Rise and Fall of the Greek Empire.doc
advertisement

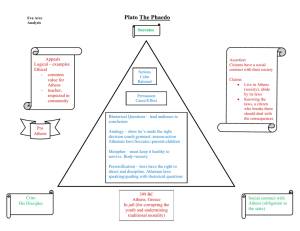
XIV) The Rise and Fall of the Greek Empire A) It starts with a war – In one corner the Persians 1) they were considered the strongest military power in the world at the time 2) they had already conquered much of Asia Minor (Turkey) and the Middle East and was slowly moving into Greece 3) they were ruled by a fierce king – Darius I 4) they had already conquered the former enemies of the Greeks – the Ionians B) In the other corner – the Greeks 1) they were considered the up and coming military power in the world 2) They were starting to conquer areas outside of Greece 3) They were ruled (for the most part anyway) by a Greek assembly 4) They had agreed to help the Ionians re-conquer their land C) The 2 sides meet – the Persian Wars 1) When Darius heard the Greeks were trying to support the Ionians he ordered his forces to attack Greece 2) At first (in 490 BCE) they tried to attack by way of the Aegean Sea but are destroyed by a storm 3) Then they attacked the city of Marathon (about 25 miles north of Athens) but the better armored Athenians defeated the larger Persian army 4) How did Athens find out that the Greek army had defeated the Persians? 1 5) The Persians, frustrated, started loading up their ships to quickly attack Athens directly by sea but it was too late 6) The army at Marathon (thanks to Pheidippides) got back to Athens and defended the city D) The Persians strike back 1) In 486 BCE Darius’ son Xerses invades Greece from the north with over 150,000 troops and 700 ships 2) this time Sparta joined Athens in fighting the Persians in the Persian War (other city-states of Greece chose to remain neutral or decided to join the Persian side) 3) the Greeks were told by the fortune tellers/Oracles at Delphi that they would be safe behind “a wooden wall” 4) the Athenian general Themistocles thought that this meant that a fleet of wooden ships was to go up against the Persians 5) One problem – ships take time to build 6) So they needed a distraction – so began the battle of Thermopylae a) the 300 Spartans led by one of their kings Leonidas, would hold off the 9,000 attacking Persians at the mountain pass of Thermopolyae while the navy was being built up b) it worked at first until a Greek traitor went to the other side and told the Persians how to outflank or outmaneuver the Greeks 2 c) the Spartans even though they realized that they would be massacred fought the Persians to the last man d) thanks to the heroic Spartans, the Athenians had enough time to organize their 200 ship navy e) Xerses and his Persians soon conquered Athens but when the Persians tried to sail out of Athens they found the Greek navy waiting for them at the port of Salamis (Xerses lost 1/3 of his ships during this battle) f) The Persian navy was defeated (thus fulfilling the oracle’s fortune telling) while the Spartans defeated the rest of the Persian army in 479 BCE at Platea E) After the Persian Wars, enter the Golden Age of Athens! (480 to 430 BCE) 1) After the Persians were defeated the Athenian ruler/general Pericles wanted to rebuild by: a) Goal 1: strengthening the democracy 1) who rules in a democracy again? 2) He made sure everyone be they rich or poor had a shot at a government job with a good salary 3) He let the entire male population vote on laws (and who to kick out of the polis for ten years) instead of just the elected representatives (this is called a direct democracy) b) Goal 2:strengthening the Greek Empire 1) he built up the Athenian navy to make it the biggest navy in the area 3 2) as a result he expanded the number of areas Athens traded with c) Goal 3: making Athens the best Greek citystate of them all 1) he bought gold, ivory, and marble for his construction projects 2) his most famous project : the Parthenon a) it was 23,000 square feet in area and took 15 years to complete b) it was built in honor of the goddess Athena – why her? 1) contained a statue of her built by the famous sculptor Phidias 2) the statue was made of gold and ivory and was over 38 ft tall! 2)He built new homes – see pg. 122-123 in the Ancient World Book a) Consisted of two main rooms with smaller rooms around it b) One main room was the dining room (called the andron) where men sat on reclining couches (women were permitted to join the men only if there were no other men around) c) Meanwhile the women (most of the time) remained in the other main room, the wool room (also known as the gynaeceum), where they spun and wove cloth d) Outside all the rooms was the courtyard where the family’s goats and chickens were kept 3)The difference between men and women in the “Golden Age” 4 a) The men 1)In the morning they worked as a) Farmers b) Artisans c) Merchants d) Pottery Makers 2)In the afternoons they attended assembly meetings and exercised in the gymnasiums 3) At night they went to the symposium a) It was a type of bar where men drank and talked b) They were entertained by dancers, singers, acrobats, and magicians c) No WOMEN were allowed! 4)Those men who were slaves (1/3 of the population) a) Did the mining b) Were servants c) Were teachers b) The women –see pg. 146 in the Ancient World book 1)In the home a) Cooked (or made sure the servants were cooking) b) Wove cloth c) Was in charge of the house’s finances or budget 2)Outside of the home a) Learned how to read and write (secretly) 5 b) Were restricted (by law) in the amount of money they could spend and could not own property c) could participate in a few religious ceremonies d) had to be chaperoned everywhere by the males of the family e) Ladies, think this is bad? – check out the laws about marriage and divorce on pg. 146 and 147 F) The Good Times come to an end – the Peloponnesian Wars 1) The Athenians were still worried about the Persians returning 2) They wanted to form an alliance with all the other Greek cities called the Delian League 3) 140 of the other Greek city-states sign up but the Spartans refused to join 4) Eventually the Delian League were successful at getting the remaining Persians out of the area 5)With the Persians out, the Athenians (more specifically their leader Pericles became too greedy) a) All of the other city-states treasuries were used to decorate the Parthenon in Athens b) They stated that all criminal cases must be tried in Athens c) All city-states must use Athenian currency d) Athens started to slowly take over all the other cities with their armies 6 5) Eventually all the other Greek cities (led by Sparta and their allies the Peloponnesian League) rebelled against Athens and so began the Peloponnesian War a) Lasted from 431to 401 BCE b) Athens at the had the best navy in all of Greece c) The superior Athenian navy didn’t help though because Sparta wasn’t located near the coast and its excellent army was able to attack the land around Athens d) Still needing some sort of navy, Sparta made a deal with the Persians to use what remained of the Persian navy e) Scared, Athens decided to evacuate its people and hide within the city walls f) Unfortunately inside the walls, Athens was hit by a deadly plague that wiped out a 1/3 of their population (including their leader Pericles) – see pg. 123 in your textbook - Academic g) Things got worse when Athens failed to defeat one of Sparta’s allies, Syracuse, in 413 BCE h) At this point most of Athens’ allies switched sides and helped the Spartan side defeat Athens once and for all in 404 BCE 6) Effects of the civil war in Greece a) Lots of dead people (due to disease or war) b) Towns/fields in ruin c) Lots of unemployment (even the soldiers had to look for work) d) No more government for the people – now they had a government where people were only concerned by how much money they could get for themselves 7) Greece was now weak and waiting for someone to conquer them 7