:011 SOURCE: Kotler, P. (2000). Marketing management (10th ed.) [pp. 501-502]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 11 11. D Employees with guidance and direction. Communicating the Internet-based business's objectives to employees and giving them guidance about doing their work in a manner that will help the firm to achieve those objectives is an important function of effective staff communication. Employees circulate rumors and information among themselves, and this communication is called the grapevine. Staff communication is not addressed to customers or stockholders. SOURCE: CO:014 SOURCE: Lesikar, R.V., Pettit, J.D., Jr., & Flatley, M.E. (1999). Lesikar's basic business communication (8th ed.) [pp. 4-5]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 12. B Join in the discussion. For staff meetings to be effective, all employees should participate in the discussion. The purpose of staff meetings usually is to discuss issues that are of importance to the Internet-based company, or to solve problems. Therefore, employees should join in the discussion rather than remain silent because their ideas and opinions are valuable. Employees should not comment on every detail. Employees should adequately explain their ideas, but it is not effective to start an argument with those who disagree. SOURCE: CO:063 SOURCE: Lussier, R.N. (2003). Management fundamentals: Concepts, applications, skill development (2nd ed.) [pp. 327-330]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 13. D Experience. When giving instructions, an Internet-based company's managers should take into consideration how much experience the employees have. New employees may need specific, detailed instructions because they are not entirely familiar with the job. Employees who have been on the job a long time may need only brief instructions because they know exactly what is expected of them. Managers should tailor their instructions to the experience level of employees. Managers do not consider the employees' level of income, professionalism, or authority when giving instructions. SOURCE: CO:139 SOURCE: Hyden, J.S., Jordan, A.K., Steinauer, M.H., & Jones, M.J. (1999). Communicating for success (2nd ed.) [pp. 109-110]. Cincinnati: South-Western Educational. 14. B To show that you fully understand the problem. Summarizing the problem shows that you fully understand the situation and gives customers an opportunity to verify the accuracy of the information. Apologizing for any inconvenience indicates empathy for customers and their situations. Deciding how a problem can be resolved occurs after you have verified your understanding of the situation. You should express your gratitude for customers' business by thanking them. SOURCE: CR:004 SOURCE: HR LAP 32—Customer-Service Mindset 15. B Service policies. Service policies are guidelines governing the support an online company provides to the customers after the sale through return, repair, and installation policies. Managers often develop service policies to meet the needs of their specific customers. The result of implementing these policies is that the online business creates positive relations with its customers. For example, offering free repair is a service policy that appeals to many customers and encourages them to remain loyal to the online business. Operating procedures are the step-by-step processes an online business follows to perform certain tasks. Sales strategies are the plans for achieving sales goals. Marketing tactics are the specific actions that will be used to carry out marketing strategies. SOURCE: CR:008 SOURCE: Longenecker, J.G., Moore, C.W., & Petty, J.W. (2003). Small business management: An entrepreneurial emphasis (12th ed.) [pp. 370-372]. Cincinnati: Thomson/South-Western. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 12 16. B Keeping inventory on hand until customer orders are received. By keeping inventory on hand until customer orders are received, the e-tailer maintains control over its inventory, packaging techniques, shipping schedules, customer service, and so forth. Outsourcing all of the processes to a fulfillment house offers the least amount of control because the etailer is not responsible for maintaining inventory, order taking, shipping, or customer service. E-tailers that hire a dropshipper lose control over picking, packing, pulling, and shipping products; however, they do maintain control over order processing. Purchasing products from a local distributor after customer orders are received causes the e-tailer to be dependent upon the distributor's inventory. SOURCE: DS:089 SOURCE: Wilson, R.F. (2002). Planning your Internet marketing strategy (pp. 148-153). New York: John Wiley & Sons. 17. D Identify discrepancies. One way to identify shipping discrepancies is for receiving clerks to count the items in a shipment and mark them off the purchase order. By counting each item, the receiving clerks will find out if certain items are missing or if more items were shipped than ordered. Labeling merchandise, distributing stock, and warehousing excess goods are other aspects of receiving. SOURCE: DS:086 SOURCE: Monczka, R., Trent, R., & Handfield, R. (2002). Purchasing and supply chain management (2nd ed.) [p. 44]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 18. D Two 40-pound packages. The least expensive shipping method is to combine the eight 10-pound packages into two 40-pound packages. The total cost for shipping the two larger packages is $16.70 ($8.35 + $8.35 =$16.70). Eight 10pound packages would cost $36.40 ($4.55 x 8 = $36.40). The cost for two 30-pound packages and one 20-pound package would be $20, and the cost for three 20-pound packages and two 10-pound packages would be $26.80. SOURCE: DS:057 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (pp. 350-351). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 19. C Color coding. The color assigned to each shipment of goods indicates the date it was received, which tells the marketer how long it has been in inventory. This makes it easy to see which goods should be used first. Tickler control is a system by which buyers estimate the entire inventory for a given period by counting portions of the stock at regular intervals. Reorder control system uses reminder cards or labels for buyers when the inventory level of an item reaches a certain level. A check-out scanner is a device used to read product information for an electronic cash register. SOURCE: DS:022 SOURCE: DS LAP 3—Unit Inventory Control Systems 20. A Know if products listed for sale on their web sites are actually in stock. By developing real time inventory systems, etailers gain important knowledge about whether the products listed on their web site are actually in stock. This is possible because inventory information is integrated with the information that is available on their web sites. E-tailers need to develop HTML coding that is free of holes in order to prevent hackers from deleting products from their web sites, not an inventory control system. Although inventory control systems might be used to indicate when backordered items appear in stock, they do not automatically send out e-mail notifications to customers. The actual software that supports the shopping cart system is what keeps track of items that customers want to purchase, not an inventory control system. SOURCE: DS:092 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (p. 442). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 13 21. D Receives the correct product. One of the functions of customer service in the distribution process is to make sure the customer receives the correct product. Customers buy specific products that meet their needs and expect to receive those products. If they are not satisfied with the products they purchase, they may return them or decide not to buy from the online business again. Taking accurate orders, following up on delivery, and handling problems or complaints are ways that customer service can make sure the customer receives the correct product. Customer service does not facilitate the distribution process by making sure the customer pays full price for the product, accepts delivery of the product, or tells others about the product. SOURCE: DS:029 SOURCE: Everard, K.E., & Burrow, J.L. (2001). Business principles and management (11th ed.) [pp. 575-576]. Cincinnati: South-Western. 