The Hellenic Age of Ancient Greece
advertisement

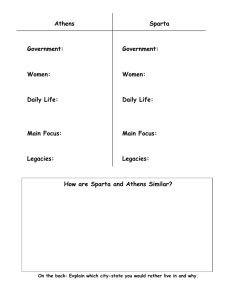
Name_____________________________ The Hellenic Age of Ancient Greece Guided Notes 1) The City-States a. The Greek Dark Ages lasted from ________________ to ________________ BC. b. The brief era of rebirth following the Dark Ages was known as the __________________ of the ____________________. c. Following the Dark Ages, the city-state or _____________ became the main focus of the ________________ of the Greeks. d. Name the various city-states and their governments. i. ____________________ & _____________________ ii. ____________________ & _____________________ iii. ____________________ & _____________________ iv. ____________________ & _____________________ v. ____________________ & _____________________ e. Cities were separated by ________________ and _________________ that kept the cities from unifying. f. Each city-state preferred to have their own _____________________. g. The _____________________ was the main gathering place, and the _____________________ was an open area for people to meet and assemble. h. City-states varied in ____________________. i. The polis was a community ___________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________. j. Who had the right to vote? Who didn’t? k. City states were extremely____________________________________________. l. Greek ______________________ were also established as city-states. m. The most notable Greek colony was that of ______________________________. n. What did the colonies do for the motherland? o. What was a tyrant in respect to Ancient Greece? How did the people feel about them? p. Tyrants were ________________________, ___________________________, citizens of their cities. q. Eventually the age of the tyrants ______________________________. 2) Sparta a. Sparta was the dominant city within the ______________________________. b. What was their real name_____________________________________. c. The Military i. The city-state of Sparta had a _______________________ culture. ii. They were the first in all of Greece to _____________________________ ___________________. iii. Spartan and Greek soldiers were called ___________________________. iv. The Spartans perfected what military formation? v. Soldiers were __________________________________. vi. vii. viii. ix. Soldiers served for how long? What age were Spartan soldiers given citizenship? The _______________________ was the training camp for all Spartans. What did the soldiers have to endure to become better soldiers? 1. _____________________________________. 2. _____________________________________. 3. _____________________________________. x. The _____________________________ was the arrangement of the men in battle. xi. The shields were meant to cover ________________ to _____________________. xii. _________________ were the primary weapons of the Spartan soldiers. xiii. What are the parts of a Spartan’s armor? 1. __________________ 2. __________________ 3. __________________ 4. __________________ 5. __________________ 6. __________________ 7. __________________ xiv. The ___________________ (their shield) was ______________ in diameter and weighed __________lbs. xv. Only the leaders and ___________________ had plumes. xvi. The Spartan armor was made from either _______________________ or _______________________. xvii. What were the two types of swords used by the Spartans? 1. _______________________ 2. _______________________ xviii. Sparta’s most memorable leader was _______________________. 1. He was famous for _____________________________. d. The City-State i. Sparta also had a ________________ and __________________ culture. 1. All ___________________ were given and ____________________. 2. Women and _____________________ enjoyed more freedom than most. 3. The military and culture of Sparta led to what is known as the _____________________________________. ii. The helots were _______________________ in ancient Sparta. iii. Occasionally the helots would ______________________ against their owners. iv. Once a year, Spartans ________________________________ war on the helots, so that they could kill suspected trouble makers. v. Along with the boys, Spartan girls attended school at the age of 7 to learn ______________________________, __________________________ and wrestling. vi. Women were also allowed to own ______________________ and _________________________. Spartan women owned more than ____________ of the property in Sparta. vii. Sparta was an ______________________________ in which a small group of people ruled. viii. Sparta was ruled by ________kings. ix. 5 ____________________ looked over the education of all Spartan citizens, and these men were _____________________ to office. x. Art and science really didn’t thrive in Sparta. 1. The _____________________________ was the only thing that they cared about. 