Math Definitions: Associative, Commutative, GCF, LCM
advertisement

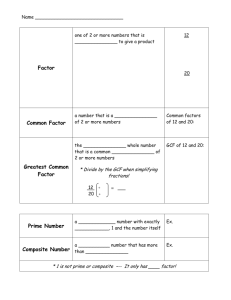
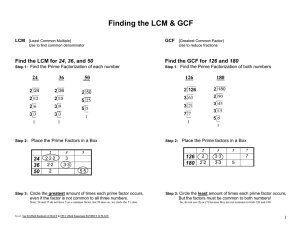
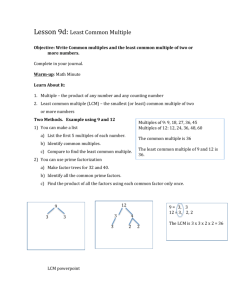
Associative Property of Addition The property that states that when the grouping of addends is changed, the sum is the same. Example: (5 + 8) + 4 = 5 + (8 + 4) (10 + 84) + 99 = 10 + (84 + 99) Commutative Property of Addition The property that states that when the order of two or more addends is changed, the sum is the same. Examples: 4+5=5+4 13 + 48 = 48 + 13 Composite Number A number having more than two factors. Divisible A number is divisible by another number if the quotient is a counting number and the remainder is zero. Factor Tree A diagram that shows the prime factors of a number. Greatest Common Factor (GCF) The greatest factor that two or more numbers have in common Example: 18: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30 6 is the GCF of 18 and 30. Ladder Diagram A diagram that shows the steps of repeatedly dividing by a prime number until the quotient is 1. (Also known as the “Upside-down cake” method.) Prime Factorization A number written as the product of all its prime factors. Prime Number A number that has exactly two factors, 1 and itself. Simplest Form A fraction is in simplest form when the numerator and denominator have only 1 as their common factor. Least Common Multiple (LCM) The smallest number, other than zero, that is a common multiple of two or more numbers Example: multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36 multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54 The LCM of 6 and 9 is 18. Least Common Denominator (LCD) The least common multiple of two or more denominators Example: