Divide Using Integer Chips

______________
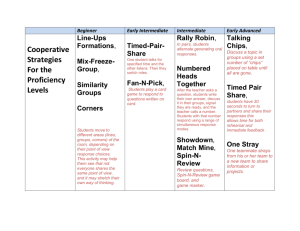
8.3 Exploring Integer Division
Working Example 1: Divide Using Integer Chips
Find each quotient using integer chips. a) (+12) ÷ (+3)
Solution
Quotient
Draw 12 positive integer chips in groups of 3.
The number of groups equals the quotient.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
is the answer when you divide.
How many groups of +3 can be made from +12?
There are 4 groups, so the quotient is +
Division statement: (+12) ÷ (+3) = +
.
-
-
b) (–12) ÷ (–3)
Solution
Draw 12 negative integer chips in groups of 3.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Separate the 12 white chips into groups of 3.
Circle the groups of 3.
There are 4 groups, so the quotient is +
Division statement: (–12) ÷ (–3) =
.
You cannot model this division by separating the 12 white chips into –3 groups.
-
-
c) (–12) ÷ (+4)
Solution
If you divide (–12) into 4 groups, how many will there be in each group?
Draw 12 negative integer chips in groups of 4.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Separate the 12 white chips into 4 equal groups.
Count the number of negative chips in each group.
There are negative chips in each group, so the quotient is
Division statement: (–12) ÷ (+4) =
.
430 MHR
●
Chapter 8: Integers
______________
Draw integer chips to solve each statement. a) (+14) ÷ (+7)
Draw 14 positive integer chips. Separate the chips into groups of 7.
Circle the groups.
There are groups of 7 positive chips, so the quotient is .
(+14) ÷ (+7) = b) (–9) ÷ (–3)
Draw
Circle the groups.
negative integer chips. Separate the chips into groups of 3.
How many groups of (–3) are there?
So, the quotient is .
(–9) ÷ (–3) = c) (–16) ÷ (+2)
Draw
Circle the groups.
There are
( ) ÷ (
integer chips. Separate the chips into groups of
chips in each group, so the quotient is
) =
.
.
8.3 Exploring Integer Division
●
MHR 431
______________
1. a) Allison modelled (+12) ÷ (+6)
using integer chips.
Tyler also modelled (+12) ÷ (+6) using integer chips.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ + + +
Explain how they each found the correct quotient (answer).
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________ b) Model (+12) ÷ (+2) in 2 different ways.
Use Allison’s and Tyler’s methods.
2.
Use the diagram to complete each division statement. a) (+10) ÷ (+2) = b) (–16) ÷ (–4) =
+ + + + +
+ + + + +
+ + +
+ + +
+
+
+
+
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - c) (–14) ÷ (+2) =
- - - - - - -
- - - - - - -
- - - - - - -
- - - - - - d) ( –15) ÷ (+3) =
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
8.3 Exploring Integer Division
●
MHR 433
______________
3.
Use the diagram to complete both division statements. a) (+14) ÷ (+2) =
(+14) ÷ (+7) = b) (–10) ÷ (–2) =
(–10) ÷ (+5) =
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + -
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + +
4.
Draw integer chips to solve each division statement.
Have a partner check your drawing. a) (+16) ÷ (+4) =
b) (–7) ÷ (+7) =
Draw 16 integer chips.
Separate the chips into groups of
. Circle the groups.
There are so the quotient is c) (–12) ÷ (–6) =
groups,
. d) (–10) ÷ (+2) =
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
5. A submarine was diving at 3 m/min. How long did it take to dive 21 m?
Diving 3 m = ( )
Diving 21 m = ( )
Sentence: ___________________________________________________________________
434 MHR
●
Chapter 8: Integers