Semester 2 Unit 3: World War II
advertisement

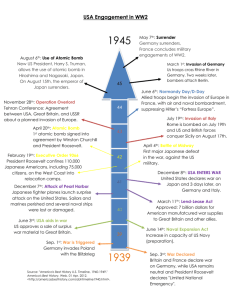
Semester 2 Unit 3: World War II Stage 1: Desired Outcomes Topic/Unit Title: World War II Did World War II change America for better or worse? NYS Content Standards 1 Common Core Skills Key Idea 2: Important ideas, social and cultural values, beliefs, and traditions; the connections and interactions of people and events across time and from a variety of perspectives. Key Idea 3: major social, political, economic, cultural, and religious developments; important roles and contributions of individuals and groups. Key Idea 4: explain the significance of historical evidence; weigh the importance, reliability, and validity of evidence; understand the concept of multiple causation; understand the importance of changing and competing interpretations of different historical developments. Reading-Social Studies (RH) 1. Use relevant information and ideas from documents to support analysis 3. Use information/ideas to determine cause and effect 6. Compare and contrast various points of view 7. Create and analyze visuals (graphs/charts) 8. Identify and analyze evidence Writing (W) 3. Produce writing appropriate to task, purpose and audience. 4. Strengthen writing by planning, revising, editing and rewriting 5. Draw evidence from informational text Speaking and Listening (SL) 1. Participate in collaborative discussion 4. Clearly present appropriate information and evidence 6. Demonstrate command of formal English Language (L) 1. Demonstrate appropriate grammar usage in writing and speaking (sentence complexity) 2. Demonstrate appropriate usage of the mechanics of language (punctuation, capitalization) 4. Build vocabulary and expand word choice Understandings: Students will be able to understand and know: The causes for WW2 The arguments for and against neutrality in the 1930’s The Neutrality Acts, Cash and Carry and Lend Lease Act The events and timeline of American and Japanese relations The Japanese decision attack Pearl Harbor The effects of World War II on women (increased employment opportunities), African Americans (decreased rational tension and increased opportunities), the economy (end of the Great Depression), individual consumers (rationing and war bonds) The effects of WW2 on Japanese Americans and the internment camps The decision of Korematsu v. U.S. Essential Questions: What were the ideals and actions of leaders in Europe and Japan that began WW2? Should America remain neutral during the 1930’s and start of WW2? Was America behaving like a neutral nation during the start of WW2? Was war with America and Japan inevitable? Did America respond appropriately to Japanese aggression in Asia? Did the war change America at home for better or worse? How did the war impact women? How did the war impact African Americans? Was American internment of Japanese Americans justified? How did the Supreme Court justify the decision in Korematsu v. U.S.? The contributions of America in helping to defeat the Axis Powers The difficulty of fighting on multiple fronts Significance of important turning points: D-Day, Midway, Iwo Jima The arguments for and against dropping the atomic bombs on Japan Americas role in the liberation of the concentration camps and the Nuremberg Trials America’s role in the creation of the United Nations The significance of the Yalta and Potsdam conference in setting up the Cold War How the end of WW2 set up the Cold War Why were rationing and war bonds important for financing the war? How did WW2 contribute to ending the Great Depression How did the American army help defeat the Axis Powers? Why did America have to fight on multiple fronts? How did America manage to fight on multiple fronts around the world? How did battles such as D-Day, Midway, Iwo-Jima change the war? Why was there a new culture of consumerism? Was the dropping of the Atomic Bomb justified? How did the Nuremberg Trials set a precedent for war crimes? How did the United Nations try to fix the problems of the League of Nations? How did the Yalta and Potsdam conference lead to the Cold War? Was Russia or America’s end and post-war actions most responsible for setting up the Cold War? Stage 2: Assessments and Tasks Common Core Literacy Tasks: Performance Tasks: Analyze and answer questions Document Analysis about primary and secondary source Scenario analysis documents. Writing Assignments Exit ticket: Should the United Persuasive Speech Writing States have remained neutral Exit ticket summary activities during the 1930s? Using at least 3 Document creation (political specifics from the lesson cartoons) Write a one-two paragraph Multiple Choice Exam persuasive speech (5-7 sentences with at least 3 details from the lesson) on why Congress should approve war against Japan. Exit ticket: Is war good or bad for a country’s homefront? Use at least 3 specifics from the lesson Create a political cartoon with 2-3 sentence explanation 2-3 details from the lesson which either supports or protests the decision of Korematsu v. United States and FDR’s actions. Exit Ticket: How did America contribute to victory in World War II? (one paragraph (5-7 sentences), using at least 3 specific examples from the lesson) Exit Ticket: Was the United States justified in dropping the atomic bomb on Japan? (one-two paragraphs (5-7 sentences), using at least 4-5 specific examples from the lesson) Multiple Choice Exam Student Reflections: - Exit Tickets Writing Assignments Document Creation Scaffolding Questions based on primary and secondary sources Graphic Organizers Multiple Choice Stage 3: Learning Plan Instructional Activities and Materials Aim #1: Should the United States have remained neutral during the 1930s? Major Ideas: - The “seeds” of World War II were sown earlier in the century from the results of World War I. - A stronger stand by the United States and the other Western democracies against fascist aggression might have prevented World War II. - The neutrality legislation of the 1930s was really designed to keep the United States out of war. Timed as it was, this legislation tended to accelerate World War II by giving encouragement to the fascist nations. United States neutrality, together with British and French appeasement, convinced the Axis Powers that they had nothing to fear from the “decadent democracies.” - After the outbreak of World War II in Europe, the American people were divided whether to become involved in the war. Basically, three different view were held by Americans: 1) the United States should eventually fight on the side of the Allies; 2) the United States should give all aid short of war to the Allies; 3) the United States should follow a strict neutrality towards the war. - President Roosevelt and those who wished to aid the Allied cause believed that the security of the United States would be imperiled by an Axis victory. - America’s progression from the neutrality acts to the Lend Lease Act to volunteers in England. Performance Objectives: - List and describe the acts of fascist aggression during the 1930s. - Describe and evaluate the responses (neutrality legislations) of the United States and the Western democracies to the acts of fascist aggression during the 1930s. - Locate on a map of the world the aggressor nations of the 1930s and those areas which fell victim to aggression. - List and explain the steps taken by President Roosevelt to lend material and moral aid to the Allies between 1939 and 1941. - Explain and evaluate the views of those who supported and those who opposed greater American involvement in World War II. - Take a position on whether or not the United States should have aided the Allies against the Axis Powers. - ACTIVTY: Exit Ticket: Answer the aim in one paragraph 5-7 sentences using at least 3 specific facts from the lesson. Aim # 2: Was war between the United States and Japan inevitable? Major Ideas: - During the 1930s and early 1940s a series of events increased tension and led to eventual conflict between the United States and Japan. These events included: (1) the United States discriminatory restrictions toward Japanese Americans; (2) Japan’s ambition and attempts to conquer and dominate China which conflicted with the United States Open Door Policy; (3) the Stimson Doctrine; (4) the unwillingness of Allied nations to support a United States proposal to impose economic sanctions against Japan; (5) the “Panay” Incident; (6) Japan’s alliance with Germany and Italy; (7) Japan’s annexation of French Indo-China; (8) United States’ extension of loans to China to buy war materials, the embargo on the sale of aviation gasoline and scrap iron to Japan, and the freezing of Japanese assets in the United States; (9) Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor, December 7, 1941. - United States’ foreign policy between the two wars was influenced by the experiences of World War I, the nation’s domestic needs and problems, and the aggressive actions of dictators both in Europe and Asia during the 1930s and 1940s. - American public opinion lagged behind the evolving viewpoint of President Roosevelt and some Congressional leaders that neutrality was a mistake, since, like appeasement, it had actually encouraged the aggressor nations of Europe and Asia. Performance Objectives: - List, explain, and describe Japan’s acts of aggression during the 1930s and early 1940s. - Describe and evaluate the responses of the United States and the other Allied Powers to these acts of Japanese aggression. - Assess whether or not the increased tension and conflict between the United States and Japan made war between these two nations inevitable. - Assess the impact of the attack on Pearl Harbor - ACTIVITY: You are President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The attack on Pearl Harbor has just taken place and you must ask Congress for a Declaration of