22. A Supplies. Supplies are products that are constantly being purchased and used up in the operation of an online business. Parts are items that will become part of a final product without additional processing. Materials become part of a finished product after they have been processed. Equipment is industrial products used in the operation of a business but not in the actual production of a good or service. SOURCE: EC:002 SOURCE: EC LAP 10—Goods and Services 23. A Competition. In market economies, competition is a very important factor in deciding how products will be produced. Producers try to choose a production method that will enable them to offer products at prices that are attractive to customers. Each producer must try to use resources in the most efficient method possible in order to compete with other producers and to make maximum profits. Tradition is an important factor in traditional economic systems. Government is an important factor in command economic systems. Distribution is not a factor. SOURCE: EC:007 SOURCE: EC LAP 17—Economic Systems 24. B The efforts of competitors. Competition can be an economic risk to an online business. The online company in this situation may be forced to lower its prices or to change its product. Shifts in customer demand are an economic risk caused by customers' changing needs and wants. Government intervention includes any actions taken by government that affect what will be profitable for a business to sell. Product obsolescence occurs when the usefulness or stylishness of a product declines. SOURCE: EC:011 SOURCE: EC LAP 3—Lose, Win, or Draw (Business Risk) 25. C A way for suppliers and demanders to interact. An e-commerce business's market structure in an industry can be described as a way for suppliers and demanders to interact. This means that the market is structured in a way that makes it easy and efficient for an e-commerce business to obtain and sell products. It is not a method of categorizing goods and services, a tool for measuring economic activity, or a means of gauging an e-commerce business's financial success. SOURCE: EC:075 SOURCE: University of Michigan. (n.d.). Deardorff's glossary of international economics. Retrieved July 27, 2007, from http://www-personal.umich.edu/~alandear/glossary/m.html 26. C How high or low prices are. Price level is one of two terms economists use to describe prices; the other is inflation. To measure price level, economists select a market basket of goods and construct a price index, such as the Consumer Price Index, which is a widely used measure of the price level. They are then able to compute price levels and rates of inflation. Price level is generally used for comparative purposes; today's price level may be higher, lower, or about the same as prices five years ago. Inflation measures the rate of increase in prices. Economists can use some of these variables in predicting prices in the future, but price level does not look at future prices. Deflation occurs when price levels drop. SOURCE: EC:080 SOURCE: O'Sullivan, A., & Sheffrin, S.M. (2003). Economics: Principles in action (pp. 58, 307). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 14 27. A Increased growth. During a mildly inflationary period, wages usually increase more slowly than the prices of goods. Therefore, the cost of the goods sold is higher than the cost of labor. As a result, businesses earn more profits which enables them to expand and hire more employees. The economy grows because more people are working and have income to spend. This situation occurs only during a mildly inflationary period because if inflation rises to a higher level, the economy experiences a decrease in prosperity. High inflation also causes increased unemployment and decreased profits for businesses. SOURCE: EC:083 SOURCE: Arnold, R.A. (2004). Economics (6th ed.) [pp. 218-219]. Cincinnati: Thomson/South-Western. 28. D Visualization. The visualization technique of stress management involves imagining a pleasant scene and invoking as many senses as possible in order to imagine being in the scene. Deep breathing involves taking deep, slow breaths to physiologically relax the body. Positive self-talk involves asking yourself questions about what is important and what you can realistically accomplish. Muscular relaxation involves focusing on relaxing muscle groups in order to reduce stress. SOURCE: EI:028 SOURCE: Sarmiento, R.F. (n.d.). Stress management. CyberPsychologist. Retrieved July 27, 2007, from http://www.cyberpsych.com/stress.html 29. C Management style. The way in which e-tail supervisors guide the work of employees depends upon their management style. Management style is the way or manner in which a person goes about the task of influencing others. Management styles include authoritarian, democratic, and laissez-faire. An e-tail supervisor's level of education, technical skills, and desire for success may affect the choice of management style. SOURCE: EI:037 SOURCE: EI LAP 5—Can You Relate? (Positive Working Relationships) 30. D Be timely. Recognition is more effective the closer it follows the behavior. When you see or experience something positive, comment on it right away. Otherwise, a person is left to wonder if you noticed the effort at all. Recognition should be personal rather than general. It is not effective to exaggerate praise or to limit compliments. The recognition should match the effort. SOURCE: EI:014 SOURCE: QS LAP 13—Gimme Five! 31. B Installment credit. Installment credit is frequently used in the purchase of big-ticket items such as furniture. An open, or regular, credit account allows credit users to buy at any time during a set period, usually 30 days. A revolving credit account limits the total amount of money that may be owed and charges interest on outstanding balances. Layaway is paying over a period of time for merchandise held by the store until the customer pays in full. SOURCE: FI:002 SOURCE: FI LAP 2—Credit and Its Importance 32. D To determine the potential for loss. Speculative risks are chances of loss that may result in loss, no change, or gain. When an Internet-based business takes a speculative risk, there is always the possibility of failure. Therefore, before taking speculative risks, Internet-based businesses usually evaluate them in order to determine the potential for loss. Internet-based businesses may decide not to take the risk because the potential for loss is too high. Internet-based businesses cannot obtain insurance for speculative risks. Internet-based businesses usually purchase insurance to cover losses due to theft or property damage. SOURCE: FI:080 SOURCE: Longenecker, J.G., Moore, C.W., & Petty, J.W. (2000). Small business management: An entrepreneurial emphasis (11th ed.) [pp. 544-545]. Cincinnati: South-Western College. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 15 33. B Loss-prevention. Loss-prevention measures that eliminate safety hazards should be part of an online business's riskmanagement plan. Risk management is the reduction of loss through prevention or transfer. Joe is trying to prevent a possible fire. Expense control is a business concept but not a risk-management measure. Security precautions reduce the risk of loss due to employee and/or customer theft. The employees are being instructed, not controlled. SOURCE: FI:084 SOURCE: BA LAP 2—Risk Management 34. C Assets, liabilities, and equity. A balance sheet is a financial statement that captures the financial condition of the webbased company at a particular moment. The web-based company summarizes its financial condition by categorizing data into three groups—assets, liabilities, and equity. An asset is anything that the web-based company owns or that can be converted into cash. Assets include cash, equipment, and sales income. Liabilities are the web-based company's debts. As a liability, a credit balance is money that a web-based company owes to its suppliers or lenders. Equity is the net worth of the web-based company after subtracting all liabilities from all assets. A budget is an estimate of income and expenses for a certain period of time. A budget is not a category of information that is listed on a balance sheet. SOURCE: FI:093 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (p. 772). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 35. C Gross margin. Gross margin on an income statement is the difference between the cost of goods sold and net sales. Gross margin is not the same as net profit, which is the money remaining after operating expenses are subtracted from gross profit. Gross sales is the total value of goods or services sold in a period of time. SOURCE: FI:102 SOURCE: Stull, W.A. (1999). Marketing and essential math skills: Teacher's edition (pp. 234-235). Cincinnati: SouthWestern Educational. 36. B 20%. Return on investment is a cost/benefit analysis that is calculated by dividing the profit by the investment, which includes the total costs and expenses. First, determine the profit by subtracting the costs and expenses from the selling price ($26.75 - $22.25 = $4.50). Then, divide that figure by the investment (4.50/22.25 = 0.202 or 20%). In this example, the online business invested $22.25 in each item, sold each item for $26.75, and achieved a 20% return on investment. Businesses calculate return on investment to determine if they are earning a sufficient profit based on the cost. SOURCE: FI:302 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (3rd ed.) [p. 453]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 37. C Productivity. Productivity is the amount of work that employees perform in a given period. Before an e-business decides to hire new employees, it must have the financial resources to pay the employee, and it must have the need to increase its outputs. When an e -business expects higher sales, it needs to increase its outputs, and therefore, needs more inputs (e.g., personnel) to satisfy the higher product demand. When deciding to hire employees, an e-business does not first consider its secondary, uniform, or temporary needs. SOURCE: HR:353 SOURCE: Dessler, G. (2000). Human resource management (8th ed.) [p.124]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 38. A Next step in the process. When concluding an interview with a job applicant, it is important for the interviewer to explain what will happen next. The interviewer might have more applicants to interview before making a decision. Each applicant should know when the process will be completed, such as by the end of the week. They also are entitled to know if they will receive a phone call if the job is being offered to them or a letter of thanks for their interest. The requirements of the position and the performance evaluation system would be discussed during the interview rather than at the conclusion. Interviewers should not explain the problems in the business with job applicants. SOURCE: HR:355 SOURCE: Lussier, R.N. (2003). Management fundamentals: Concepts, applications, skill development (2nd ed.) [p. 245]. Mason, OH: South-Western. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 16 39. D Learn their jobs. A e-tailer's current employees can help new employees learn their jobs and provide them with information about company procedures. Businesses often assign new employees to work with experienced employees who will be able to help train them and give them directions about job duties. Current employees usually are able to answer new employees' questions. New employees are expected to possess the work skills necessary to do the jobs for which they were hired. New employees negotiate contracts with businesses before starting to work. SOURCE: HR:360 SOURCE: Jackson, S., & Schuler, R. (2003). Managing human resources through strategic partnerships (8th ed.) [p. 368]. Cincinnati: Thomson/South-Western. 40. C Population to be served. In order for the e-tailer to get the best return from its training and development expenditures, it should try to spend the funds where they will do the maximum amount of good. This means providing training and development opportunities for the population with the most pressing problem first. The trainees' personal needs and the training offered by competitors are not factors in this decision. The implementation checklist helps the training process to go smoothly. SOURCE: HR:363 SOURCE: MN LAP 50—Manager/Supervisor Training 41. B Information gathering. The basic function of a marketing-information management system is to gather information important to the business. This information should be gathered from both internal and external sources on an ongoing basis. Information processing involves examining the collected data and putting them into formats that are useful to the business. Information reporting involves distributing information to those who make marketing decisions. A sales forecast is not a function of a marketing-information management system. Instead, it is a prediction of future sales over a specific period of time. SOURCE: IM:001 SOURCE: IM LAP 2—Marketing-Information Management 42. C Internet. The Internet is the interconnection of thousands of computers and computer networks all over the world. The Internet allows computer users to exchange information, search for data in remote locations, and communicate with others throughout the world. Marketing-information managers often use the search capabilities of the Internet to look for data that they otherwise would not be able to access because it is available in remote locations. E-mail is the electronic transmission of messages across computer networks. Cookies are bits of data stored on an Internet user's computer. Cell phones are a personal communication device. SOURCE: IM:183 SOURCE: Hair, J.F., Jr., Bush, R.P., & Ortinau, D.J. (2000). Marketing research: A practical approach for the new millennium (pp. 120-124). Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 43. D Exploratory. Exploratory research collects information to help the e-business define its issue, situation, or concern and decide which direction to go in order to address it. Descriptive research is used to gather specific information that is related to the identified issue, situation, or concern. Causal research focuses on cause and effect and tests "what if" theories. Predictive research is used to help the e-business forecast future business developments. SOURCE: IM:010 SOURCE: IM LAP 5—Nature of Marketing Research 44. B Decide which products to feature. Most e-businesses use some type of tracking method to obtain information about visitors to their web sites such as how often they visit the site and what they buy. The purpose of tracking this information is to use it to make decisions to make the site more effective. One way that an e-business might use the information is to decide which products to feature. If tracking information indicates that customers prefer certain products, the e-business probably would feature those products in order to satisfy customers and increase sales. Tracking methods collect primary data, but that data is helpful only if e-businesses use it to make decisions. An ebusiness does not use tracking information to prepare privacy statements or negotiate with key suppliers. SOURCE: IM:234 SOURCE: Broadbent, B. (1998). Using the internet smarter & faster (pp. 125-126). Menlo Park, CA: Crisp Publications. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 17 45. B Decreasing job opportunities. Many businesses are only selling their products online. This decreases the need for experienced salespeople to answer customer questions and encourage purchase decisions. In many cases, the Web is becoming the selling tool, and the traditional sales positions are no longer needed. Online businesses that employ salespeople still expect those employees to be knowledgeable about the products they sell. The sale of goods and services on the Internet does not increase commission rates or promote customer contact. However, if it did, those would be positive benefits rather than negative effects. SOURCE: MK:010 SOURCE: BA LAP 3—Internet's Impact on Marketing 46. C Achieving planned goals. The e-business's goals and strategies for achieving those goals may change frequently. Changing the e-business's image, increasing its profits, or improving management techniques might be specific goals at any point in time. SOURCE: MP:001 SOURCE: IM LAP 7—Pick the Mix 47. D Consumers' characteristics. In order to satisfy their customers, many e-businesses segment the whole market into smaller groups and focus their marketing efforts on a specific group. Consumer characteristics that they consider include age, occupation, gender, educational level, and life stage. Mass marketing is designing products and directing marketing activities in order to appeal to the whole market. A firm's employees would not necessarily provide information about the target market. Studying human relations—all the ways that people form and conduct relationships with one another—would not help a firm to segment its market. SOURCE: MP:003 SOURCE: IM LAP 9—Have We Met? 48. D Accessible. So that an e-business can promote and sell products, it must be able to reach its target market; so, the market must be accessible. Undifferentiated refers to a marketing strategy in which a business offers one option to the entire segment without considering market segments' differences. Concentrated refers to a tactic in which a business appeals to one or a few small markets with the goal of developing and maintaining customer loyalty. Inflexible means unwilling to adapt and is not usually a characteristic of a desirable target market. SOURCE: MP:005 SOURCE: Armstrong, G., & Kotler, P. (2000). Marketing: An introduction (5th ed.) [p. 199]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 49. B To understand change. E-businesses need to understand changes in their external environment in order to adapt and remain competitive. To do this, they often conduct situational analyses to gather information about changes or trends that are beginning to develop in the environment or marketplace. This procedure allows e-businesses to identify changes at an early stage and decide if they present a threat to the way the e-business is currently operating. Ebusinesses do not analyze their external environment in order to be socially responsible, behave ethically, or calculate profit. SOURCE: MP:008 SOURCE: Zikmund, W., & d'Amico, M. (2001). Marketing: Creating and keeping customers in an e-commerce world (7th ed.) [pp. 41-42]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 50. A Financial resources. A SWOT analysis is the systematic evaluation of an e-business's internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. One of the internal strengths that a SWOT analysis might identify is a business's financial resources. Having sufficient financial resources to develop new products and services is an internal strength that a business can use to grow and prosper. Extensive regulations is an external threat, while limited competition is an external opportunity. Increased expenses is an internal weakness. SOURCE: MP:010 SOURCE: Churchill, G.A., Jr., & Peter, J.P. (1998). Marketing: Creating value for customers (2nd ed.) [pp. 88-90]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 18 51. D Decreased trade regulation. Internet-based businesses often assess global trends in order to identify possible opportunities. Decreased trade regulation in certain parts of the world is a trend that presents an opportunity for many Internet-based businesses. For example, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the European Union have eliminated or lessened many trade restrictions between the countries involved. As a result, businesses in those countries have more opportunities to market their products in other countries. Increased political unrest, decreased population growth, and increased language barrier are potential threats rather than opportunities. SOURCE: MP:011 SOURCE: Boone, L.E., & Kurtz, D.L. (2004). Contemporary marketing (11th ed.) [pp. 102-103]. Mason, OH: Thomson/South-Western. 52. B Production should decrease. Businesses need to forecast the amount of products they can expect to sell in order to plan the most efficient production of those products. In this case, anticipated decreases in sales should be matched by decreased production in order to meet the shift in demand. Increasing production or keeping it at the same level will create too much inventory. The business might have to reduce its prices in order to sell the inventory. SOURCE: MP:013 SOURCE: IM LAP 3—Nature of Sales Forecasts 53. A Marketing plan, financial plan, and business situation analysis. A well-organized business plan consists of three major sections. The business situation analysis is the first section of the business plan. It provides a description about the business including the type of business, philosophy, product description, and self-analysis for entrepreneurs. The second section describes the web-based business's marketing plan and also addresses organizational issues. The last section is the financial plan, which discusses the web-based business's overall financial status and needs. The market segment analysis, SWOT analysis, and trading area analysis are components of the business situation analysis. The manufacturing plan applies only to manufacturing businesses and is a component of the organizational section of the business plan. The projected income report is a component of the financial plan. SOURCE: MP:018 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (4th ed.) [p. 740]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 54. D Eliminate certain items from the product mix. A profitability analysis measures whether an e-tailer is making an acceptable profit on the sale of goods and services. After conducting a profitability analysis, an e-tailer will be able to decide whether to make adjustments to its marketing plan. For example, if the profitability analysis indicates that certain items are not generating enough profit, the e-tailer might decide to eliminate those items from its product mix. By deciding not to market certain products, the e-tailer will be able to concentrate on promoting those items that generate the desired amount of profit. Reducing the number of employees in the accounting department, buying more equipment for the warehouse, and increasing the compensation and benefit package are not adjustments that an etailer would make to its marketing plan. SOURCE: MP:019 SOURCE: Kotler, P. (2000). Marketing management (10th ed.) [pp. 701-702]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 55. A Can return a large number of hits. A search engine is a software program that crawls the Web looking for information pertaining to specified search terms that an Internet user types into a search field, and then retrieves and displays the information for the Internet user. Search engines that use web spiders to obtain information can find data for narrow or very specific searches and return a large number of hits. The display results may contain secure and unsecured information. Metacrawler search engines search all other search engines. However, the disadvantage of using Metacrawler search engines is that they tend to have a high rate of repetitive hits because many web sites are registered on all major search engines. Meta tags are HTML codes that display information about web pages. SOURCE: NF:029 SOURCE: Kleindl, B.A. (2001). Strategic electronic marketing: Managing e-business (p. 62). Cincinnati: SouthWestern College. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 19 56. C Link to. An online business's web site usually contains several pages so specialized information can be explained in more detail. For example, online businesses often have pages that describe the history of the company, list the key employees, explain products, provide shopping options, offer customer service, etc. It is important that each page include a link to the home page so users can return to the main page easily. Users often want to access each page, and it is easier to do so if they can quickly link to the home page. It is not necessary to include a summary of the home page or a reason for the home page. Online businesses usually include illustrations or pictures on the home page, although that is not necessary. SOURCE: NF:042 SOURCE: Locker, K.O. (2000). Business and administrative communication (5th ed.) [pp. 142-143]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 57. B Hypertext markup language (HTML). Hypertext markup language is the most basic programming language used to create web pages. It tells a web browser how and when to display words and images on the computer screen. Secure sockets layer is a security measure that protects online credit-card transactions using encryption and a mechanism by which only the merchant's software is able to unscramble the data. Hypertext transport protocol (HTTP) is what is used to link web pages together, not to create web pages. An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that provides access to web pages. SOURCE: NF:062 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (3rd ed.) [pp. 165-166]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 58. B Accessed when needed. Online businesses need to organize their records in a systematic manner so that information can be accessed when it is needed. This is what record keeping is all about—managing the information that an online business needs in order to make operational and financial decisions. Some business records contain confidential information and should not be distributed freely, available to everyone, or published in newsletters. However, this information should be organized so that employees who are supposed to use it can access it when needed. SOURCE: NF:001 SOURCE: NF LAP 1—Record It (Business Records) 59. A Economic. An environmental scan is an analysis of external forces that influence a business's success. The fluctuation of unemployment rates is an economic factor because unemployment has an effect on consumers' ability to buy goods and services. If consumers are unemployed, they do not have income to spend. As a result, businesses (e.g., e-tailers) do not sell as much because consumers are not buying. When this situation occurs, businesses often reduce expenses in an attempt to stay in business until the rate of employment starts to rise again. The rate of unemployment is not a geographic, political, or cultural factor. SOURCE: NF:015 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (pp. 30-32, 84-86). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 60. B Hire a professional to try to break into the system. Professionals can recognize flaws in the security system and make recommendations to make it more secure. Encryption algorithms protect transaction information in transit, but do not stop dishonest merchants or employees. While having an 800 number for customers to call and charge purchases may reassure customers who do not wish to disclose their credit-card numbers online, it may dissuade customers who want the convenience of purchasing online. Transferring the user to a page that explains transaction security gives the purchaser peace of mind; however, some online companies do not provide adequate protection of records stored in their computers. SOURCE: OP:125 SOURCE: Strauss, J., & Frost, R. (1999). Marketing on the Internet: Principles of online marketing (pp. 382-384). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 20 61. B Pilferage. Pilferage is the theft of small sums of money or inexpensive items from an online business. Shoplifting is the theft of goods by customers. Burglary is any illegal entry into a building to commit a theft. Robbery is theft that involves the use of force, violence, or fear. SOURCE: OP:013 SOURCE: RM LAP 4—Security Precautions 62. C Outputs. Outputs are the goods and service produced as the result of combining inputs. In other words, outputs are finished products. Inputs are the specific economic resources that a business uses to produce goods and services. Raw materials, or items in their natural state, are inputs. Robotics is a mass production technique in which equipment is programmed to do a manufacturing task with little or no help from humans. SOURCE: OP:018 SOURCE: Clark, B., Sobel, J., & Basteri, C.G. (2006). Marketing dynamics (pp. 290-291, 296). Tinley Park, IL: Goodheart-Willcox. 63. D $234,750. Gross profit results from the subtraction of cost of goods sold from total revenue. In this case, the e-business had sales of $370,500 and $135,750 in cost of goods sold ($370,500 - $135,750 = $234,750). Net profit results from subtracting operating expenses from the gross profit. Fixed costs and charitable donations are included in operating expenses. SOURCE: OP:024 SOURCE: MN LAP 57—Operating Expenses 64. D To determine a product's possible range of profit. The purpose of conducting a break-even analysis is to identify the level of sales needed to reach the break-even point at various prices. The break-even point is the level of sales at which revenues equal total costs. To determine break-even point, an e-business must consider three factors—the price per unit, the cost per unit, and the total fixed costs. An e-business does not conduct a break-even analysis so it can receive a tax break from the government, so it can evaluate product sales from the previous year, or to determine the approximate consumer demand levels. SOURCE: OP:192 SOURCE: Burrow, J.L. (2006). Marketing (2nd ed.) [pp.155, 386]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 65. A Hiring part-time employees. Payroll is usually an Internet-based business's greatest expense. One way of controlling payroll expenses is to hire part-time employees who work only when needed. Part-time employees receive an hourly wage, but the company saves money because it doesn't have to pay them for vacation or sick time or provide additional costly benefits that full-time employees receive. Scheduling overtime shifts would increase payroll expenses. Monitoring operating costs and changing purchasing policies will not help an Internet-based business to control payroll expenses. SOURCE: OP:029 SOURCE: Meyer, E.C., & Allen, K.R. (2000). Entrepreneurship and small business management: Teacher's manual (2nd ed.) [pp. 345-346]. New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 66. B $40,661.60. Businesses use budget information to monitor sales and expenses and predict future income and costs. In this example, the e-tailer's actual sales are expected to increase but so will the amount budgeted for expenses. To determine the amount the e-tailer will spend on expenses next month, first calculate the increase in sales by multiplying current sales by the estimated increase ($68,500 x 6% or .06 = $4,110), and add that figure to current sales ($68,500 + $4,110 = $72,610). The e-tailer expects $72,610 in sales next month. The e-tailer usually spends 52% of sales on expenses but expects a 4% increase next month for a total of 56%. To determine the amount the e-tailer will spend on expenses next month, multiply next month's sales by 56% ($72,610 x 56% or .56 = $40,661.60). SOURCE: OP:030 SOURCE: Louderback, J.G., Holmen, J.S., & Dominiak, G.F. (2000). Managerial accounting (9th ed.) [pp. 228-232, 235-238, 284]. Mason, OH: South-Western. