Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 1
advertisement

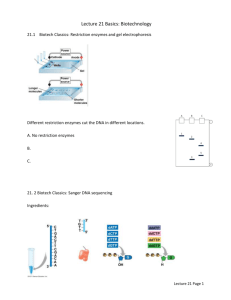
Apple Molecular Biology Modeling DNA sequencing with Lego blocks Directions 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Sequencing. 4. After reading the introduction click on the animation to learn more about sequencing. 5. Then complete the review questions on this worksheet using what you learned from the reading and animation. What is DNA Sequencing? DNA sequencing today is largely based on the methods of Fred Sanger. One method involves the use of modified nucleotide bases to terminate chain elongation. Using those dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (commonly referred to as dideoxynucleotides or ddNTPs), which cannot form the phosphodiester bonds necessary for chain elongation, the DNA synthesis process can be stopped anytime one of these molecules is incorporated into a forming strand. Four reactions are set up to replicate a given portion of DNA. Each includes all four normal bases plus one of the ddNTPs. As the normal bases are incorporated, the chain elongates. Every so often, a modified base is incorporated and the elongation process stops. Because there are many chains being formed simultaneously, the result of the reaction is a large pool of various-sized chains of DNA. Given a sequence of ATAGCA, the possible chains would be A, AT, ATA, ATAG, ATAGC, and ATAGCA. Using special fluorescent dyes, automated sequencing machines perform dye-enhanced sequencing and use lasers to excite the molecules as they pass through a separation column. The color produced is analyzed and recorded as a base identification. This automatic reading process eliminates the need for manual reading. The output is digital and usually includes some basic analysis information The sixth animation describes the process of DNA sequencing in which the four bases of DNA are used to determine specific information regarding what genes are being expressed. DNA sequencing provides a graphic view of how this process occurs. What is the real value of measuring level of nucleic acids and/or proteins? Knowing how much of a given gene is expressed is not useful unless you know when and where it is being expressed. Only then can conclusions be drawn about its importance in the plant. Studies are often restricted to specific tissue types to understand what genes are responsible for activities in certain regions of a plant. Nucleic acids and proteins taken from these tissues are studied using the methods mentioned above. By sampling the same tissue types at various intervals, a gene profile can be established. The study of these tissues may be expanded to include several days, and if the pattern holds true, a basic hypothesis may be formed in order to further understand what it is that you are studying. In the case of the apple, studies could be performed on flowering. Experiments involve such studies as the comparison of similar genes expressed in different cultivars, expression as different stages of flowering, or genes expressed in different stages of fruit development. Key Terms: Define the following key terms that were discussed in the reading and or the animation. 1. Dideoxynucleotide Triphosphates 2. DNA Polymerase 3. Nucleotide What Did You Learn? Answer the following questions using complete sentences. 4. Draw and Describe. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA molecules. Draw and label a diagram of a nucleotide. 5. Use a dictionary to look up the definition of the word template. Write that definition below. Then describe how strands of DNA are used as templates by DNA polymerase. 6. Explain the importance of the hydroxyl (-OH) group on the sugar component of a nucleotide. What important role does it play in DNA sequencing? 7. Many tools are used by scientists to sequence DNA. Describe the roles of the following tools used in DNA sequencing. gel-filled capillary tube: laser: detector: computer: 8. Summarize the steps in DNA sequencing.