2. Most Spartans believed that their kings descended from _______________________, the might Greek hero. 3) Athens a. The City-State i. The most famous city-state in Greece is/was ______________________. ii. It is the primary city-state in _____________________. iii. In the beginning Athens was ruled/ governed by ____________________. iv. The first man to gain sole control over Athens was __________________. And he was elected/ appointed by the citizens because of his ideas on ______________________. v. Around 510 BC, Athens throws out a wicked tyrant and appoints _______________________ to govern Athens. 1. He created a __________________ of 500 male citizens that overlooked all aspects of Athenian life. 2. He helped to create all of the foundations for Athenian democracy. vi. Athens eventually forms an alliance with surrounding city-states and it is known as the __________________________________, because of its headquarters on the island of __________________. vii. _____________________ was the commanding city-state of the Delian league. viii. Entering into this alliance had caused Athens to build an ______________________. ix. Eventually a man by the name of ____________________ comes to power in Athens. x. Athens ___________________ under his guidance. xi. This time period is known as the _________________________________ or Athens’ “__________________________.” xii. ____________________________ was the brain child of Pericles, and the first form of democracy in the world. xiii. He also created the practice of ostracism. What is this policy? xiv. Athens had established itself as the __________________ or central area of the Greek world. xv. Pericles commissioned great buildings such as the __________________________. xvi. The Parthenon was a temple to the goddess ______________________, and Athens was named after her. b. The Military i. Unlike the Spartans, Athens’ military power was on the _________________________. ii. Their navy was exceptionally trained and powerful, why was this? iii. What was the “crown jewel” of the Athenian navy? iv. The Athenian fleet never exceeded ____________________ triremes. v. What was the trireme’s purpose? vi. The ram of the trireme was made of solid ____________________. 4) War With Persia a. The Persians and the Greeks never really ________________ one another. b. The Greek colonies of ______________________ led a revolt against the Persians in 499 BC. i. Which Greek city-state aided in the revolt? c. The revolt left Darius (King of Persia) bitter and in 490 BC he __________________________. d. The Athenians put up a fight at the ________________________. i. The Athenians ______________________ the forces of Darius. e. f. After winning the battle, a man named _______________________ ran the 26 miles from Marathon to Athens. i. He promptly _____________________ after shouting “Nike!” or “________________” after running into the streets of Athens. g. Darius never forgave the Ionians or the ____________________ for what they did at Marathon. h. Darius’ son ____________________ vowed ________________ against the Athenians what happened at Marathon. i. The land defense of Greece was led by _______________________ and Athens built their _____________________ due to the origins of _________________________. j. Xerxes force of _______________________ and brought thousands of _________________ with him. k. The first skirmish of the war was at _________________________________. l. ________________ Spartans led _____________________ Greek soldiers and both armies were led by King ______________________. m. King Leonidas’ body wasn’t returned to Greece for _______________ years. n. The battle of Salamis was what kind of battle? o. p. q. r. The Greeks were outnumbered ____ to ______. The Athenian navy _________________ the navy of the Persians. The final battle was at the patch of earth known as ______________________. This battle was the largest ___________________________ of the Greeks up until this point. s. Send Xerxes packing, after a massive _________________________. t. The war’s significance was that it _____________________________________ _________________________________________________________________. u. Gave all the Greeks a sense of _________________________________. 5) The Peloponnesian War a. Following the defeat of Persia, the Greeks ____________________________ with themselves. b. The two largest instigators were ___________________ and ________________________. c. Sparta feared the power of the growing _____________________________. d. Both nations thought they could win. i. The Athenians remained in a _____________________ position. ii. They relied on their allies to bring them _____________________. iii. Sparta wanted to fight _______________________________. e. Bad luck strikes Athens. i. The plague hits Athens and ________ of __________ people died. f. Pericles ____________________ following the outbreak of the plague. i. Sparta eventually ______________ the Athenians into surrender. ii. Sparta ___________ he city of Athens. iii. For half a century, _________________, ______________, _____________________ fought over control of Greece.