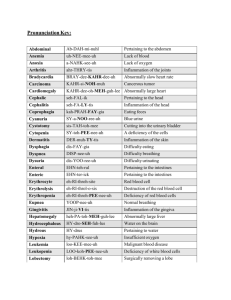
pertaining fever
advertisement

1. 1. 1. Cardi/o, Cardi- Cyt/o, -cyte Ect/o, Ex/o, Extra- 1. 1. 1. End/o, Ent/o Enter/o, Enter- Epi- 1. 1. 1. Gastr/o, Gastr- Hepat/o, Hepat- Heter/o, Heter- 1. 1. 1. Hist/o, Histi/o Hom/o, Home/o Macr/o, Macr- 1. 1. 1. Micr/o, Micr- Ossi-, Oste/o, Oste- Path/o, path-, -pathy Ect/o, ex/o Cyt/o, -cyte Cardi/o, Cardi- Without, outside of Examples: Ectoderm – the outer layer of cells in a developing embryo Exocrine – external secretions of a gland, which reach an epithelial surface either directly or through a duct Extracellular – outside the cell Cell Heart Examples: Cytology – the science which deals with the formation, structure, and function of cells Osteocyte – a bone cell Examples: Cardiac – pertaining to the heart Epi-, Ep- Enter/o, Enter- End/o, ent/o On, upon, over Examples: Epigastric – pertaining to the region over the pit of the stomach; the uppermiddle region of the abdomen Epicardium – the serous membrane on the surface of the myocardium Intestine Within, inner, inside Examples: Enteric – pertaining to the small intestine Enteral – within or by way of the intestines Parenteral – denotes any medication route other than the alimentary canal (such as intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, or mucosal) Examples: Endocarditis – inflammation of the endocardium (inner lining of the heart) or of the heart valves Entocranial – within the skull; also called endocranial or intracranial Heter/o, Heter- Hepat/o, Hepat- Gastr/o, Gatr- Other, different Liver Stomach Examples: Heterochromia – difference in coloration in two structures or parts of a structure which are normally alike in color Heterocellular – composed of different kinds of cells Examples: Hepatotoxic – relating to an agent that damages the liver; or pertaining to such an action Hepatology – the study of the liver Hepatolytic – agent/substance that is destructive to tissues of the liver Example: Gastroenteritis – inflammation of both the stomach and intestinal tract causing vomiting, diarrhea, or both, and which is commonly caused by viruses or bacteria in food and water Macr/o, Macr- Hom/o, home/o Hist/o, histi/o Large Like, similar, same Tissue Examples: Macroscopic – large enough to be seen with the naked eye Macrocyte – an abnormally large erythrocyte (exceeding 10 µm in diameter) Examples: Homogeneous – of uniform structure or composition throughout Homeostasis – the state of equilibrium in the body with respect to various functions and chemical compositions of the fluids and tissues Example: Histology – the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells, tissues, and organs Path/o, path-, -pathy Ossi-, oste/o, oste- Micr/o Disease Bone Small Examples: Neuropathy – any disease of the nervous system Pathogen – a microorganism that is capable of producing disease Examples: Ossicle – a small bone Osteogenesis – the formation of bone Osseous – pertaining to bone; also osteal Osteitis – inflammation of a bone; also ostitis Examples: Microcyte – abnormally small (5μm or less) red blood cell; also a microerythrocyte Microorganism – a living organism too small to be seen with the naked eye, such as a virus or bacterium Cardiology – the study of the physiology and pathology of the heart 1. 1. 1. Peri- Reno-, Reni-, Ren Cell/i, Cellul/o 1. 1. 1. -ac, -ar, -ary -al, -eal -e 1. 1. 1. -ia, -y -ic, -tic, -ical -itis 1. 1. 1. -ium -m, -um -logy, -ology 1. 1. 1. -osis, -iasis -sis, -asis, -esis -stasis, -stasia Cell/i, cellul/o Reno-, Reni-, Ren Peri- Cell or compartment Kidney Around, near Examples: Cellulitis – a spreading inflammation of subcutaneous and associated connective tissues Cellular – pertaining to, composed of, or derived from cells Examples: Renal – pertaining to or of the kidney(s) Renovascular – pertaining to the vascular supply of the kidneys Reniform – shaped like a kidney Examples: Periosteum – the thick fibrous membrane covering the entire surface of a bone except its articular cartilage Pericellular – around a cell -e -al, -eal -ac, -ar, -ary Often means instrument (noun-forming) Pertaining to (adjective-forming) Pertaining to (adjective-forming) Example: Microtome – an instrument for making thin sections