53: Properties of Operations What is Commutative Property? What
advertisement

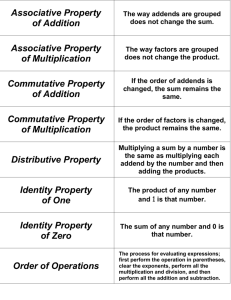
5­3: Properties of Operations What Commutative Property ? is Addition: a+b=b+a Multiplication: a(b) = b(a) What is Associative Property ? the Additive Identity : Multiplication Identity : Addition: a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c Multiplication: a(b∙c) = (a∙b)c a+0=a a∙1=a The commutative property states that the order in which numbers are added or multiplied does not change the sum or product. The associative property states that the way in which numbers are grouped when they are added or multiplied does not change the sum or product. When 0 is added to any number, the sum is the number. When the number is multiplied by 1, the product is the number. Multiplicative Property of Zero : Example 1a: Page 368 a∙0=0 When any number is multiplied by 0, the product is 0. Name the 1. Name property shown in property. the statement: a) 4 2 + x + y = 42 + y + the x What is Counterexample ? Example 2c: Page 369 15 ÷ 3 = 3 ÷ 15 If you find a counterexample , an example that shows that a conjecture is false, the property does not apply. State whether the following conjecture 1. True or false? is true or false. If 2. Write an false, provide a example to show it. counterexample. The difference of two different whole numbers is always less than both of the two numbers. Summary: Example 3d: Page 369 Lance made four phone calls from his cell phone today. The calls lasted 4.7, 9.4, 2.3, and 10.6 minutes. Use mental math to find the total amount of time he spent on the phone. Example 4­5e: Page 370 Simplify each expression. Justify each steps. 4 ∙ (3c ∙ 2) Summary: