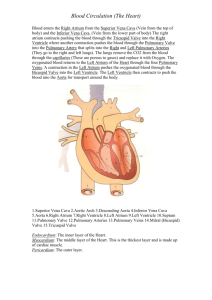
Sheep Heart Dissection
advertisement

Biology 30S Name Pig Heart Dissection Objective Using a pork heart, students will observe the major chambers, valves, and vessels of the heart and be able to describe the circulation of blood through the heart to the lungs and back and out to the rest of the body. (The pig heart is used because it is very similar to the human heart in structure, size, & function.) Review the diagram below and familiarize yourself with all of the structures and the blood path through the heart. Head and neck Trunk and legs Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve 1 Materials: Preserved pork heart. Dissection scissors (sharp tip) Pins Dissecting Apron Safety glasses Dissection tray probe ruler laminated flags/labels Part 1: Procedure – External Anatomy Most heart diagrams show the left atrium and ventricle on the right side of the diagram. Imagine the heart in the body of a person facing you. The left side of their heart is on their left, but since you are facing them, it is on your right. As you progress through the dissection, write the bolded labels onto the paper labels. Near the end of the external observation and again near the end of the internal dissection, you will be asked to place these labels on your heart. Your groups’ ability to do this correctly both times will constitute 10 marks of your lab. 1. Place both hearts in a dissecting pan & rinse off the excess blood with tap water. Pat the heart dry. (This step may not be necessary) 2. Examine the heart and locate the thin membrane or pericardium that still covers it. The pericardium or pericardial sac, is a double-layered closed sac that surrounds the heart and anchors it. The pericardium is a sac continuous to where the vessels enter or leave the heart. 3. Locate the lower two chambers (ventricles) of the heart. 4. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex. 5. Place the heart in the dissecting pan so that the front or ventral side is towards you (The major blood vessels are on the top and the apex is down). The front of the heart is recognized by a groove that extends from the right side of the broad end of the heart diagonally to a point above & to your left of the apex. 6. The heart is now in the pan, in the position it would be in a body as you were facing that body. BE SURE YOUR TEACHERS HAS CONFIRMED THE ORIENTATION (VENTRAL/FRONT) OF YOUR HEART BEFORE LABELING. 7. Label the following on the exterior of the heart: a. Left atrium - upper chamber to your right b. Left ventricle - lower chamber to your right c. Right atrium - upper chamber to your left d. Right ventricle - lower chamber to your left 2 8. While the heart is still in this position in the dissecting pan, locate the following blood vessels at the broad end (superior aspect/top) of the heart and label them: a. Coronary artery - this blood vessel lies in the groove on the front of the heart & it branches over the front & the back side of the heart to supply fresh blood with oxygen & nutrients to the heart muscle itself. b. Pulmonary artery - this blood vessel branches & carries blood to the lungs to receive oxygen & can be found curving out of the right ventricle (upper chamber to your left) c. Aorta - major vessel located near the right atria & just behind the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. Locate the curved part of this vessel known as the aortic arch. Branching from the aortic arch is a large artery that supplies blood to the upper body. d. Pulmonary veins - these vessels return oxygenated blood from the right & left lungs to the left atrium (upper chamber on your right) e. Inferior & Superior Vena Cava - these two blood vessels are located on your left of the heart and connect to the right atrium (upper chamber on your left). Deoxygenated blood enters the body through these vessels into the right receiving chamber. Use your probe to feel down into the right atrium. These vessels do not contain valves to control blood flow. Place your labels on the external anatomy of the heart. Let the teacher know this is done so it can be evaluated. DO NOT START DISSECTING THE UNLABELED HEART UNTIL THIS EVALUATION IS DONE. Part 2: Procedure – Internal Anatomy 1. Insert your dissecting scissors into the superior vena cava and make an incision down through the wall of the right atrium and ventricle, as shown by the dotted line in the external heart picture. Pull the two sides apart and look for three flaps of membrane. These membranes form the tricuspid valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle. The membranes are connected to flaps of muscle called the papillary muscles by tendons called the chordae tendinae or "heartstrings." This valve allows blood to enter the ventricle from the atrium, but prevents backflow from the ventricle into the atrium. Gently pull on the chordae tendinae to see how they move the valves. 2. Insert your probe into the pulmonary artery and see it come through to the right ventricle (recall blood direction is right ventricle to the pulmonary artery). Make an incision down through this artery and look inside it for three small membranous pocket-like structures. These form the pulmonary semilunar valve which prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle. 3 3. Insert your dissecting scissors into the left atrium at the base of the aorta and make an incision down through the wall of the left atrium and ventricle, as shown by the dotted line in the external heart picture. Locate the mitral valve (or bicuspid valve) between the left atrium and ventricle. Is this valve also controlled by papillary muscles connected to tendons?