of biological tissue for microscopic examination Example: Periosteal – relating to the Periosteum Neural – pertaining to any part of the nervous system Examples: Tonsillar – pertaining to the tonsils Biliary – pertaining to the bile, bile ducts, or gallbladder Iliac – pertaining to the ilium of an os coxa Ileac – pertaining to the ileum of the small intestine -itis -ic, -tic, -ical -ia, -y Indicates the specific condition of inflammation (noun-forming) Pertaining to; having the property of (adjective-forming) Sometimes the name for a condition (noun-forming) Example: Gastritis – inflammation of the stomach Example: Cephalic – pertaining to the head or head end of the body Necrotic – pertaining to dying cells/tissues Pathological – pertaining to pathology; morbid or diseased Examples: Bradycardia – abnormally slow heart rate Cardia – region of the stomach where the esophagus enters (near the heart) Nephropathy – any disease/condition of the kidney(s) -logy, -ology -m, -um -ium The science or study of (noun-forming) Name of an object or place (noun-forming) Location; often denotes a membrane (noun-forming) Example: Dorsum – the back; the upper or posterior surface of a part of the body Example: Epithelium – the tissue or cellular membrane that covers all free surfaces of the body -stasis, -stasia -sis, -asis, -esis -osis, -iasis Indicates a state of standing still, halting; stopping; controlling (nounforming) Name for a condition or state of being Examples: Prognosis – prediction of the course and end of a disease, and the estimate of chance for recovery Diagnosis – use of scientific or clinical methods to establish the cause and nature of a person’s illness Abnormal condition or process (both) indicates a slight increase in numbers when referring to blood cells (-iasis) Examples: Leukocytosis – abnormally large increase in the number of white blood cells Nephrolithiasis – the presence of calculi in the kidney; kidney stones Example: Physiology – the science of the functions of living things Example: Hemostasis – the control and/or arrest of bleeding 1. 1. 2. Inter- Intra- Corpus, corpor/o, Corpus- 2. 2. 2. Gluc/o Glyc/o Hydr/o 2. 2. 2. Hyper- Hypo- a-, an- 2. 2. 2. Chrom/o, chromat/o Iso- Lip/o 2. 2. 2. Mono- Oxy-, ox/i Plasm/o, Plasm-, -plasm Corpus, Corpor/o, Corpus- Intra- Inter- Body Within Between Examples: Extracorporeal – outside of the body Corpus – the principle part of any organ; any mass or body Corpuscle – 1. any small rounded body 2. an encapsulated sensory nerve ending Examples: Intracellular – within a cell or cells Intragastric – within the stomach Intra-alveolar – inside of an alveolus Examples: Intercellular – Between or among cells Intercostal – between the ribs Intermembranous – between membranes Hydr/o Glyc/o Gluc/o Water Sweet, sugars in general Glucose Example: Hydrocephalus – condition marked by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the ventricles of the brain; sometimes the accumulated fluid leads to increased intracranial pressure Examples: Glycolipid – a lipid containing a sugar molecule found in the myelin sheath of nerves Glycolysis – the energy-yielding conversion of glucose to 2 pyruvic acid molecules in cells Examples: Glucogenic – giving rise to or producing glucose Glucometer – a device used to measure levels of glucose in the blood, usually sampled by sticking the finger a-, an- Hypo- Hyper- Without, lack, no Below normal, under, deficient, beneath Above normal, beyond, excessive Examples: Acardia – congenital absence of the heart Apnea – temporary cessation of breathing Anosmia – a loss of the sense of smell Anoxemia – insufficient oxygenation of the arterial blood Example: Hypertrophy – increase in the size of a tissue or organ due to growth rather than tumor formation; increase in size results from an increase in cellular components (such as proteins), NOT from an increase in cell number. Lip/o Examples: Hypotonic – 1. describes a solution having a lower osmotic pressure than another solution. 2. state of muscle having less tension than normal Hypoxia – an oxygen deficiency, short of anoxia; decrease below normal levels of O2 in inspired air Iso- Fat or lipid Equal Color Example: Hyperlipemia – the presence of an abnormally high concentration of fats in the blood; also hyperlipidemia Example: Isotonic – 1. describes a solution having the same osmotic pressure as another solution. 