Civil War Notes (Chapter 11) - Warren Hills Regional School District
advertisement

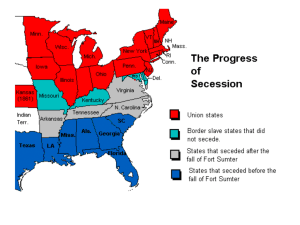
Civil War Notes (Chapter 11) Introduction -Fought 1861-1865 -Fought between the United States of America & the Confederate States of America o USA also known as- Union, North, or Yankees o Confederate States of America also known as- Confederacy, South, or Rebels -North wore blue; South wore gray -Washington, D.C, -North Capital; Richmond, VA- South Capital -Civil War goes by many names: o The War Between the States o The War for Southern Independence o The War of Northern Aggression o The War Between the Blue and the Gray o Freedom War States Involved -The Border States were states that had slaves but stayed in the Union: o Maryland o Delaware o Kentucky o Missouri -Lincoln wanted to keep these states in the Union since he thought their location and industries were vital to the North’s successes -The South consisted of the following states: o South Carolina o Mississippi o Florida o Alabama o Georgia o Louisiana o Texas o Virginia o Arkansas o Tennessee o North Carolina -The North consisted of all other existing states of time, including the newly formed West Virginia Causes of War 1) Disagreement over slavery 2) Disagreement over State’s rights vs. power of the Federal Government 3) Election of Lincoln-South felt they had no political power 4) Economic differences between the North & South 5) Firing on Fort Sumter Civil War Figures 1) Jefferson Davis a. President of the Confederacy b. Did not raise enough $ for the Confederacy, but did raise a formidable army c. Was imprisoned for treason for about a year after the war, but was eventually released 2) Clara Barton a. Worked during the Civil War to collect and distribute supplies b. Founder of the American Red Cross 3) Ulysses S. Grant a. Commander of the Union army b. Was known for his brutal fighting tactics; would do anything to win and achieve unconditional surrender (“The Butcher”) c. Later became 18th president 4) Abraham Lincoln a. Elected as 1st Republican President in 1860; began term in March 1861 b. Was president during the Civil War-his original goal was to preserve the Union c. Issued “The Emancipation Proclamation” which freed all slaves in rebellion states (not slaves in border states) and gave a moral purpose to the war (Jan 1, 1863) d. Wrote/ read “The Gettysburg Address” to commemorate loss at Gettysburg; also stated Union worth fighting for (Nov 1863) e. Re-elected in Nov. 1864; began term in March 1865 f. Lincoln believed in peace & forgiveness towards the South g. April 14, 1865- Lincoln was the first president to be assassinated; he was killed by John Wilkes Booth (Southern supporter) in Ford’s Theater; VP Andrew Johnson became president 5) Robert E. Lee a. Famous military family; went to West Point b. Was considered to be the best General of the day; Lincoln asked him to lead Union army, but Lee turned him down when VA seceded c. Proved to be a brilliant general- however, the lack of supplies, materials, and men lead to defeat d. After war, his plantation became Arlington National Cemetery; Lee became president of Washington College in Lexington, VA (today Washington & Lee University) 6) Frederick Douglass a. Born a slave, but was educated b. Meet with Lincoln; helped persuade him to issue “The Emancipation Proclamation” c. Campaigned for use of African American soldiers d. Continued to fight for equality and civil rights for African Americans after the war 7) David Farragut a. Life-long member of the Navy b. Fought for North c. Most famous naval commander of the era d. Had many naval triumphs; helped to capture the Mississippi River 8) George McClellan a. Union general at start of war; at battle of Antietam b. Fired by Lincoln for being too indecisive 9) William Tecumseh Sherman a. General for North b. Used total warfare- path of destruction through the South-destroyed farms, food, railroads, schools, buildings, etc. (Sherman’s March)- Civilians were also targeted with this strategy Key Battles 1) Fort Sumter a. Union controlled fort in port of Charleston, S.C. b. First shots of the war c. No one killed during shooting, but six killed during accidental explosion st 2) 1 Battle of Bull Run a. Stonewall Jackson received his nickname b. South won & believed they had won the war; many soldiers went home 3) Shiloh a. 25,000 casualties b. Showed how bloody the war would be c. Taught generals the importance of strategy- digging trenches, sending scouts, & building fortifications 4) Antietam a. Bloodiest single-day battle in American history (26,000 casualties) 5) Gettysburg a. Lee decided to press his advantage and invade North; also wanted supplies b. Lee did not have Stonewall Jackson- he died after the battle of Chancellorsville c. 3 day battle fought on July 1, 2, & 3, 1863 d. Turning point of the war- Lee never had enough men to invade North- was on defensive; lost men he could never replace e. Bloodiest Battle in American history- Union=23,000; Confederacy=28,000 6) Vicksburg a. City on the MS River-last holdout preventing Union from controlling river b. Battle ended on July 4, 1863 after a month-long siege c. Confederacy was cut into 2 7) Fighting in Virginia a. May 1864 to June 1865 b. Fighting in wilderness of Virginia c. High losses for both sides- South could not replace the men lost Strengths of the North 1) Large population due to immigration 2) 90% of the country’s industry and factories 3) More railroads Strengths of the South 1) Superior military leadership 2) Most of war fought in South- home field advantage 3) More of a reason to fight Andersonville o Located in Georgia; Union prisoners were kept in this camp o 12,000 died out of 45,000- no food, shelter, clean water lead to disease/death o Henry Wirz, camp commander, only person to be executed as a war criminal African Americans & the Military o Allowed to join Union army after the Emancipation Proclamation o Put in segregated units, had higher mortality rates, & paid less Surrender o April 9, 1865 o Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Court House in Virginia; the South had run out of men & supplies- Sherman’s March had wrecked complete havoc on South o Unconditional surrender- South had to give up completely Effects of War Political Change: 1) 13th Amendment- ended slavery in entire country; 14th Amendment- made former slaves citizens; 15th Amendment- gave African American Males the right to vote 2) Federal government- proven to be the most powerful gov’t; never again is secession attempted; income tax also adds to power of federal gov’t. Economic Change: 1) Total destruction of the South- economy ruined by very high inflation (money worthless); Sherman’s March destroyed physical landscape; much of the population killed; South’s economy takes decades to recover 2) The North’s economy grew and North became wealthy Technological Change: 1) Weapons become more deadly 2) New military strategies developed (trenches) Social Change 1) 4 million freed slaves 2) Terrible loss of life 3) Family life very disrupted 4) Many men were amputees/disabled Major Issues after War: 1) Integration of the 4 million newly freed slaves into society 2) Restoration of Southern states to the Union