Mesopotamia & Fertile Crescent Worksheet: History
advertisement

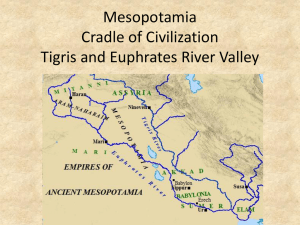
Name:________________________________ Section:__________________ Teacher: __________________ Chapter 2 vocabulary Chapter 2 Vocabulary Scribe: Fertile Crescent: City-state: Polytheism: Myth: Empire: Babylon: Caravan: Bazaar: Battering ram: Code: Hammurabi: Cuneiform: Alphabet: Monotheism: Famine: Exile: Covenant: Moses: Prophet: Diaspora: Lesson 2.1 Land Between Two Rivers p. 34-39 1. Think about it: How does geography affect the way people live? _______________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 2. Where were the first schools? ____________ When were they created? _____________ 3. Students (who were mostly boys) went to school to learn how to __________ so that when they graduated they could become __________ (professional writers) The Geographic Setting 4. Where was Sumer located? __________________________ (find this location on the map above and circle it!) 5. Why would farmers and city builders want to live in Mesopotamia? _______ _________________________________________________________ 6. Due to its _______________ in the ancient world, Sumer became once of the most wealthy areas in the ancient world. (find Sumer on the map on page 35 in your textbook and add it to the map at the top of this page!) 7. Why is this area of the world called Mesopotamia? ___________________ _________________________________________________________ Which two rivers does the region fall between? __________ and ________ 8. Mesopotamia is part of the larger area known as the _________________, which was the site of the world’s first ___________________. (notice the crescent shape of the region on the map) The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers 9. Why were these two rivers important for the people of Mesopotamia? ________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 10. Although the floods were helpful to the people of Mesopotamia because they helped to create the rich topsoil used for farming, they were also sometimes a problem for the people of the area. Why did they bring trouble to the region as well? _____________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ The First Cities 11. As farming succeeded in Mesopotamia, communities began to get a ___________ of food. This means that there is ___________ food, beyond that of which is needed to support you and your family. 12. Mesopotamia was made up of several _____________ that were politically independent from one another, each with his own ruler. a. Each ______________ had its own religious beliefs, government system, and eventually its own king. 13. Describe what a Sumerian city looked like. ____________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Sumerian Religion 14. What was at the center of each city? ________________ What was it used for? _________________________________________________________ 15. Describe a Sumerian temple (ziggurat). _______________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 16. Since the people of Sumer worshipped many gods/goddesses they were _______________________. People that worship only a single god or goddess are ___________________ (hint: you have to change the prefix of the word). 17. Sumerians had stories about their gods that explained people’s beliefs. These stories are called __________. 18. Sumerian gods were honored in ____________________, and statues of the gods were washed before and after each __________ was offered. The fall of Sumer 19. What caused the breakdown of Sumer? ______________________ 20. City-states ________ each other over Sumer’s _______ and use of the ____________. a. After changing hands several times, Sumer was conquered by _____________________ in 2300 B.C. i. Once conquered, the city-states were _________ and the government and military in the area improved. ii. The _____________ lasted about _____ years until it dissolved once more into independent city-states. iii. Sumer fell to its northern rival, __________, in the 1700s B.C. and was no longer a major power from that point on. Lesson 2.2 Babylonia and Assyria p. 42-46 The Two Empires of Mesopotamia 1. Why was Mesopotamia a target for conquests? ___________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ 2. The two most important empires of Mesopotamia were ______________ and ______________. a. In order to be considered an empire the area must have ____________ ______________________________________________________ 3. What traits did Babylonians and Assyrians have in common? ______________ ___________________________________________________________ The Babylonian Empire 4. The Babylonian Empire was created by King ________________ when he united the cities of Sumer and conquered lands all the way to Asia Minor. (find Asia Minor on the map on page 43 and add it to the map on the top of this page!) 5. During Hammurabi’s rule the creation of a system of roads helped to improve ___________, ________________, and _____________ in the empire. a. Babylon was a crossroads for trade because of its _______________. (find Babylon on the map above and circle it!) 6. What factors led to Babylonia’s early growth? _________________________ ___________________________________________________________ a. Despite its wealth, Babylon could not withstand conquests and after numerous attacks it would continue to shrink until it was finally destroyed. The Empire of the Assyrians 7. Assyria was located to the ____________ of Babylon. 8. Assyrians were skilled ______________ because of the need to constantly defend their land. a. Using their skill, they decided to attack surrounding lands as their method of defense and were eventually able to extend their empire from the ___________ River to the ___________________. (using the map above: About how many miles did the empire span? _______ miles.) 9. Assyrians were well equipped for war with many different types of weaponry and protection, but are often known for their creation of the _____________, a powerful wooden beam mounded on wheels. 10. As Assyrians continued to conquer lands they didn’t gain very many friends, rather the conquered people tried to ____________ against them. a. The __________ and ___________ were successful in the attacks and were able to ___________ the empire. Babylonia Rises Again 11. Although the Assyrians destroyed the city of Babylon when they invaded, the city was rebuilt with the efforts of King _____________________. 12. How did the Chaldeans show their interest in science and learning? _________ ___________________________________________________________ Lesson 2.3 The Legacy of Mesopotamia p. 47-51 1. Think about it: How would you feel if you lived in a civilization where laws like those in Hammurabi’s code were the rules you followed? Do you think they are fair?________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Hammurabi’s Code 2. The purpose of a written code, or organized list of ________ is so that people know __________________ ___________________________________________. 3. Hammurabi’s code was a very detailed set of laws. It contained __________ laws that were organized into different _______________. 