Work with radicals and integer exponents.
advertisement

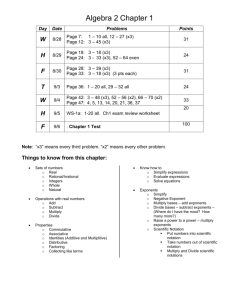
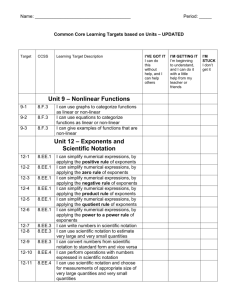
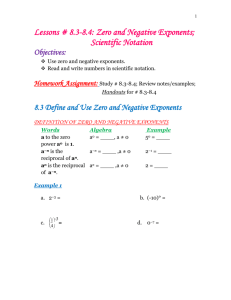
Grade/Course: Grade 8 Instructional Unit 6: Exponents Instructional Schedule: Third Nine Weeks (suggested for 15 days) ( Bold text is new content ) Adapted from Timothy Kanold Scope-and-Sequence documents Standards: Evidence Of Standard: (student should be able to…) Work with radicals and integer exponents. (BA/PASS 2.2a) Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, 32 ∙ 3−5 = 1 1 3−3 = 3 = . 3 27 -Identify the properties of integer exponents (laws of exponents). -Apply properties of integer exponents when multiplying and dividing with like bases. -Simplify numerical expressions by applying the properties of integer exponents: 1. zero rule (𝑎0 = 1). 2. product rule (𝑎 𝑥 ∙ 𝑎 𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥+𝑦 ). 𝑥 3. quotient rule (𝑎 ⁄𝑎 𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥−𝑦 ). 1 (PASS 2.2c) Recognize positive and negative rational numbers and use the order of operations to simplify numerical expressions that include rational numbers and exponents. 4. negative rule (𝑎−1 = 𝑎 ). 5. power rule (𝑎 𝑥 )𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥∙𝑦 ). -Classify expressions according to whether or not they are equivalent with one, two, or three properties. -Recognize positive and negative rational numbers and use the order of operations to simplify numerical expressions that include rational numbers and exponents. Prerequisite Knowledge: (standards linked to content taught in previous grades) Assessment Tools: (formative assessments, quizzes, mastery tasks/activities) (BA/PASS 2.1, 2.2b) Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 (scientific notation) to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as 3 × 10^8 and the population of the world as 7 × 10^9, and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. (BA/PASS 2.2b) Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. -Write numbers in scientific notation. -Apply the laws of exponents to the power of 10. -Use scientific notation to estimate very large and/or quantities. -Use scientific notation to determine how many times as large one number is in relation to another. -Convert numbers from scientific notation to standard form and vice/versa. -Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation without technology. -Use scientific notation and choose measurements of appropriate size of very large and/or small quantities. -Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology (ex: Recognize 3.7E-2 from technology as 3.7 𝑥 10−2). -Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation with technology. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving volume of cylinders, cones, and spheres. (BA/PASS 4.1) Know the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres and use them to solve realworld and mathematical problems. (PASS 1.1d) Rewrite and solve problems using appropriate formulas (literal equations). -Identify the shapes of cones, cylinders, and spheres. -Use appropriate formulas for volume of cones, cylinders, and spheres in mathematical and real-world situations. -Manipulate multi-variable equations. -Solve a multi-variable for a designated variable using appropriate formulas (literal equations). Resources/Exemplar Tasks: ( list possible task/activities students could engage in within this unit) Standards for Mathematical Practice: (highlight practice standards to be emphasized in the instructional unit) 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of instruction. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. ( BA: Broken Arrow rigor standard; PASS: Priority Academic Student Skills standard; BA/PASS: Combination standard )