Ancient India

Ancient India
The student will explain how geography of the Indian Subcontinent contributed to the movement of people and ideas.
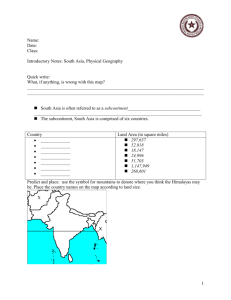
Directions : Students should read in their text pg 44-5 and complete the chart below and identify each geographic feature on the provided map of the Indian subcontinent.
Geography
Geographic Feature What it is How did it affect India?
Subcontinent
Himalaya Mountains
Thar Desert
Indus River
Ganges River
Indo-Gangetic Plain
Deccan Plateau monsoons
GPS-SSWH2e
Ancient India
The student will explain how geography of the Indian Subcontinent contributed to the movement of people and ideas.
Geography
Geographic Feature What it is
Subcontinent A large area of land that is part of a continent but is also separated from the continent. India’s subcontinent includes the modern countries of
India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal,
Sri Lanka, and Bhutan
Himalaya Mountains The tallest mountains in the world is located to the north of India
Thar Desert
Indus River
Dry area that occupies the lower Indus valley
River that flows southwest from the
Himalayas to the Arabian sea
How did it affect India?
India is separated from the rest of the continent with large mountain range in the north and Indian Ocean on either side
Protects the Indus valley from invasion
Farming was made possible only in the areas directly watered by the Indus
Important link from the interior of the subcontinent to the sea. Carry water for irrigation and silt to produce rich land for agriculture
Ganges River River that drops from the Himalayas and flows eastward across northern
India. Joins Brahmaputra River as it flows into the Bay of Bengal
Indo-Gangetic Plain Large area that stretches 1,700 miles across northern India
Deccan Plateau Southern region of India where the peninsula thrust into the Indian Ocean monsoons has low mountains called the Eastern and Western Ghats that prevent moisture from reaching Plateau so it is very dry.
A wind that changes direction. Can also mean heavy rain
Fertile area for development of civilization
A narrow border of lush, tropical land lies along the southern coast leading into the plateau.
Dominates India’s climate
GPS-SSWH2e
Ancient India
The student will explain how geography of the Indian Subcontinent contributed to the movement of people and ideas.
Geography
Geographic Feature What it is
Subcontinent A large area of land that is part of a continent but is also separated from the continent. India’s subcontinent includes the modern countries of
India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal,
Sri Lanka, and Bhutan
Himalaya Mountains The tallest mountains in the world is located to the north of India
Thar Desert
Indus River
Ganges River
Dry area that occupies the lower Indus valley
River that flows southwest from the
Himalayas to the Arabian sea
River that drops from the Himalayas and flows eastward across northern
India. Joins Brahmaputra River as it flows into the Bay of Bengal
Indo-Gangetic Plain Large area that stretches 1,700 miles across northern India
How did it affect India?
Deccan Plateau monsoons
Southern region of India where the peninsula thrust into the Indian Ocean has low mountains called the Eastern and Western Ghats that prevent moisture from reaching Plateau so it is very dry.
A wind that changes direction. Can also mean heavy rain
GPS-SSWH2e
Ancient India
GPS-SSWH2e