2. having equal tension. 3. type of muscular contraction in which shortening occurs while tension remains unchanged Examples: Chromosome – thread-like structures in the nucleus that contain genes; forms a darkly-staining body during cell division Hypochromia – condition in which the percentage of hemoglobin in the red blood cells is below the normal range Plasm/o, Plasm-, -plasm Oxy-, ox/i Mono- The living substance of a cell; blood plasma Sharp, acid, acute, or oxygen Examples: Anoxia – absence of oxygen from inspired gases, arterial blood, or tissues; often used incorrectly to indicate hypoxia Oxidation – 1. process of combining oxygen with a substance 2. loss of electrons in an atom, accompanied by increase in positive valence Single, one, alone Examples: Cytoplasm – the substance of a cell, exclusive of the nucleus Plasmolysis – shrinking of cytoplasm in a living cell caused by loss of water by osmosis Chrom/o, chromat/o Examples: Monocyte – a type of white blood cell that is relatively large and contains a single oval-shaped nucleus; also called mononuclear leukocyte. Monoclonal – arising from a single cell 2. 2. 2. Poly- Reticul/o Som/a, somat/o, -some 2. 2. 2. Ton/o -ase -cle, -ule, -ole, -cule 2. 2. 2. -lysis -lytic Phag/o, -phagy, -phagia, -phage 2. 2. 2. -plasty -plasia -trophy 2. 2. 2. -emia, -cemia Erythr/o Leuk/o, leuc/o Som/a, somat/o, -some Reticul/o Poly- Body Network Many Examples: Somatic – relating to the trunk, the wall of the body cavity, or to the body in general Lysosome – membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle which contains hydrolytic enzymes Examples: Reticulocyte – an immature red blood cell with a network of precipitated basophilic material in the cytoplasm Reticulum – a network of tubules or blood vessels (e.g endoplasmic reticulum) Examples: Polychromatophilic – pertaining to the property of staining readily with acid, neutral, and basic dyes, especially certain red blood cells Polyphagia – excessive eating, in multiple sittings -cle, -ule, -ole, -cule -ase Ton/o Diminutive, small in size Denotes an enzyme Tone, tension Examples: Corpuscle – a small rounded body, esp. a blood cell Venule – a tiny vein that drains blood from capillaries Arteriole – a tiny artery that takes blood into capillaries Examples: Cholinesterase – a family of enzymes capable of catalyzing the hydrolysis of acylcholines (e.g. acetylcholinesterase) Lipase – an enzyme capable of catalyzing the hydrolysis of lipids Example: Atony – relaxation, flaccidity, or lack of tone or tension Phag/o, -phagy, -phagia, -phage -lytic -lysis Eating, devouring Pertaining to that which causes lysis or to the process of lysis Process of breaking down, decomposing, or loosening Examples: Hemolytic – relating to that which is destructive to red blood cells Thrombolytic – describing an agent that breaks up blood clots Example: Hemolysis – destruction of red blood cells with liberation of hemoglobin into the surrounding medium -trophy -plasia -plasty Nourishment, development, or growth Process of cellular multiplication, formation Process of shaping, or the surgical formation of a structure or part Example: Hyperplasia – the increased production and growth of normal cells (not tumor cells) in a tissue or organ, resulting in an abnormal increase in size of the tissue or organ (e.g. increase in breast size during pregnancy) Examples: Chondroplasty – reparative or plastic surgery of cartilage Rhinoplasty – plastic surgery to change the shape or size of the nose Leuk/o, leuc/o Erythr/o -emia, cemia White Red Blood Examples: Leukocyte – a white blood cell Leukoderma – an absence, either partial or total, of pigment in the skin Example: Erythrocyte – a red blood cell Example: Anemia – any condition in which the red cell count, hemoglobin level, and/or hematocrit are less than normal Examples: Phagocytosis – the process of ingestion and digestion of solid substances (e.g. bacteria or particulate matter) by cells Hyperphagia – overeating, in a single sitting Example: Atrophy – wasting away of a normally developed organ or tissue due to degeneration of cells caused by undernourishment, lack of use, or aging 2. 