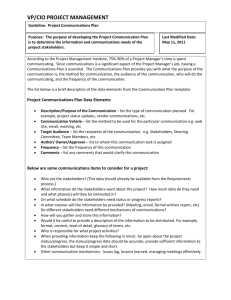
In-Class Participation Grading Scale
advertisement
5600 City Avenue Philadelphia, PA 191311395 Management Support Concepts & Technologies (MIS 2571) Draft Syllabus ‡ Instructor Name: Office Location: Tel. No.: Fax No.: Email Address: Homepage: Class Meetings: Starting Date: Office Hours: Rubén A. Mendoza Mandeville Hall 378 (610) 660-1639 (610) 660-1229 RMendoza@sju.edu http://www.sju.edu/~rmendoza/ Tuesdays & Thursdays, 10:00-11:15am August 26th, 2003 Tuesdays & Thursdays, 1:00pm to 4:00pm. Other times by appointment COURSE DESCRIPTION The course introduces students to Information Technologies (ITs), methods, and services in a decision-support context. The course emphasis is on understanding the impact of all technologies (older, current, and emerging) on organizational activities and the pursuit of competitive advantage. The course is not a technical course, but it is about technologies, and the primary objective is the development of a technology-literate, technically-savvy manager. The course will cover technologies used by managers to generate, collect, analyze, and disseminate information and to help them make decisions based on that information. The impact of these technologies on business processes, the structure of organizations, and their relationships with business partners will also be discussed. This study will be grounded on the impact of these technologies on a firm’s data and communications architecture, development and deployment activities, and technology and end-user support processes. These objectives will be accomplished through the use of lectures, relevant readings from all available sources, and self-guided student learning and exploration. Students will learn to research established and emerging technologies, summarize their findings, and present them to the class in a context and manner appropriate for making business decisions regarding the use of those technologies. COURSE GRADING POLICY Final course grade will be assigned based on the following scale: Group Assignments Three (3) assignments Details will be announced in class Peer Evaluation In-group individual evaluations Details will be announced in class Individual Assignment 60% 15% 10% Case Study write-up Details will be announced in class Individual Participation TOTAL 15% 100% In-Class Participation Grading Scale * Student contributions should be Original Relevant Timely Thoughtful Appropriately brief Student contributions, as defined above, will be graded as follows: 15 pts. - Regular contributions 10 pts. - Frequent contributions 7 pts. - Occasional contributions 4 pts. - Rare contributions 1 pt. - No contributions made 0 pts. - Disruptive classroom, computing, telephone behaviors * In-between scores at instructor’s discretion TEXTBOOK(S) Required: End-User Information Systems, 2nd Edition. E.A. Regan and B.N. O’Connor. Prentice Hall. ISBN: 0-13-018264-8 Supplemental Readings as listed in the syllabus and/or announced in class. HONOR CODE POLICIES Students are expected to adhere to University and Haub Business School rules and guidelines for student behavior. COURSE SCHEDULE ‡ Date Topic(s) Aug 26 Course Introduction and Overview Aug 28 Sep 2 Life in the Networked Organization Sep 4 Sep 9 Innovation and Strategic Planning Sep 11 Assessing the Value of Information Technology – I Sep 16 Assessing the Value of Information Technology - II Sep 18 Productivity Tools for Individuals Sep 23 Work Group Computing Readings/Activities Recklies, D. (2001) “Porter’s Five Forces,” TheManager.org (http://www.themanager.org/Models/p5f.htm) Recklies, D. (2001) “Beyond Porter,” TheManager.org (http://www.themanager.org/Strategy/BeyondPorter.htm) The Value