4. What did Hammurabi’s Code tell us about the social class system in Babylonia? a. The classes were ______________. b. The __________ classes were more valued than the ___________ classes since punishments for crimes against the higher classes were more _____________. 5. Hammurabi’s code was not the first attempt to set up a code of laws in early civilizations but it is the first organized, __________ laws that we have found. 6. Examine the sample set of laws from Hammurabi’s code on pg. 49, this is just a small sample of the nearly 300 laws from Hammurabi’s code. Which law deals with the crime of kidnapping? (write out the law) _________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ The Art of Writing 7. Writing was important to the Sumerians because they used it to keep __________. 8. What kinds of things did Sumerian Scribes record? ________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 9. The records of Mesopotamia were written on _____________________________. What do you think are the advantages of writing on clay tablets? ______________ ____________________________________________ The Disadvantages? _______________________________________________________________ 10. The clay that was used to write on came from the _____________ and _________ rivers. 11. Written words started off as ____________ that represented objects. The symbols eventually evolved into groups of ___________________ known as cuneiform. 12. How does the way that the Sumerians organize their writing and read their text compare to the way that we organize ours? _______________________________ 13. Looking at the Development of Writing chart on page 51, how did the symbols for each word change over time? _________________________________________ ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Civilizations A Civilization is ________________________________ It comes from __________________________________ Characteristics of civilization 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Lesson 2.4 Mediterranean Civilization p. 52-57 Phoenician Sea Power 1. Using the map on pg. 53 in your text, locate Phoenicia and its colonies. Circle or highlight those regions on the map to the right on this page. 2. The two most plentiful resources that the Phoenicians had were ___________________ and _____________. 3. Which two main bodies of water did the Phoenicians use to trade their goods? ________________________________________ (circle these bodies of water on the map above). 4. How did the Phoenicians discourage others from trading in the Atlantic Ocean? ________________________________________________ Why did they do that? ___________________________________________ The Phoenician Alphabet 5. The Phoenician alphabet had only _______ symbols and is the basis for many modern _______________ used today (including _____________!) 6. How did the Phoenician alphabet spread throughout the ancient world? ______ ________________. 7. The Phoenician alphabet is different from cuneiform because it is __________ ________________. The Rise of the Israelites 8. Although the _________________, originally known as Hebrews were a small group of people, they had great influence on our civilization. a. Much of what we know about them comes from the stories in the _______, including that of the story of Abraham. 9. According to the Torah, Abraham taught his followers to practice _________, a belief in one god. a. He also led his people from Mesopotamia to __________, however due to a __________ they then fled south to ___________. 10. After more than a __________ years in Egypt, Moses eventually led his people out of Egypt because _______________________________. The exit from Egypt is known as an _______________. a. From Egypt the Israelites wondered through the desert for ____ years, at which time they were given the _____________________ from God. i. Eventually the Israelites returned to ______________ and began to build cities. The capital eventually became _______________ 11. After several changes in leaders, the instability led the people to be divided and many were ___________ to distant parts of the Assyrian Empire. Lesson 2.5 Judaism p. 60-64 1. The most sacred text of Judaism in the ___________, which records events and _______ important to the Israelites. a. The text is made up of ______ books that the Christians later adopted as the first five books of the _______ ____________. The Beliefs in Judaism 2. The beliefs of the Israelites developed into the religion of _______________ which is different than the beliefs of other nearby people because _________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. According to the Torah, God promised _________________ that his people would be leaders of nations, and, therefore the _________________ considered themselves “God’s chosen people.” a. By following ____________, an Israelite leader, to the promised land and obeying God, his covenant (promise) was renewed. 4. The Israelites believed that God delivered the _____ Commandments to them through _____________. They outline religious duties and correct ________. 5. In addition to the Ten Commandments the Torah outlined many other laws, including how food should be prepared. a. Many times today you will hear about food being Kosher. What does the word Kosher mean? ____________________ 6. ________ were considered head of the family and were considered owners of his ___________ and ______________. 7. Prophets, or religious _____________ speaking for God, told the Israelites how to live including a code of ethics, or moral behavior. a. Describe the code of ethics preached to the Israelites by prophets. __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ The Effects of Judaism 8. The followers of Judaism, known as the _______, are scattered throughout the world but remain united because they work to preserve their __________ and traditions. 9. Judaism influenced the religions of _____________ and ____________. All three religions are similar because they all believe in _______ God, are originate from same ________________, all honor ____________________, and all share the same __________ point of view. Study Topics 1. When and where were the first schools created? 2. What was a scribe and why were they important? 3. Why did settlements develop around the Fertile Crescent? How did they benefit from the physical geography of the area? 4. Mesopotamia was located between what two important rivers? 5. Cities in Sumer remained politically independent and developed into ____________. 6. Describe the difference between monotheism and polytheism. 7. Name the two important empires of Mesopotamia. 8. Who was King Hammurabi and why was he important? 9. Why was Babylon important as a center of trade? 10. What was the significance of Hammurabi’s code? 11. What did Sumerian scribes write on? 12. How has writing developed/changed over time? 13. What is civilization? What are the 6 characteristics of civilization? 14. How did civilization spread throughout the Mediterranean? 15. What is the Torah? 16. Judaism influenced what other religions? How are they similar?