2. 3. Hem/o, hemat/o Dys- Embolus, emb/o 3. 3. 3. Kary/o Anti-, ant- Mega-, megal/o, -megaly 3. 3. 3. Morph/o Myel/o Nucle/o 3. 3. 3. Pan- Pro- Thrombus, thromb/o 3. 3. 3. -blast Auto- -gen Embolus, emb/o Dys- Hem/o, hemat/o A plug Difficult, painful, bad Blood Examples: Embolism – obstruction or occlusion of a vessel by an embolus Embolus – a plug composed of a detached thrombus, mass of bacteria, or other foreign body that travels through the bloodstream and suddenly blocks a vessel Examples: Dysphagia – condition in which swallowing is difficult or painful Dysplasia – condition of abnormal tissue development Example: Hematology – the study of blood and blood-forming tissues, and the disorders associated with them Mega-, megal/o, -megaly Anti-, ant- Kary/o Large, oversized Against, opposing Nucleus of a cell Examples: Cardiomegaly or Megacardia – enlargement of the heart Megakaryocyte – A large cell in the bone marrow that has an irregularlyshaped, multi-lobed nucleus, and that produces platelets Examples: Anticonvulsant – agent that prevents or reduces the severity of convulsions Antimuscarinic – inhibiting or preventing the actions of muscarine or the effects of parasympathetic stimulation at neuroeffector junctions (e.g. atropine) Example: Karyolysis – Dissolution of the cell nucleus Nucle/o Myel/o Morph/o Nucleus Bone marrow OR spinal cord Shape, form Example: Enucleated or Anuclear – having no nucleus Examples: Myelitis – 1. inflammation of the bone marrow. 2. inflammation of the spinal cord Myeloid tissue – tissue in the bone marrow in which the various classes of blood cells are produced Example: Morphology – the science of the form and structure of organisms and their parts Thrombus, thromb/o Pro- Pan- Blood clot Before, a precursor, for All, entire Examples: Thrombosis – 1. the presence of an intravascular clot at the site of its formation. 2. formation of a clot within a vessel or the heart. Thrombus – a blood clot Example: Prothrombin – a substance found in blood plasma that is the precursor to (that is converted into) thrombin in the coagulation of blood Examples: Pancytopenia – a pronounced reduction in all of the cellular elements in blood Panosteitis – inflammation of an entire bone -gen Auto- -blast Name of the agent that produces the state or object indicated by the word stem Self, same Immature precursor cell Examples: Autolysis – digestion of cells or tissues by the cell’s own enzymes Autotrophic – self-nourishing; pertaining to the ability of an organism to produce its own nutrients from inorganic compounds Example: Fibroblast – an elongated cell in connective tissue that is capable of forming collagen fibers Example: Immunogen – substance which stimulates the production of “active” immunity, also called an antigen. 3. 3. 3. -genesis -genous, -genic -in, -ine 3. 3. 3. -ism -oid -ous 3. 3. 3. -penia -philia, -phil -phobia, -phobe 3. 3. 3. -poiesis -rrhage, -rrhagia Kal/i 3. 3. 3. Natr/i Allo- Drom/o- -in, -ine -genous, -genic -genesis Compound formed in the body or a drug Pertaining to production, origin Production, formation, or development Examples: Thrombin – an enzyme formed in the plasma that is involved in blood coagulation Acetylcholine – the neurotransmitter substance that is released at the synapses of parasympathetic nerves and at neuromuscular junctions Example: Chondrogenic – giving rise to or forming cartilage Examples: Histogenesis – the formation and development of the tissues of the body Osteogenesis – the formation of bone -ous -oid -ism Pertaining to, made of, containing Resembling, like, having the form of Example: Squamous – scale-like; relating to or covered with scales Examples: Sigmoid – resembling the letter “S” or the Greek sigma Nucleoid – shaped like or having the appearance of a nucleus 1. Medical condition or disease resulting from or involving some specified thing. 