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 21 67. D Delegate responsibility. The ability to delegate responsibility is a characteristic of someone who has leadership skills. Individuals who are leaders realize that they cannot do all of the work or make all of the decisions. Therefore, they delegate responsibility to others while continuing to guide and direct the actions of others so they will perform in a desired manner. To move up the career ladder, e-tail employees need to exhibit leadership skills, which include delegating responsibility. Dominating others, ignoring personal rights, and assigning blame are not skills. They are characteristics of individuals who might have difficulty moving up the career ladder. SOURCE: PD:035 SOURCE: Kimbrell, G., & Vineyard, B.S. (2006). Succeeding in the world of work (pp. 285-286). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 68. B Delegating activities. Julie is delegating, or giving, one of her duties to another capable e-tail employee. She is not procrastinating, or postponing, the job because another employee is doing the job. Setting objectives involves establishing goals to be met. Standardizing tasks creates a method of performing a duty that will stay the same. SOURCE: PD:019 SOURCE: PD LAP 1—Time Management 69. C The price must satisfy both buyers and sellers. Buyers want low prices, and sellers want high prices. Both groups must feel that they are getting the most value from the product in order for customers to be satisfied and the e-tailer to be successful. Customers associate price with quality. If a price is lower than a customer expects to pay, the customer may not buy. Businesses (e.g., e-tailers) must be willing to adjust their prices according to circumstances. Selling price includes the cost of the product and all of its associated costs, such as transportation charges and promotion expenses. SOURCE: PI:001 SOURCE: PI LAP 2—Pricing 70. C Fixing. Price fixing is an illegal business agreement in which businesses agree on prices of their goods and services, resulting in little choice for the consumer. Price discrimination is an illegal activity in which a business charges different customers different prices for similar amounts and types of products. Coercion is forcing a person to do something s/he does not want to do. Altering is changing prices, which is not always an illegal action. SOURCE: PI:017 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (p. 536). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 71. B Total amount of its income from sales. The purpose of sales-oriented pricing objectives is to increase the total amount of income from sales. In most cases, this results in more efficient use of human resources. The e-tailer may need to increase its promotion, but that is not a goal of the pricing objective. The e-tailer would need to control its marketing costs, not increase them, in order to be successful. SOURCE: PI:002 SOURCE: PI LAP 3—Factors Affecting Selling Price 72. D Life cycle. The course that a product follows in the market, including the stages of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline, is known as the product life cycle. After being introduced on the market, all products move through the lifecycle stages at different rates, requiring different marketing strategies. Online businesses should plan marketing strategies that will be most effective for the product at each stage of its life cycle. Research studies are often used to aid product/service management in order to gather information concerning consumer needs and preferences. Testmarketing is the process of introducing a new product to a limited market to determine what its acceptance will be. Feasibility analysis is examining such factors as demand, costs, competition, capital investment required, and potential profit of a good or service to determine how it will fit into the online company's product mix. SOURCE: PM:001 SOURCE: PP LAP 5—Product/Service Planning Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 22 73. D Maturity. Maturity is the stage in the product life cycle in which sales peak and profits increase. However, many businesses are competing for those sales because the product is popular and in demand. Businesses expect to make money selling products in the maturity stage, but they realize that they will need to be competitive. During the introduction phase of a product, a business is more likely to lose money than to make it. Universal and existing are not stages of a product life cycle. SOURCE: PM:024 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (pp. 644-645). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 74. D Tracking visitors to their web sites. Computer technology allows businesses to have web sites and makes it possible for those businesses to track the visitors to their web sites. As a result, they can obtain information about them such as name, address, type of purchase, amount of sale, etc. Online businesses often use this information to improve their product/service mix. For example, if an online business determines that customers are not buying a certain product, they might improve the product or replace it. Online businesses do not use computer technology to mail questionnaires to customers' homes. Online businesses often compile the information they obtain through their web sites in databases. However, the information is not useful until the online businesses analyze it. Simply preparing interactive software programs will not help online businesses to obtain information. SOURCE: PM:039 SOURCE: Zikmund, W., & d'Amico, M. (2001). Marketing: Creating and keeping customers in an e-commerce world (7th ed.) [pp. 127-128]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 75. D Specific details. A common use of synectics is to describe a topic in great detail. The goal is to generate ideas by focusing on the details of a situation. The technique is often useful to develop ideas when a good or service exists. Often, the goal is to determine potential market opportunities and identify unique attributes of the product that might appeal to the potential market. To identify the market opportunities, the synectics' process involves identifying many specific details about the product and the potential market. The detail-orientation synectics' technique might begin by addressing general needs, personal wants, or positive attributes; however, the creative-thinking process must evolve and identify all components in great detail. SOURCE: PM:127 SOURCE: PM LAP 11—Unleash Your Oh! Zone 76. B Value. A feasible or practical product idea should provide the product purchasers or users with a certain amount of satisfaction or value. Developing and marketing products is an expensive process, so it is important to make sure that the product idea translates into sellable goods and services. An attribute is a characteristic. Depth describes a productmix dimension referring to the number of products and the assortment of sizes, colors, and models offered in a product line. Standards are specifications or statements that are used as a basis for comparing goods or services. SOURCE: PM:129 SOURCE: Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (1999). Principles of marketing (8th ed.) [p. 277]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 77. C Quality. Many e-businesses establish quality standards that indicate the degree of excellence to be expected from a good or service. In some cases, perfection may be the only acceptable standard for an e-business's goods and services. For example, an invoice containing pricing errors cannot be sent to a customer. Industry standards are standards that all businesses in a particular industry are expected to follow. Quantity standards specify the amount of work to be done. Activity is not a type of standard. SOURCE: PM:019 SOURCE: PM LAP 8—Grades and Standards Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 23 78. D To encourage repeat business and to attract new customers. Internet businesses often add and delete items from their product line or change pricing. Therefore, it is important that updated information is posted on their web sites. To encourage repeat business, Internet businesses often update their web sites by enhancing the pages' appearance and by making the web site more user-friendly. Networking systems do not necessarily influence web-site maintenance needs. Successful Internet businesses update and maintain their web sites on a regular basis by in-house personnel or outsourced services. Updating information on a web site does not necessarily eliminate the need for businesses to promote their web sites. Not all businesses outsource their web-site maintenance needs. SOURCE: PM:113 SOURCE: PM LAP 9—WWW Site Maintenance 79. C Unique characteristics. The online office supply store is positioning its product according to unique characteristics because it is claiming that its product does something that no other product can do. The ink changing color in light is a feature, but it is a unique characteristic that is not available on other pens. The store is not positioning according to the quality or price of the pens or their relationship to other products. SOURCE: PM:042 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (3rd ed.) [pp. 559-561]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 80. B Brand mark. The hollow tree on a box of Keebler cookies is an example of a brand mark. A brand is the name, term, symbol, or design that identifies a product and distinguishes one product from another. The trade name identifies a company or organization. The trade character is a lifelike symbol associated with a product or company. SOURCE: PM:021 SOURCE: PM LAP 6—It's a Brand, Brand, Brand World! (The Nature of Branding) 81. C Sales volume. To survive in today's competitive marketplace, an e-tailer must make a profit. By providing good customer service, the e-tailer builds ongoing customer relationships. These relationships lead to repeat business, which increases sales volume. Employee responsibility and the number of salespeople may not increase, as the service offered may attract only a limited number of customers who purchase a lot of products or high-priced products. Increased use of facilities may result from customer services but would not be a primary reason. SOURCE: PM:013 SOURCE: PM LAP 1—Customer Service Supersized! 82. B A brand's personality. Brands connect with customers on emotional and rational levels. It is often a brand's personality that establishes and maintains emotional links to customers, when brands have features and characteristics that customers can readily relate to, much as they do other people. An e-business owner's personality may influence the development of an e-business's brand but does not have a direct impact on emotional connections with consumers. An attractive web site will entice customers to frequent a business but will not likely, in and of itself, be a key influence on the brand's emotional connection with consumers. An e-business should not change its core values to meet the changing needs of customers. It can adapt its operations, policies, etc., but should always keep its core values intact. SOURCE: PM:126 SOURCE: PM LAP 10—Building Your Business's Brand 83. A Planned purchases minus goods on order. Open-to-buy is the amount of merchandise that can be purchased in a particular period. It is calculated by subtracting goods on order from planned purchases. The dollar amount of open-tobuy determines the number of goods to be ordered. The percentage of markup and the ratio of sales to stock are separate calculations. SOURCE: PM:064 SOURCE: Cash, R. P., Thomas, C., Wingate, J. W., & Friedlander, J. S. (2006). Management of retail buying (pp. 99101). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 24 84. C Timely. A business must make sure that the content that it posts on its web site is accurate and timely. If information is incorrect (e.g., product pricing) or outdated, customers may develop a negative view of the company and not purchase its products. Content does not necessarily need to be in-depth, complex, or bilingual. SOURCE: PM:180 SOURCE: Hanson, W. (2000). Principles of Internet marketing (pp. 410-411). Cincinnati: South-Western College. 85. A Prior to peak selling season. An e-tailer's peak selling season occurs when customer demand for certain products is very high. For example, the demand for beachwear is usually highest during the spring and summer months in the northern hemisphere. Therefore, e-tailers generally try to order these types of items so they have enough on hand to meet demand. If e-tailers order higher quantities of items while in the peak season, they run the risk of stockouts or back orders from their vendors. As a result, e-tailers cannot meet customer demand for seasonal products. Therefore, it is best to order higher amounts of inventory prior to peak season. Most e-tailers do not order higher amounts of stock before conducting physical inventory counts because the process involves more counting and administrative work. Although it is possible that businesses order higher quantities of products after a physical inventory, that it is not always true. SOURCE: PM:261 SOURCE: Berman, B., & Evans, J.R. (1998). Retail management: A strategic approach (7th ed.) [p. 454]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 86. C How long it takes to order and receive goods. Lead time is the amount of time that passes between placing an order and receiving the stock. When deciding when to buy goods, an online business considers a supplier's lead time because that has an effect on when the goods will actually be delivered. If an online business knows that it usually takes a supplier approximately 15 days to process an order and deliver the goods, the online business will place an order at least 15 days before it needs the goods. An online business also considers how quickly the merchandise turns over when deciding when to buy, but this does not involve lead time. Lead time does not involve the number of steps in the receiving process or the location of shipping and delivery companies. SOURCE: PM:262 SOURCE: Berman, B., & Evans, J.R. (2004). Retail management: A strategic approach (9th ed.) [pp. 356-357]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 87. D Communicate the benefits of products to online buyers. Sellers need to point out the benefits of products sold via the Internet because people buy benefits, not features. Promotion contributes to the marketing effort, but it does not enable marketers to distribute online products carefully or create new products. Manufacturers produce goods and are not middlemen. SOURCE: PR:001 SOURCE: PR LAP 2—Promotion 88. B A business must understand that the laws governing promotional activities vary by country. Some countries have strict promotional laws that marketers must follow, while other countries' laws are lenient. A business that breaks a promotional law may have to pay government fines, which is costly to the business. Therefore, it is important for marketers to understand which promotional activities are, and are not, permissible in the countries where they sell and promote products. The International Ad Coalition is a fictitious organization. In some countries, industry and consumer groups influence how the governments regulate promotion. Some, rather than most, countries have a system of checks and balances to verify that promotion regulations are fair. SOURCE: PR:101 SOURCE: Arens, W.F. (2004). Contemporary advertising (9th ed.) [pp. 74-76]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw Hill. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 25 89. A Opt-in e-mail. Opt-in e-mail refers to electronic messages that are sent with a recipient's permission and allow the recipient to request removal from the subscriber list at any time. Since a specific, interested audience can be targeted, the online business does not waste time and energy promoting products to uninterested people. An online newspaper and closed-circuit television attract audiences that may or may not include the online business's preferred customers. Compulsory e-mail is a fictitious term. SOURCE: PR:007 SOURCE: PR LAP 3—Ad-quipping Your Business (Types of Promotional Media) 90. C Several times during. As a form of direct advertising, an infomercial is a lengthy commercial (broadcast advertisement) that looks like a television program. To increase the number of viewers who respond to the advertisement, the ebusiness should request a call to action (e.g., place order, ask for more information) several times during the duration of the infomercial. This is because viewers do not always watch the entire infomercial. If the call to action appears only at the beginning, in the middle, or at the end of the broadcast, the viewers may miss it and not respond to the advertisement. When requesting a call to action, the infomercial should repeat the phone number, e-mail address, or web address many times, which may increase response rates. SOURCE: PR:089 SOURCE: O'Guinn, T.C., Allen, C.T., & Semenik, R.J. (2003). Advertising and integrated brand promotion (3rd ed.) [pp. 688-689]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 91. A Purchase lists from providers. To increase the number of e-mail recipients, businesses often purchase or rent e-mail lists from list providers. However, care should be taken to ensure that the recipients are part of the target market that the business wants to receive its e-mails. Otherwise, the recipients might believe the e-mail is spam and delete it. Businesses do not increase the number of people who receive their e-mails by renting space on web sites, using information in telephone directories, or sending questionnaires to customers. SOURCE: PR:166 SOURCE: PR LAP 14—Executing Targeted E-Mails 92. D To support customers. Many different objectives can be served on a single web site. One of the most common objectives is to support customers. One way that a web site supports customers is by providing a variety of features such as a "Frequently Asked Questions" page that helps customers troubleshoot any problems they are having. Other objectives include informing, selling products, and providing a service. Policies and systems are components of a web site rather than objectives. SOURCE: PR:103 SOURCE: PR LAP 15—Planning Your Web Site 93. C Printable coupons. All aspects of a promotional campaign should be coordinated in order to obtain maximum results. For example, if a business advertises a product and directs the customer to the company's web site to print a coupon, the coupon should be posted on the web site and in a printable format for use. Trade shows are exhibitions at which manufacturers and suppliers in a particular industry display their goods. Special orders are orders placed to meet customers' specific wants. Target markets are particular groups of customers that businesses seek to attract. SOURCE: PR:076 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (3rd ed.) [pp. 308, 319]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 94. B Including helpful information on the business's web site. It hardly costs the business anything to post a frequently asked questions page that provides information that customers commonly seek. All of the other alternatives involve hiring customer-service representatives to communicate with customers, which can cost the Internet-based business a significant sum of money. For example, staff members with good writing skills would be needed to respond to e-mail inquiries and to chat with customers online. Also, customer-service representatives with good oral communication skills would be needed to answer telephones at a customer call center. SOURCE: SE:304 SOURCE: Rayport, J. F., & Jaworski, B. J. (2004). Introduction to e-commerce (2nd ed.) [p.175]. New York: McGraw-Hill. Test 926 INTERNET MARKETING — KEY 26 95. A Increased sales volume. A clientele is a group of regular, repeat customers. An increase in sales is a direct result of building a clientele. Loyal customers return to buy regularly, thus providing the financial backbone for a growing online business. Building a clientele helps to reduce selling costs. Personal satisfaction and increased knowledge are salesperson benefits of building a clientele. SOURCE: SE:828 SOURCE: SE LAP 115—Keep Them Loyal 96. D Spray paint. Products which are hazardous if not properly used, handled, or stored usually are labeled with safety information. Information is attached to the product so consumers will know how to use it safely. For example, spray paint may be toxic if not used in a well-ventilated area. None of the other products would be considered hazardous products that would require safety information. SOURCE: SE:062 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (pp. 665-666). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 97. A High-priced products. When people are planning to purchase high-priced items such as cars, computers, fine jewelry, or vacation packages, they tend to comparison shop. When consumers are buying expensive items, they usually want to get as many benefits and features as possible—they want to get the most out of their hard-earned money. Staple goods are items that people use or need everyday, such as milk or socks. Value-priced items are usually cheaper and include generic goods and products that have minimal features and benefits. Novelty items are often unusual, nonessential goods that vary in price range. People do not tend to comparison shop when purchasing staple goods, value-priced items, and novelty items. SOURCE: SE:109 SOURCE: SE LAP 113—Find Features, Boost Benefits (Feature-Benefit Selling) 98. C Brand-name items are generally cheaper for customers to buy. Brand-name items are usually more highly priced than generic items. All of the other alternatives are reasons for using brand names in selling. Customers are usually familiar with established brands, and the brands' reputation for quality and performance makes customers more comfortable about purchasing them. SOURCE: SE:019 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (pp. 656-658). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 99. D To avoid spending time and money on customers who will not buy. It is important for online businesses to evaluate their prospects to reduce the amount of time and money they spend on customers who will not buy. One way to do this is to design and post a detailed response form that obtains valuable information about customers. The information requested will help the business decide if the prospect has a need for the product, the authority to make the purchase, and the financial resources to pay. Once the business identifies a legitimate prospect, it can send follow-up information or have a salesperson call on the customer directly. It is not important for businesses to evaluate online prospects to identify customers who visit the sites of competitors, to prevent unauthorized customers from viewing a web site, or to control the number of customers who make daily purchases. SOURCE: SE:309 SOURCE: Wilson, R.F. (2002). Planning your Internet marketing strategy (pp. 13-14). New York: John Wiley & Sons. 100. C Management. Management is the process of coordinating resources in order to accomplish an organization's goals. The functions of management include planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives. Economizing is deciding how scarce resources will be used. Research is an investigation or inquiry. SOURCE: SM:001 SOURCE: BA LAP 6—Manage This!