2 *Factor 3 Common Factor 4 *Greatest Common Factor 5 *Multiple
advertisement

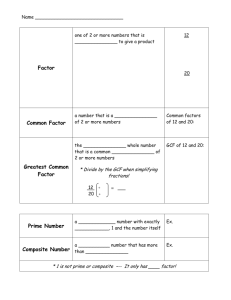
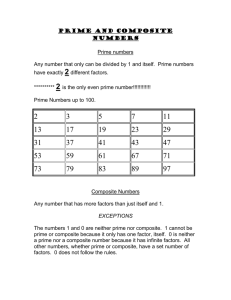
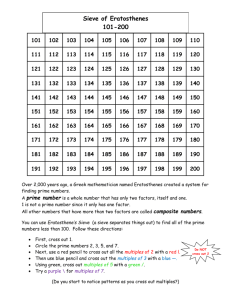
6th Grade Numbers & Operations 2 *Factor 17 Factor Tree 3 Common Factor 18 Exponent 4 *Greatest Common Factor 19 Simplify 5 *Multiple 20 Integer 6 Common Multiples 7 *Least Common Multiples 8 Product 9 Quotient 10 Sum 11 Difference 12 Order of Operations 13 Estimate 14 *Prime Number 15 *Composite Number 16 *Prime Factorization 1 Factor A number that is multiplied by another number to find a product Examples: 4 x 7 = 28 4 x7 28 The factors are 4 and 7. Back to List 2 Common Factor • A number that is a factor of two or more numbers Example: factors of 6: 1, 2, 3, 6 • factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 • The common factors of 6 and 12 are 1, 2, 3, and 6. Back to List 3 greatest common factor (GCF) • The greatest factor that two or more numbers have in common Example: 18: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30 6 is the GCF of 18 and 30. Back to List 4 Multiple • The product of a given whole number and another whole number Example: Back to List 5 Common Multiple • A number that is a multiple of two or more numbers Example: multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48 . . . multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48 . . . • A common multiple of 4 and 6 is 24, 48, 36 Back to List 6 least common multiple (LCM) • The smallest number, other than zero, that is a common multiple of two or more numbers Example: multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36 multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54 The LCM of 6 and 9 is 18. Back to List 7 Product • The answer to a multiplication problem Example: 6 x 2 = 12 • The product is 12. Back to List 8 Quotient • The number, not including the remainder, that results from dividing Back to List • Example: quotient 9 sum The answer to an addition problem Example: 12 + 7 = 19 The sum is 19. Back to List 10 Difference • The answer in a subtraction problem Example: 8–5=3 • 3 is the difference. Back to List 11 Order of Operations • The rules for performing operations in expressions with more than one operation; 1. first perform the operations in parentheses, 2. clear the exponents, 3. perform all multiplication and division, left to right 4. and then perform all addition and subtraction, left to right Example: 10 ÷ 2 + 8 x 23 - 4 Clear exponent. 10 ÷ 2 + 8 x 8 - 4 Multiply and divide. 5 + 64 - 4 Add and subtract. 65 Back to List 10 ÷ (2 + 8) x 23 - 4 10 ÷ 10 x 23 - 4 10 ÷ 10 x 8 - 4 8-4 4 Add inside parentheses. Clear exponent. Multiply and divide. Subtract. 12 Estimate • To find a number that is close to an exact amount Example: 32x9 30x10= 300 estimate 32 x 9 is about 300. Back to List 13 Prime Number • A whole number greater than 1 whose only factors are 1 and itself Example: Prime Number Factors Back to List Not Prime Number Factors 3 1, 3 6 1, 2, 3, 6 5 1, 5 9 1, 3, 9 2 1, 2 4 1, 2, 4 14 Composite Number • A whole number that has more than two factors Examples: Composite Numbers Back to List Not Composite Numbers Number Factors Number Factors 4 1, 2, 4 1 1 6 1, 2, 3, 6 2 1, 2 8 1, 2, 4, 8 3 1, 3 9 1, 3, 9 5 1, 5 15 Prime Factorization • A number written as the product of all its prime factors Example: Back to List 16 Factor Tree • A diagram that shows the prime factors of a number Example: The prime factors of 24 are 2 and 3. Back to List 17 Exponent • The number that tells how many times a base is to be used as a factor Example: The exponent is 3, indicating that 8 is used as a factor 3 times. Back to List 18 Simplify • Simplifying (or reducing) fractions means to make the fraction as simple as possible. Example Why say four-eighths (4/8) when you really mean half (1/2) ? 4/ 2/ 1/ • ==> ==> 8 4 2 (Four-Eighths) (Two-Quarters) (One-Half) Back to List 19 Integers • The set of whole numbers and their opposites Example: Back to List 20