2. A practice, doctrine -phobia, -phobe -philia, -phil -penia Unfounded fear, have an aversion to To love, have an affinity for Condition of lack, deficiency Example: Hematophobia - also called hemophobia, this is an unfounded and morbid (abnormal) fear of blood and/or bleeding Example: Eosinophil – also called an eosinophilic leukocyte, this is a white blood cell whose cytoplasmic granules stain readily with an acidic dye called eosin Example: Granulocytopenia – A condition in which the number of granulocytes in the blood is lower than normal Kal/i -rrhage, -rrhagia -poiesis Potassium Condition of excessive or abnormal discharge, esp. bleeding Making or producing Examples: Hyperkalemia – A condition in which there is a greater than normal concentration of potassium ions in the circulating blood Kaluretic – relating to, causing, or characterized by the increased excretion of potassium in the urine Example: Hemorrhage – excessive bleeding; a flow of blood, esp. profuse Example: Hypnotism – the process or act of inducing a condition resembling sleep, in which the subject is susceptible to suggestion Example: Hematopoiesis – also hemopoiesis, this is the process of formation and development of the various types of blood cells and other formed elements in the plasma Drom/o Allo- Natr/i A running Other, different from normal Sodium Example: Dromic – relating to the propagation of a nerve impulse along an axon in the normal direction Example: Allograft – also called a homograft, this is the transplant of tissue from one member of a given species to a non-identical member of the same species Examples: Hypernatremia – an abnormally high concentration of sodium ions in the plasma Natriuretic – a substance, such as a diuretic, that increases excretion of sodium, usu. as a result of decreased tubular reabsorption of sodium ions from glomerular filtrate 4. 4. Derm/a, derm/o, dermat/o, -derma Ec-, ex-, e(sometimes “e” with the consonant the word root begins with, as “ef-” in efferent) 4. Electro- 4. 4. 4. Febrile Ad-, a(sometimes “a” with the consonant the word root begins with, as “af-” in afferent) Myo-, my- 4. 4. 4. Asthenia, -asthenia Neur/o, neur/i, nerv/o, nerv/i Phylaxis, -phylaxis 4. 4. 4. Puri-, puro- Py/o Pyret/o 4. 4. 4. Pyro- Sarc/o Sepsis, septic/o, -septic Electro- Ec-, ex-, e- Derm/a, derm/o, dermat/o, -derma Electricity Out of, away from, outside Skin Example: Electromyogram – a graphic representation of the electrical currents associated with muscular contraction, obtained by inserting electrodes into the muscle fibers Examples: Efferent – conducting ouward, away from Ectopic – out of place; in an abnormal location Exocrine – denoting a gland that secretes outwardly through ducts Examples: Pyodermatitis – also called pyoderma, this is a pus-producing inflammation of the skin Dermatology – the medical specialty concerned with diagnosis and treatment of skin disorders Myo-, my- Ad-, a- Febrile Muscle To, toward, near Denoting or relating to a fever; feverish; having a fever; pyretic Examples: Myositis – inflammation of muscle tissue, esp. voluntary muscles Myalgia – pain in the muscles Examples: Afferent – bringing toward or into Adduct – to move a limb or any other part toward the midline of the body Phylaxis, -phylaxis Neur/o, neur/i, nerv/o, nerv/i Asthenia, -asthenia Protection against infection; to guard Nerve, nervous tissue, nervous system Weakness Example: Prophylaxis – the prevention of disease; preventative treatment Example: Neurospasm – muscular spasm or twitching caused by a disordered nerve supply Neurology – the branch of medical science concerned with the nervous system and its disorders Example: Myasthenia – muscular weakness Pyret/o Py/o Puri-, puro- Fever Pus Pus Example: Antipyretic –relieving or reducing fever, or a substance/agent that has such an action Examples: Pyogenesis – producing pus Pyogen – an agent that causes the formation of pus Examples: Puriform – resembling pus Purulent – containing, consisting of, or forming pus Sepsis, septic/o, -septic Sarc/o Pyro- The presence of various pus-forming and other pathogenic organisms, or their toxins, in the blood or tissues; putrifaction Denotes a muscular substance or a resemblance to flesh Heat, fire, fever, or produced by fire Examples: Aseptic – condition in which living pathogens are absent Antiseptic – substance/agent capable of preventing infection by inhibiting growth of infectious agents Examples: Sarcolemma – the plasma membrane sheath enveloping a muscle fiber Sarcomere – the basic contractile unit of striated muscle; the segment of a myofibril between two adjacent z-lines Examples: Pyrogen – a fever-producing substance Pyrosis – also called heartburn; substernal pain or burning sensation, usu. associated with regurgitation of gastric juices into the esophagus 4. 4. 4. Sept-, septo-, sept/i Spasm, -spasm, spasm/o Syn(appears as Sym- in word roots beginning with b, p, ph, or m) 4. 4. 4. Tetan/o -ferent, -ferous -lemma 4. 4. 4. -gram -graph -graphy 4. 5. 5. Clonus, -clonus, clon/o Algesi/o, alge-, algo-, -algia Audi/o 5. 5. 5. Dia- Esthesi/o, -esthesia Kines/i Syn-, sym- Spasm, -spasm, spasm/o Sept-, septo-, sept/i With, together A sudden, involuntary muscular contraction, convulsion 1. septum (dividing wall) 2. seven Examples: Syndrome – the aggregate of signs and symptoms associated with any disease Sympathomimetic – denotes mimicking of the actions of the sympathetic nervous system Example: Spasmolytic – an agent that relieves smooth muscle spasms Example: Septal – relating to a septum -lemma -ferent, -ferous Tetan/o Sheath or envelope To convey, produce, or bear Convulsive tension Example: Neurolemma – also neurilemma; the sheath encasing the axon of a nerve fiber Example: Ossiferous – containing or producing bone; bony Example: Tetanus – 1. acute infectious disease marked by tonic spasms, esp. of jaw and back muscles. 2. sustained muscular contraction caused by a series of nerve stimuli repeated resulting in a sustained/continuous contraction of muscle (no twitching) -graphy -graph -gram Process of recording, writing or description An instrument that records; sometimes a writing A recording, record, or tracing Example: Electrocardiography – (EKG or ECG) – the process of recording electrical currents from the heart; the study and interpretation of such recordings Example: Electrocardiograph – instrument used for recording the potential of the electrical currents that traverse the heart and initiate its contraction Audi/o Algesi/o, alge-, algo-, -algia Clonus, -clonus, clon/o The sense of hearing Pain or painful condition Rapid alteration between contraction and relaxation of muscle Example: Audiology – also otology; the study of hearing disorders through the identification and measurement of loss of hearing function as well as the rehabilitation of people with hearing Impairments Example: Algesimeter – also algesiometer; instrument used for measuring the degree of sensitivity to a painful stimulus Kines/i Esthesi/o, -esthesia Dia- Motion, movement Sensation, perception Through, throughout, across, completely Examples: Kinesia – any form of motion sickness Kinesiology – the science or the study of movement, and the active and passive structures involved Examples: Anesthesia – loss of sensation Kinesthesia –sense that allows the brain to be constantly aware of the position and movement of muscles in different parts of the body (without this, coordinated movements with your eyes closed would be impossible) Example: Electrocardiogram – the graphic record/ representation of the heart’s electrical activity Example: Blepharoclonus – alternate contraction and relaxation of the muscles of the eyelids Example: Diapedesis – passage of blood cells through the unruptured walls of capillaries into the tissue spaces (an important part of the inflammatory response mechanism) 5. 5. 5. Litho-, lith- Metr/o, metri/o Muc/o, myx/o, muci- 5. 5. 5. Myco-, mycet-, -myces, -mycin Myring-, Myring/o Osmo-, olfact/o 5. 5. 5. Ot-, ot/o, auri- Hemi- Para- 5. 5. 5. Presby-, presbyo-, gero- Salping/o Stereo- 5. 5. 5. Tinnitus Tympan-, tympan/o, tympani- Vertigo Muc/o, myx/o, muci- Metr/o, metri/o Lith/o, -lith Mucus or mucous 1. Uterus 2. Measurement Stone or calculus Examples: Myxedema – accumulation of mucus-like material under the skin Mucoenteritis – inflammation of the intestinal mucosa Mucus – viscous fluid secreted by mucous membranes that functions to protect and lubricate the membrane Examples: Endometrium – the mucous membrane that lines the inner wall of the uterus Hypermetria – condition in which voluntary movements overreach their goal, due to an inability to control the distance, power, and speed of the movement Example: Lithotomy – an incision