______ 4. Insert a probe into the aorta and observe where it connects to the left ventricle. Make an incision up through the aorta and examine the inside carefully for three small membranous pocketlike structures. These form the aortic semilunar valve which prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle. Place your labels on the internal anatomy of the heart. Let the teacher know this is done so it can be evaluated. Part 3 – Blood Flow Now consider all the parts you've found and how the blood flows through them. In the list of structures below, correctly colour each arrow (blue for deoxygenated blood and red for oxygenated blood) to indicate the type of blood flowing between the structures: Blood from the tissues right atrium tricuspid valve semilunar valve left atrium superior and inferior vena cava pulmonary artery right ventricle pulmonary lungs bicuspid (mitral) valve aortic semilunar valve aorta pulmonary veins left ventricle body tissue. 4 Part 4 – Diagrams Label the following diagrams to test your knowledge of heart anatomy. EXTERNAL ANATOMY 5 INTERNAL ANATOMY – RIGHT SIDE OF THE HEART 6 INTERNAL ANATOMY – LEFT SIDE OF HEART http://www.hometrainingtools.com/misc/Heart4Blank.pdf Use as alternative to wet lab http://www.gwc.maricopa.edu/class/bio202/heart/anthrt.htm 7 Pork Heart Dissection Marking Rubric External Labels Internal Labels Work Ethic Questions Diagrams All structures successfully labelled (8 marks) One error in labels (7 marks) Two errors in labels (6 marks) More than two errors in labels (5) All structures successfully labelled (8 marks) One error in labels (7 marks) Two errors in labels (6 marks) More than two errors in labels (5) Treats specimen respectfully, makes careful cuts, take time to study structures, strong effort in attending to labels. Clean up is thorough, utensils washed and replaced as expected. Uses the right tool for the job (10 marks) Treats specimen with respect, makes careful cuts, takes time to study structures, some recklessness either in comments or treatment of specimen. Thorough clean-up, utensils washed and replaced as expected. Uses the right tool for the job (8 marks) Treats specimen with respect, cuts require greater care and attention to detail is required. No inappropriate comments. Clean up may not have been thorough (utensils washed but not replaced or replaced unwashed). May have used a tool inappropriately but not disrespectfully (6 marks) Specimen needs to be treated more respectfully. Recklessness noted in dissection. Inattention to detail OR inattention to clean up and inattention to proper tool usage. (4 marks) Specimen treated with disrespect. Recklessness in dissection. Inattention to detail & clean up. (0 marks) All questions completed correctly. (4 marks) One or two errors in questions. (3 marks) One or two questions not attempted. (2 marks) Questions are answered poorly – require more complete sentences. (1 marks) Too many omissions or not done. (0 marks) Diagrams are completed well, spelling is correct. (5 marks) A diagram or more than 2 labels missing. Spelling errors. (3 marks) Not completed (0 marks) TOTAL /35 8 Human Anatomy Terms The following terms are those which are used to identify the location of parts of the human body in medicine and academic study. These terms are often used to describe a specific portion of a structure or to compare the locations of two different structures. "The hand is distal to the forearm" or "the medial portion of the frontal bone contains the frontal sinus" are examples of this. This list is organized by keeping similar pairs or groups of terms together instead of by alphabetical order so that you will find them easier to learn and remember. Superior - toward or in reference to the head Inferior – below the head in perspective Anterior - the front of the body or front of body part (as in the the heart is anterior to the spinal column) Posterior - the back of the body or body part or in reference to behind a structure (our kidneys are posterior to the intestines) Medial - toward the midline that divides left and right. Our heart lies along the medial, tilted to the left lateral slightly Lateral - to the side away from the midline Ventral – toward the bottom, toward the belly (a dogs belly is ventral, our intestines are ventral to our kidneys, which lie to the back) Proximal - closer to the torso or in reference to a limb attachment (the femor is proximal to the hip; the rotator cuff is proximal to the clavical) Distal - farther away from the torso (the fingers and toes are distal compared to the thigh which is proximal) Caudal – towards the tail (mostly in terms of animal dissections as in rats, dogs, cats etc.) or towards the feet in bipeds. Palmer – towards the palms Plantar – towards the sole of the foot 9 Anatomical position - standing erect, facing the observer, arms are at the sides, palms toward you. The diagrams below shows the planes of symmetry (or asymmetry) 10 Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve 11 Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve 12 Biology 30S Name Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve 13 Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Rt Ventricle Bicuspid valve Pulmonary Artery Left Ventricle Pulmonary valve Pulmonary Vein Rt Atrium Aortic valve Sup Vena Cava Left Atrium Septum Inf Vena Cava Tricuspid valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve 14 Aortic valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Rt Ventricle Bicuspid valve Pulmonary Artery Left Ventricle Pulmonary valve Pulmonary Vein Rt Atrium Aortic valve Sup Vena Cava Left Atrium Septum Inf Vena Cava Tricuspid valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve Cut out the following exterior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Sup Vena Cava Left Ventricle Apex Pulmonary Artery Inf Vena Cava Rt Atrium Coronary Artery Pulmonary Vein Rt Ventricle Left Atrium Cut out the following interior anatomy flags/labels from the laminated sheet: Aorta Inf Vena Cava Left Atrium Aortic valve Pulmonary Artery Rt Ventricle Tricuspid valve Septum Pulmonary Vein Left Ventricle Bicuspid valve Sup Vena Cava Rt Atrium Pulmonary valve 15