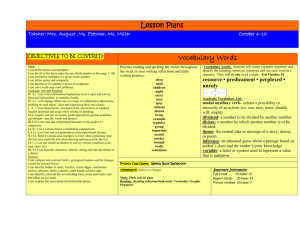
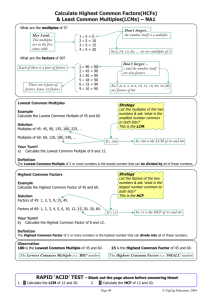
Lesson Notes
advertisement

T344
Mathematics Success – Level D
LESSON 12: Least Common Multiple
[OBJECTIVE]
The student will investigate and use least common multiples.
[PREREQUISITE SKILLS]
step counting, basic multiplication (0-9), ability to compare numbers
[MATERIALS]
Student pages S116–S122
Transparencies T353, T355, T357, and T359
Centimeter cubes (20 per student pair)
Colored pencils
Scissors
Paper for foldable (1 sheet per student)
[ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS]
1. What is the most important word in “least common multiple”? Explain.
2. How can I determine the least common multiple of two numbers?
3. How can I determine the least common multiple of three or more numbers?
[WORDS FOR WORD WALL]
multiple, common multiple, least common multiple
[GROUPING]
Whole Group (WG), Cooperative Pairs (CP), Individual (I)
*For Cooperative Pairs (CP) activities, assign the roles of Partner A and Partner B to
students. This allows each student to be responsible for designated tasks within the
lesson.
[LEVELS
OF
TEACHER SUPPORT]
Modeling (M), Guided Practice (GP), Independent Practice (IP)
[MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS]
SOLVE, Graphic Organizer, Verbal Description, Pictorial Representation, Concrete
Representation
[WARM-UP] (5 minutes – IP, I, WG) S116 (Answers on T352.)
• Have students turn to S116 in their books to begin the Warm-Up. Students will
work with skip counting. Monitor students to see if any of them need help during
the Warm-Up. Give students 3 minutes to complete the problems and then spend
2 minutes reviewing the answers as a class. {Verbal Description}
Mathematics Success – Level D
T345
LESSON 12: Least Common Multiple
[HOMEWORK] (5 minutes)
Take time to go over the homework from the previous night.
[LESSON] (60 minutes – M, GP, IP, WG, CP, I)
SOLVE Problem
(3 minutes – GP, WG) T353, S117 (Answers on T354.)
Have students turn to S117 in their books, and place T353 on the overhead. The
first problem is a SOLVE problem. You are only going to complete the S step with
students at this point. Tell students that during the lesson they will learn how
to find least common multiples. They will use this knowledge to complete this
SOLVE problem at the end of the lesson. {SOLVE, Graphic Organizer}
Least Common Multiple – Concrete
(19 minutes – M, GP, IP, WG, CP)
T353, S117 (Answers on T354.)
12 minutes – M, CP, GP, WG: Students will investigate multiples. Assign the
roles of Partner A and Partner B for designated
tasks during the lesson. Use the following activity
to help students understand multiples and least
common multiple at the concrete level. {Concrete
Representation, Graphic Organizer}
MODELING
Least Common Multiple – Concrete
Step 1: Have students count to 50 by twos. Then, have students count to 50 by
fives. Explain to the class that they counted by multiples. Explain that a
multiple of a number is the product of that number and another number.
For example, a multiple of 2 is 4, which is the product of 2 and 2.
Step 2: Distribute 20 centimeter cubes to each pair of students. Have students
work together using the hundred chart in Partner A’s book.
Step 3: Partner A, name the multiples of 2 up to 20. Have Partner B place a
centimeter cube over each of the multiples on the hundred chart as you
model on the overhead. (Centimeter cubes will remain on the multiples
for the next step.)
Step 4: Partner B, name the multiples of 3 up to 20. Have Partner A place a
centimeter cube over each of these multiples on the hundred chart as
you model on the overhead. Point out to students that they will stack two
centimeter cubes on top of some numbers. For example, 6 is a multiple
of both 2 and 3, so there will be two centimeter cubes on top of the 6.
T346
Mathematics Success – Level D
LESSON 12: Least Common Multiple
Step 5: Discuss the common multiples with students. (6, 12, 18)
• What does common mean? (It means something that is shared.)
