Electric Motor
advertisement

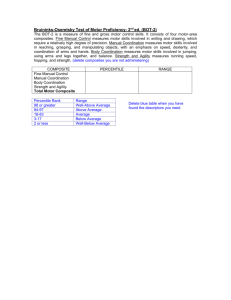
Yousif 1 George Yousif Jared Grogan ENG 3060 10 June 2009 Mechanism Description: The Electric Motor Civilization as we know it would seize to exist without a simple yet very important invention; that being the electric motor. This description paper is to help people understand more about the electric motor and its operation. Throughout this description process it will start to become evident on how and why the electric motor is so important to the culture we live in today. The electric motor transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy, which in turn makes motion possible (Electric Motor). To better understand electric motors, one should first understand the basics of an electric motor’s operation. This operation involves understanding the magnetic field and how magnets are used while also learning how the seven parts of the motor incorporate the principle of electromagnetism. You can create an electromagnet by running an electric current through a wire which in turn will create a magnetic field. An electromagnet may only be a temporary magnet but it has the same magnetic properties as a permanent magnet. Any type of magnet will create a magnetic field and this magnetic field will contain two ends or polls, one North and one South. The fundamental law of magnets states that Opposites attract and likes repels and the same holds true with an electromagnet (Brain, Marshall). A simple electromagnet can be created by the use of a power or voltage source and a piece of wire. The magnetic field created will be stronger than the magnetic field of the earth; this can be seen by placing a compass near the newly created magnetic field and noticing the direction change. Yousif 2 As current flows through the wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. The magnetic field itself is invisible, but the magnetic field strength can be measured through the use of special equipment. The magnetic field weakens the further you move away from the wire and the fields direction depends on the direction the current if flowing. Since the magnetic field is always circular and perpendicular to the wire, the magnetic field can be increased simply by creating a coil of wire (Electric Motor and Generators). An electric motor depends upon magnetism to function, to be more specific, electromagnetism. By continuously changing the direction of the electromagnetic field in a motor, we take advantage of the basic magnet principle that, “opposites attract and likes repel” (Brain, Marshall). This allows an electric motor to rotate. In order to continuously change the direction of the electromagnetic field in a motor, we will need to continuously change the direction of the electrical current to the electromagnet. This can easily be done just by constructing the motor in a certain way. Now moving on to the parts of a very simple DC electric motor (see figure 1). The motor is made up of seven main parts which include the armature or rotor, commutator, brushes, coil, axle, field magnet and a DC power source (Brain, Marshall). An electric motor operates in the following manner. Electric current is supplied from the power source and it travels through wire to the brushes which are flexible pieces of metal that allow for rotary contact with the commutators. The commutators are metal contacts that connect to the electromagnet coil which is wrapped around the armature all riding on the motors axel. Yousif 3 Figure 1: Computer generated image of an electric motor. The armature will rotate in the clockwise direction because it is being pulled and pushed by the field magnet (opposites attract & likes repel). This is when the direction of the electric current is changing due to the switching of the commutators. Now the magnetic field is quickly flipped in the opposite direction. The armature will continue to rotate in the clockwise direction because it is being pulled and pushed by the field magnet. In order to change the speed of the motor, the strength of the magnetic field will need to change. This can be accomplished by changing the current or voltage being supplied by the power source to the coil. The motor will continue to rotate as long as electricity is flowing. The operational principle of an electric motor is simple to understand as it all revolves around magnetism. They are an integral part of modern civilization and are often taken for granted. They surround us in our homes, running our wash machine, cool our houses and let us watch our favorite DVDs. They allow the average person to ride the elevator to the top floor, pump water for you to drink and are used to start you gas powered car. In the near future you will be driving around town in an electric powered vehicle that would reduce our dependencies on fossil fuels, which would help keep from polluting the environment as we all need to be good stewards of the earth. Yousif 4 Works Citied Brain, Marshall. "How Electromagnets Work." 01 April 2000. HowStuffWorks.com. 10 June 2009. <http://science.howstuffworks.com/electromagnet.htm> “Electric Motor.” 10 June 2009. Wikipedia.org 10 June 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_motor> “Electric Motor and Generators.” 18 February 2009. University of South Wales 10 June 2009. <http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/motdc.html#c1> “Figure 1: Electric Motor.” 18 October 2008. Photo. Wikipedia.org. 08 June 2009. <http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Electric_motor_cycle_3.png>