Subtraction YR Subtraction as `taking away` from a group
advertisement

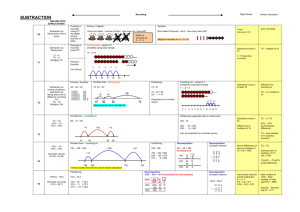
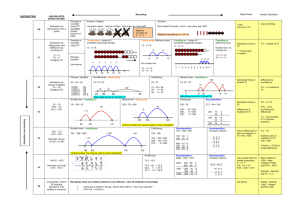
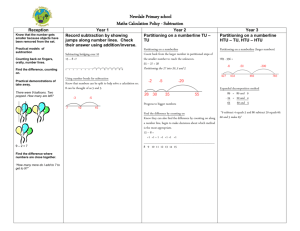
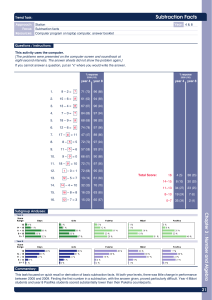
Recording Subtraction Age-related expectations Mental calculation (calculations that may require use of strategies or jottings) Subtraction as ‘taking away’ from a group YR Vocabulary: estimate, less, take away, fewer, less than, subtract, add, count back Pictures / Objects Symbols I have five cakes. I eat two of them. How many do I have left? Mum baked 9 biscuits. I ate 5. How many were left? 1 less (numbers up to 20) (see recording) Unifix Number track ? I had 13 sweets. I gave three to my brother. How many were left 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Songs / rhymes Straws Number facts to 5 1 Resources Rapid Recall Counting sticks 13 Concrete apparatus Taking away (efficient jumps) Subtraction as ‘taking away’ (by counting back) Y1 U–U TU – U (bridging 10) Vocabulary: estimate, less, take away, fewer, less than, subtract, add, count back Taking away – jumps of 1 (modelled using practical apparatus) Find the difference – jumps of 1 (modelled using bead strings) 13 – 5 = 8 Model using practical apparatus, counting back or removing items -1 -1 -1 -1 -2 -3 +1 10 10 11 Beadstrings Subtraction facts to 10 (7-5=2) TU multiple of 10 e.g. 13 – 5 = 8 12 13 1 / 10 less than a number up to 100 13 8 9 +1 Multiple of 10 - U -1 8 8 +1 Subtraction facts of 10 (10-4 = 6) 9 10 11 11 – 8 = 3 No number line 13 – 3 = 10 10 – 2 = 8 Numicom Subtraction as inverse of addition TU – TU (bridging 10s) Vocabulary As above plus Find the difference Number lines – find the difference 71– 24 (with exchange supported by practical) Number lines - taking away Subtraction facts of at 20 Find the difference Subtraction facts to at 20 TU – U / multiple of 10 74 -57 = 17 70 & 1 = 60 + 11 20 & 4 = 20 + 4 74 -27 = 47 +3 +10 +4 exchange Y2 -3 47 -4 50 -20 54 ______ ______ Subtraction facts of 100 (multiples of 10 e.g. 100-70 = 30) 74 57 60 70 74 Vocabulary: TU – TU HTU – TU HTU – HTU Estimation and checking Y3 Number line – find the difference Number line - taking away Decomposition with exchange either from tens or hundreds: 326 -178 = 148 326 –178 = 148 325 – 118 = 207 +22 178 200 -6 +126 -70 - 100 326 300 + 20 + 5 + 15 - 100 + 10 + 8 +8 200 + 0 146 156 326 226 +7 = 207 Move to compact vertical method -9 -11 Subtraction facts to 100 (multiples of 10 e.g. 80-70 = 10) Number facts of 100 (using multiples of 5) e.g. 100 – 15 = 85 = 300 + 10 100 + 10 Pictures / symbols e.g. 73-22 = 51 Number facts to100 (using multiples of 5) e.g. 85 – 25 - 60 Number facts of multiples of 10 that bridge 100 e.g. 130 – 50 = 80 TU – TU TU – near multiple of 10 (positive answers) 123 + 12 = 135 HTU – multiples of 100 Diennes Place value counters Y4 HTU –TU HTU – HTU Decimals: money and measures (£7.85 - £3.49) Number lines – find the difference or take away (only if not secure with Y3 expanded method) Decomposition (exchanging both hundreds and tens) using expanding method Decomposition (compact vertical method) 754 – 186 = 568 723 – 458 = 265 +500 +54 Number facts of 100 (e.g. 100 – 46 = 54) +14 186 200 Number facts of 1000 (using multiples of 50, 100) 700 754 Decomposition (compact method) Use number line method if appropriate : ThHTU – HTU Decimals up to 2dp (72.5 – 45.7) Decimals, including measures e.g. £80.00 - £36. 78 Y5 Also with Th, H, T and U or 506 378 Y6 Consolidate / extend Y5 including: Decimal to 3 dp relating to measures Consolidation of compact method Mixed operations e.g. 3485 + 4936 – 3265 Mixed operations including brackets (BODMAS) Use number facts for mental subtraction 9–2=7 0.9 – 0.2 = 0.7 0.09 – 0.02 = 0.07 Number facts to 1 (2dp) Number facts to 10 (1dp) (as above) Rapid recall of number facts involving money HTU – TU Subtract pairs of multiples of 10 / 100 / 1000 HTU – HTU (small difference) Subtraction in the context of measure, including conversion of units e.g. £5.00 – 23p Decimal – Decimal (eg 9.5 – 3.7) Integer / decimal (2dp) – Integer / decimal (1dp)