Chain (http://www.themanager.org/Models/ValueChain.htm) Chapter 1 (Light review) Cairncross, F. (1997) “Trendspotters,” The Death of Distance website (http://www.deathofdistance.com/trend.html) Chapter 2 (Light review) Chapter 13.1-13.5 The Alliance Strategic Planning FAQ (Sections 1-5) (http://www.allianceonline.org/) Chapter 9 Brynjolfsson, E. 1993 "The Productivity Paradox of Information Technology," Communications of the ACM (36:12) McCune, J. (1998) “The Productivity Paradox,” Management Review 87 Knowledge at Wharton (2002) “Back to the Basics: Accounting for IT in Business Performance” (http://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/microsoft/070302.html) Violino, B. (1998) “ROI in the Real World,” InformationWeek (679:60) Varon, E. (2003) “R.O.Iowa,” CIO.com Case Files (http://www.cio.com/archive/060103/iowa.html) Chapter 3.4 Gaskin, J. (April, 2003) “Inside Office Productivity Suites” (http://www.nwfusion.com/) Group Assignment #1 Announced (Office Productivity Tool) Chapter 4 IBM Lotus Domino is # 1 at Hertz (June 2003) (http://www3.ibm.com/software/swnews/swnews.nsf/np/jmae5mzn44) Sep 25 Knowledge Management Sep 30 Knowledge Management Group Assignment #2 Announced (Group Productivity Tool) Chapter 5 PricewaterhouseCoopers, LLP Profile (1999) American Productivity & Quality Center website (http://apqc.org/portal/apqc/site/content?docid=102755) Developing Rewards and Recognition for Knowledge-sharing (2001) American Productivity & Quality Center (http://apqc.org/portal/apqc/site/content?docid=106982) Hildebrand, C. (1999) “Does KM = IT?” CIO.com (http://www.cio.com/archive/enterprise/091599_ic.html) Oct 2 Data Warehousing Oct 7 Data Warehousing Santosus, M. (June, 2003) “Below the Surface,” CIO.com (http://www.cio.com/research/knowledge/edit/k060503_tacit.html) Santosus, M. (May, 2003) “P&G’s Streamlined Design,” CIO.com (http://www.cio.com/research/knowledge/edit/k050803_proctor.html) Chaudhuri, S. & Dayal, U. (1997) “An Overview of Data Warehousing and OLAP Technology” ACM SIGMOD Record (56:1, March, pp. 65-74) (ftp://ftp.research.microsoft.com/users/surajitc/sigrecord.pdf) Greenfield, L. (February, 2002) “The Case for Data Warehousing” The Data Warehousing Information Center website (http://www.dwinfocenter.org/casefor.html) Greenfield, L. (December, 2002) “The Case Against Data Warehousing,” The Data Warehousing Information Center website (http://www.dwinfocenter.org/against.html) Raizada, S. “Eleven Steps to Success in Data Warehousing,” Syntel website (http://www.syntelinc.com/syntel/english/00000290/Syntel_dw_11steps.pdf) Peterson, T. (2003) “Data Scrubbing,” ComputerWorld, February 10 (http://www.computerworld.com/databasetopics/data/story/0,10801,78230,00.html?nas=DM-78230) Oct 9 Student Presentations Oct 14 Fall Semester Break - No Class Oct 16 Data Warehousing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Paul, L. (1997) “Anatomy of a Failure,” CIO.com (http://www.cio.com/archive/enterprise/111597_data.html) Villano, M. (1999) “Data Gets a Makeover,” CIO.com (http://www.cio.com/archive/100199/lore.html) Group Assignment #1 Due Deck, S. (2001) CRM?” CIO.com May 1 (http://www.cio.com/research/crm/edit/crmabc.html) Tuck, L. (2003) Must-Have CRM Application,” CRMDaily.com June 9 (http://www.crmdaily.com/perl/story/21685.html) Morphy, E. (2002) “What’s in a ‘CRM” Suite?” CRMDaily.com, May 17 (http://www.crmdaily.com/perl/story/17800.html) Costello, D. (2001) “What is “The “Consolidating CRM Resources,” DestinationCRM.com November 26 (http://www.destinationcrm.com/articles/default.asp?ArticleID=1855) Surmacz, J. (2003) Second Look at CRM,” CIO.com, June 11 (http://www2.cio.com/metrics/2003/metric558.html) Bass, A. (2003) “CIGNA’s Self-Inflicted Wounds,” CIO.com March 15 (http://www.cio.com/archive/031503/cigna.html) Morgen, S.D. (2003) “A “People Power: Simple Factors for CRM Success,” IntelligentCRM.com Oct 21 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) & Enterprise Application (http://www.intelligentcrm.com/feature/2003/01/0301feat1_1.shtml) Koch, C. (2002) “The ABCs of ERP,” CIO.com ERP Research Center (http://www.cio.com/research/erp/edit/erpbasics.html) Slater, D. (1999) “What is ERP?” CIO.com May 15 Integration (EAI) (http://www.cio.com/archive/enterprise/051599_curve.html) Greenemeier, L. (2001) “ERP: It’s Not Just for Big Companies,” InformationWeek.com, October 29 (http://www.informationweek.com/story/IWK20011025S0010) Taylor, C. (2003) “Eat… Or Be Eaten,” TIME.com, Jun 17 (http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1101030623-458757,00.html) Oct 23 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) & Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) Deck, S. (2001) “How Indian Got Its Vroom Back,” CIO.com, June 15 (http://www.cio.com/archive/061501/indian.html) Koch, C. (2002) “Hershey’s Bittersweet Lesson,” CIO.com, Nov 15 (http://www.cio.com/archive/111502/tl_hershey.html) Worthen, B. (2002) [Optional Reading] “Nestlé’s ERP Odyssey,” CIO.com, May 15 (http://www.cio.com/archive/051502/nestle.html) Samtani, G. & Sadwhani, D. (2001) “EAI and Web Services: Easier Enterprise Application Integration?” WebServicesArchitect.com, October 17 (http://www.webservicesarchitect.com/content/articles/samtani01.asp) Oct 28 Support and Help Desk Management – I Group Assignment #3 Announced (KM, DW, DSS, CRM, ERP, or EAI Tool) Chapter 7 (Light review) Connor, D. (1999) “Dell Adopts Online Support; Compaq Soon to Follow,” Network World (16:35) (http://www.nwfusion.com/news/1999/0830support.html) Holt, S. (1999) “Help Desks Must Help Themselves,” InfoWorld, January 25 Build-A-Bear Workshop Case Study (2001) Applied Innovation Management website (http://www.innovate.com/corporate/success/buildabear/buildabear.pdf) Oct 30 Support and Help Desk Management – II Heineken Case Study (2002) Applied Innovation Management website (http://www.innovate.com/corporate/success/heineken/heineken.pdf) King, J. (1999) “Users Discover Dark Side of Help Desk Outsourcing,” ComputerWorld, January 25 (http://www.computerworld.com/news/1999/story/0,11280,33696,00.html) Overby, S. (2003) “Inside Outsourcing in India,” CIO.com, June 1 (http://www.cio.com/archive/060103/outsourcing.html) Nov 4 Guest Speakers: David Y. Sharp, Assistant Vice President, Global Operations, ACE INA Holdings, Inc. Donald Hanson, H.L. Yoh Company, LLC Nov 6 Project consultancy Nov 11 Student Presentations Nov 13 Management Issues Nov 18 Human Factors: Workplace Design Organizational Change Nov 20 Business Process and Job Redesign In-class group work Group Assignment #2 Due Intellectual Property in Everyday Life – A Virtual Tour World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) website (http://www.wipo.int/athome/index.shtml) HBS Case “Network Associates: Securing the Internet” (9-799-087) Individual Assignment Due Onepage case analysis. Details will be announced in class Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.4 Chapter 11 Chapter 12.1-12.5 Nov 25 Project Management: Foundations and Overview Nov 27 Thanksgiving Break - No Class Dec 2 Student Presentations Dec 4 ‡ Hammer, M. (1990) “Reengineering Work: Don’t Automate, Obliterate,” Business Review, July-August (pp. 104-112) Readings will be announced in class Group Assignment #3 Due Contents and dates subject to change. Guest Speakers may be featured during the term, depending on availability and appropriateness to the topics being discussed. Harvard