• What is the smallest multiple that 2 and 3 share, or have in common?
(6) Tell students that this is called the least common multiple, which
is abbreviated as LCM. Have students remove all the centimeter cubes
from the hundred chart.
Step 6: Ask students to use their centimeter cubes and hundred charts to find
the multiples of 2, 3, and 4 up to 16 as you model on the overhead. Point
out that the common multiples will have three centimeter cubes stacked
on top of them. Ask students what the least common multiple (LCM) of
2, 3, and 4 is. (12)
5 minutes – IP, CP:
Have students work in partners to complete
Problems 1 – 4 at the bottom of S117. Tell students
that they will only need to use the first three rows
of the hundred chart in order to find each LCM.
{Concrete Representation, Graphic Organizer}
2 minutes – WG:
Bring the class back together and discuss
students’ answers. {Graphic Organizer, Concrete
Representation}
Least Common Multiple – Concrete to Pictorial
(14 minutes – M, GP, IP, WG, CP)
T353, T355, T357, S117, S118, S119 (Answers on T354, T356, T358.)
6 minutes – M, CP, WG, GP:
Pass out colored pencils (red, blue, and green)
to students. Use the following activity to model
a pictorial approach to finding the LCM of two
or more numbers on the hundred chart on
S117 (T353). {Pictorial Representation, Verbal
Description, Graphic Organizer}
Mathematics Success – Level D
T347
LESSON 12: Least Common Multiple
MODELING
Least Common Multiple – Concrete to Pictorial
Step 1: Tell students that they are going to find the least common multiple of
2, 7, and 4. On the hundred chart, have students draw a red diagonal
line from the top left to the bottom right of each square that contains a
multiple of 2 (up to 36). Model on the overhead.
Step 2: Next, have students draw a blue diagonal line from the top right to the
bottom left of each square that contains a multiple of 7 (up to 35). Model
on the overhead.
• What are the common multiples of 2 and 7? (14, 28)
• What is the least common multiple (LCM) of 2 and 7? (14)
Step 3: Finally, have students draw a green horizontal line in each square that
contains a multiple of 4 (up to 32). Model on the overhead.
• What number(s) is/are marked with all three colors? (28)
• What is the common multiple of 2, 7, and 4? (28)
• What is the least common multiple of 2, 7, and 4? (28) Record the
answer for Problem 5.
6 minutes – IP, CP:
Have students complete Problems 1–4 on S118
and S119 with a partner. Remind them to identify
multiples by drawing diagonal and horizontal lines,
using the colors indicated in the problems. Have
students identify the least common multiples by
drawing a circle. Have students complete the
problems on the left side of the vertical line only.
{Graphic Organizer, Verbal Description, Pictorial
Representation}
2 minutes – WG:
Bring the class back together and discuss students’
answers. Use the answers on T356 and T358 and
write them on T355 and T357 as students share
their answers. {Graphic Organizer, Verbal Description,
Pictorial Representation}
Least Common Multiple – Pictorial to Abstract
(6 minutes – M, GP, IP, WG, CP)
T355, T357, S118, S119 (Answers on T356, T358.)
3 minutes – M, CP, WG, GP:
Have students turn back to S118 in their books, and
place T355 on the overhead. Use the following activity to
help students move from the pictorial to the abstract in
understanding LCM. {Pictorial Representation, Verbal
Description, Graphic Organizer}
T348
Mathematics Success – Level D
LESSON 12: Least Common Multiple
MODELING
Least Common Multiple – Pictorial to Abstract
Step 1: Have students look at Problem 1 on S118 (T355).
• Partner A, explain the process to determine the LCM of the set of
numbers. (Cross out the multiples using colored pencils and then find
the multiples each of the numbers share. Circle the smallest value
shared.)
Step 2: Model how to record the multiples of the numbers on the graphic organizer
to the right of the hundred chart beside Problem 1. Have students list
the multiples of 3 up to 30 in the first two rows of squares. Then, have
students list the multiples of 5 through 30 in the third row of squares.
• Partner B, identity the LCM for 3 and 5.(15) Shade the boxes with the
multiple of 15.