War. Write a one-two paragraph speech (5-7 sentences with at least 3 details from the lesson) on why Congress should approve war against Japan. Aim # 3: How did World War II affect the American Homefront? Major ideas: - With the outbreak of World War II, women in the United States assumed numerous roles to assist in the war effort. - Women assumed new roles in the military, in industry, and various roles in the household to support the war effort. - Increased cooperation and reduction of racial tension - Increased economic mobility - Impact of war bonds, rationing and saving on the economy - Post war baby boom Performance Objectives: - Identify the new opportunities for women and African Americans - Describe the various roles that women played in World War II. - Evaluate whether women played a significant role in World War II. - Evaluate the impact of World War II on the American Economy - ACTIVITY: Answer in one paragraph 5-7 sentences: Is war good or bad for a country’s homefront? Use at least 3 specifics from the lesson. Aim # 4: Was the treatment of Japanese Americans during World War II a setback for democracy? Major Ideas: - Racial and ethnic prejudices and deprivation of human rights tend to be reactivated during times of perceived national danger. Performance Objectives: - Describe the antagonism and opposition to Japanese-Americans prior to 1941. - Describe the circumstances leading to the relocation of Japanese-Americans during World War II. - Describe the impact of the relocation camp experience on the lives of Japanese-Americans. - Analyze the issues in the case of Korematsu v United States. - Discuss the Japanese-American campaign to gain redress and reparation for their treatment in the United States during World War II. ACTIVITY: Create a political cartoon with a 2-3 sentence explanation that includes details from the lesson which either supports or protests the decision of Korematsu v. United States and FDR’s actions. Aim #5: How did America contribute to victory in World War II? Major Ideas: - America had to fight the war on several fronts - Key turning points helped to slowly defeat the Axis - America decided to concentrate on winning the war against Germany - The war time conferences between the “Big Three” helped to both settle issues yet also lead to post war tensions. - The importance of the Nuremberg Trials in holding war criminals accountable for their actions Performance Objectives: Students will be able to: - Explain the contributions of the American military to WWII victory - Analyze how issues in WWII helped to set up the Cold War - Analyze if the United Nations will solve the problems of the League of Nations. - Identify the importance of the Nuremberg Trials. - Assess whether the Harlem Renaissance was a celebration or a revolt ACTIVITY: EXIT TICKET: Answer the aim in one paragraph (5-7 sentences), using at least 3 specific examples from the lesson. Aim #6: Was the United States justified in dropping the atomic bomb on Japan? Major Ideas: - The atom bomb was dropped to force Japanese leaders to agree to a quick surrender, save hundreds of thousands of American lives that would surely die in any conventional invasion of Japan, and to end the Pacific war before the Soviet Union could intervene effectively and thus claim a role in the peacemaking negotiations. - The atom bomb would “put us in a position to dictate our own terms at the end of the war and make Russia more manageable in Europe.” (Secretary of State James F. Byrne) - By striking a major city the atom bomb would bring death to tens of thousands of Japanese civilians, far more Japanese people (and American soldiers) would have perished if Japan had been invaded. - Generals Eisenhower and MacArthur as well as several scientists who developed the atom bomb had reservations about the need to use this weapon. The dropping of the second bomb was far less defensible morally, but it had the desired result---Japan surrendered. Performance Objectives: - Explain and analyze the arguments used to defend and attack the use of the atom bomb. - Describe the effect of the atom bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. - Evaluate whether or not the United States was justified in dropping the atomic bomb. Activity: Answer the Aim in 1-2 paragraphs (5-7 sentences each) with 4-5 details from the lesson. Culminating Activity: Multiple Choice Test Questions will include political cartoons, cause and effect, poster-analysis, quotes and key vocabulary terms and their significance. Stage 4: Reflection Teacher Reflection and Planning Evaluate exit tickets, graphic organizers, writing assignments, scaffolding questions, and Multiple Choice. Will use these to review content and vocabulary building, essay writing skills, document analysis Will explore test results to look common content and skill errors, as well as document analysis. Will explore helpfulness of graphic organizers and writing activities