into an organ or duct for the removal of a calculus (stone), especially from the urinary bladder Osm/o, olfact/o Myring-, myring/o Myco-, mycet-, -myces, -mycin 1. Smell, odor 2. Osmosis Tympanic membrane (eardrum) Fungus Example: Osmometer – Instrument for measuring osmotic pressure Olfactometer – Instrument for testing sense of smell Myringoscope – Instrument for examining the tympanic membrane (eardrum) Myringoplasty – surgical repair of a damaged tympanic membrane Mycosis – any disease induced by fungus Mycetism – also called Mycetismus; poisoning by certain species of mushrooms Para- Hemi- Ot-, ot/o, auri- 1. Adjacent, alongside, near, beside 2. Involvement of a pair or two like parts 3. Abnormal One-half Ear Examples: Hemisphere – Half of any spherical structure; lateral half of the cerebrum or of the cerebellum Hemiplegia – Paralysis of one side of the body, due to brain injury on the opposite side Examples: Otitis – inflammation of the ear Otitis media – inflammation of the middle ear (the chamber containing the auditory ossicles) Stereo- Salping/o Presby-, presby/o, gero- Three-dimensionality; a solid A tube (usually either the uterine or auditory tubes) Old age Examples: Paravertebral – alongside or near a vertebra or the vertebral column Paraplegia – paralysis of both lower extremities and generally the lower trunk, due to lumbar spinal cord injury Example: Astereognosis – The inability to recognize objects by touch alone, even though there is normal sensation in the hands Example: Salpingotomy – Incision into the uterine tube Salpingostomy – establishment of an artificial opening in a uterine tube, primarily as surgical treatment for ectopic preganacy Examples: Presbyopia – the physiologic loss of accommodation in the eyes due to advancing age Geriatrics – the branch of medicine concerned with the medical problems and treatment/care of the aged Vertigo Tympan-, tympan/o, tympani- Tinnitus A disabling sensation in which the subject/patient feels that either himself or his surroundings are in a state of constant movement (usually spinning); not the same as faintness 1. The tympanic membrane (ear drum) 2. The middle ear Noises in the ears, such as ringing, buzzing, whistling, roaring, etc. Example: Tympanitis – inflammation of the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Tympanoplasty – surgical correction of a damaged middle ear 5. 5. 5. -meter -metry -odynia 5. 5. 5. -osmia -phasia -plegia 5. 5. 6. Tax/o, -taxia, -taxis, -taxy Acous/o, -cusis, -acusis, -acousis Cephal/o 6. 6. 6. Cortic/o, cortex Cycl/o Encephal/o 6. 6. 6. Gangli/o, ganglion/o Gli/o, -glia Gnos/o, -gnosis -odynia -metry -meter Pain in (a specified part) Measuring or measurement Measure or Instrument to measure Example: Cardiodynia – also cardialgia; pain in the heart Example: Craniometry – measurement of the skull and the study of its topography Examples: -plegia -phasia -osmia Paralysis, stroke Speech Smell, odor Example: Quadriplegia – paralysis affecting all four extemities, due to injury at the cervical level of the spinal cord Example: Aphasia – a disorder of language in which the generation and comprehension of speech is impaired or absent, and which is commonly also accompanied by difficulties in reading and writing Example: Anosmia – loss or lack of the sense of smell Cephal/o Acous/o, -cusis, -acusis, -acousis Tax/o, -taxia, -taxis, -taxy Head Hearing Arrangement, coordination, order Examples: Cephalocaudad – proceeding toward the tail from the head Cephalodynia – headache Examples: Hyperacusis – abnormally acute sensitivity to sounds Acusis – the ability to perceive sound normally Acoustic – pertaining to hearing and the perception of sound Example: Encephal/o Cycl/o Cortic/o, cortex Brain A cycle, circular, or relating to the ciliary body of the eye Outer region; outer portion of an organ Example: Encephalitis – inflammation of the brain Example: Cycloplegia – paralysis of the ciliary muscle, causing loss of accommodation; is usually accompanied by paralysis of the muscles of the pupil, resulting in mydriasis Thermometer – instrument for measuring temperature Diameter – the length of a straight line connecting the center of a circle with two points on its perimeter (or the