2 minutes – IP, CP:
Have students complete Problems 2–4 on S118
and S119 with a partner. Remind them to record
their answers by shading in the boxes for Problems
2–4. {Graphic Organizer, Verbal Description, Pictorial
Representation}
1 minute – WG:
Bring the class back together and discuss the
answers. Use the answers on T356 and T358
and write them on T355 and T357 as students
share their answers. {Graphic Organizer, Verbal
Description, Pictorial Representation}
Least Common Multiple – Abstract
3 minutes – M, CP, GP, WG:
(6 minutes – M, IP, GP, WG, CP) T357,
S119 (Answers on T358.)
Use the following activity to help students solve LCM
problems at the abstract level. {Verbal Description,
Graphic Organizer}
Mathematics Success – Level D
T349
LESSON 12: Least Common Multiple
MODELING
Least Common Multiple – Abstract
Step 1: Have students look at Problem 4 on S119 (T357). Ask students how they
were able to determine the LCM of the set of numbers. (They crossed
out the multiples using colored pencils and then found the multiples of
each of the numbers shared. They also listed the multiples in a graphic
organizer and shaded the LCM.)
Step 2: Direct students’ attention to Problem 5.
• Partner A, identify the multiples of 2 up through 30. (2, 4, 6, 8, 10,
12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30)
Record on T357 as students record on S119.
• Partner B, identify the multiples of 6 up through 30. (6, 12, 18, 24,
30) Record the multiples of 6.
• Partner A, identify the multiples of 10 up through 30. (10, 20, 30)
Record the multiples of 10.
• Partner B, identify the LCM. (30)
Explain to students that one way they can find the LCM is to list multiples of
the greatest number first and then record multiples for the lesser numbers
until they determine the least common multiple.
2 minutes – IP, CP:
Have students complete Problems 6 and 7 on S119 with
a partner. {Graphic Organizer, Verbal Description}
1 minute – WG:
Bring the class back together and discuss students’
answers. Use the answers on T358 and write them on
T357 as students share their answers. {Verbal Description,
T350
Mathematics Success – Level D
LESSON 12: Least Common Multiple
Graphic Organizer}
Foldable
(5 minutes – M, WG)
Use the following activity to help students begin their foldables for least common
multiple, greatest common factor, and prime and composite numbers. Students will
complete this foldable as they learn about the other concepts. {Verbal Description,
Graphic Organizer}
MODELING
Foldable
Step 1: Place the sheet of paper horizontally on your desk in front of you.
Step 2: Fold the top of the paper down to almost the bottom of the page, leaving
about half of an inch at the bottom. Crease the fold at the top.
Step 3: Turn the paper vertically. Fold up once, and then fold again to create four
sections.
Step 4: Lift the top flap up and cut along each crease to create four flaps.
Step 5: Push the four flaps down and fold the half of an inch of paper, which was
left at the bottom, up over the flaps.
Step 6: On the outside of the first flap, at the top, have students write “Least
Common Multiple.” Inside, on the first flap at the top, have students
write the information for the LCM. You can create a transparency to
model for students what should be written on the flap. Use your foldable
at the back of your teacher’s edition for the information.
SOLVE Problem
(5 minutes – GP, WG) T359, S120
(Answers on T360.)
Remind students that the SOLVE problem is the same one from the beginning
of the lesson. Complete the SOLVE problem with your students. Ask them for
possible connections from the SOLVE problem to the lesson. (Students will use
information about common multiples to solve the problem.) {SOLVE, Verbal
Description, Graphic Organizer}
Mathematics Success – Level D
T351
LESSON 12: Least Common Multiple
If time permits…
(10 minutes – IP, I) S121 (Answers on T361.)
Have students complete Problems 1 – 5.
[CLOSURE] (2 minutes)
To wrap up the lesson, go back to the essential questions and discuss them with
students.
• What is the most important word in “least common multiple”? Explain. (Least is
the most important word because we are looking for the smallest number that is
a multiple of two or more whole numbers, except for 0.)
• How can I determine the least common multiple of two numbers? (List the multiples
of both numbers and find the lowest multiple in common to both numbers.)
• How can I determine the least common multiple of three or more numbers? (List
the multiples of all the numbers and find the lowest multiple in common to all the
numbers.)
[HOMEWORK] Assign S122 for homework. (Answers on T362.)
[QUIZ ANSWERS] T363
The quiz can be used at any time as extra homework or to assess how students
progress on understanding least common multiples.