center of a sphere with two points on its surface) Ataxia – Inability to coordinate muscle activity during voluntary movements, resulting in shaky/tremor-like movements Taxonomy – the systemic classification of organisms based on degrees of similarity or presumed evolutionary relationships Example: Corticospinal – pertaining to the cerebral cortex and the spinal cord Gnos/o, -gnosis Gli/o, -glia Gangli/o, ganglion/o Knowledge Glue; neurological tissue (supportive tissue of the nervous system) Ganglion, knot, swelling, collection of nerve cell bodies Example: Neuroglia – non-conducting cells of nervous tissue with supportive and metabolic functions Example: Post-ganglionic – distal to or beyond a ganglion (a cluster of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS); referring to nerve fibers originating from cells in an autonomic ganglion Example: Prognosis – foreknowledge; forecast of the probable outcome/result of a disease or attack Diagnosis – process of determining the nature of a disorder by considering the signs, symptoms, medical history, etc. of a patient 6. 6. 6. Ker/a, kerat/o Lacrim/o Medull/o, medulla 6. 6. 6. Mes-, mes/o Met/a Mio-, meio- 6. 6. 6. Mydriasis Myopia Nystagmus 6. 6. 6. Ophthalm/o Opt/o, optic/o -ptosis, ptosis 6. 6. 6. Scler-, scler/o Tel-, tel/e, telo- -ectomy Medull/o, medulla Lacrim/o Ker/a, kerat/o Soft, inner part; any soft, marrow-like structure, esp. in the center of a part or organ Tear, tears 1. hard, horny tissue or cells 2. cornea Example: Medullary – pertaining to the marrow or to any medulla (as medulla oblongata or adrenal medulla) Examples: Lacrimation – secretion of tears, esp. in excess Lacrimal – relating to the tears, their secretion, the secretory glands, and the drainage apparatus Mio-, meio- Met/a Mes-, mes/o Less or smaller 1. after, beyond, between, distal to, over 2. change, transformation 1. middle, partial 2. mesentery or mesentery-like Examples: Metaphysis – the flared portion of a long bone, between the diaphysis (shaft) and the epiphyseal plate Metastasis – literally meaning, beyond control, this is the transfer of disease from one organ or tissue to another that is not directly connected to it Examples: Mesencephalon – the midbrain Mesocolon – the mesentery (folds of peritoneum) that attach the colon to the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity Nystagmus Myopia Mydriasis An involuntary, rhythmic oscillation of the eyeballs; may be lateral, vertical, or rotary Nearsightedness; the condition in which parallel rays of light are brought into focus in front of the retina, rather than on it Dilation of the pupil of the eye -ptosis, ptosis Opt/o, optic/o Ophthalm/o A falling, downward displacement, prolapse Relationship to the eye or to vision Eye Example: Gastroptosis – downward displacement of the stomach Example: Optometrist – a non-medical specialist who measures powers of vision and fits corrective lenses to correct visual defects Examples: Ophthalmoptosis – also exophthalmos; the abnormal protrusion of the eyeball Ophthalmologist – a physician specializing in diagnosis and medical and surgical treatment of diseases and defects of the eye -ectomy Tel-, tel/e, telo- Scler-, scler/o Excision; surgical removal of a segment of or an entire part or organ 1. end or ending 2. distance 3. complete 1. hardness 2. relationship to the sclera of the eye Examples: Miosis – constriction of the pupil Meiosis – cell division comprising two nuclear divisions in rapid succession, which results in halving of the number of chromosomes; makes gametes Example: Gastrectomy – surgical removal of the stomach Appendectomy – surgical removal of the vermiform appendix Examples: Telencephalon – the anterior portion of the brain, including the cerebral hemispheres and lamina terminalis Telophase – the final stage of mitosis or meiosis Telomere – the distal end of a chromosome Examples: Keratinization – also cornification; keratin formation, or the development of a horny layer of tissue, esp. in the epidermis Keratitis – inflammation of the cornea Example: Sclerosis – also induration; the process of becoming extremely firm or hard, or having such properties Scleritis – inflammation of the sclera 6. 6. 6. -ist -opia, -opsia, -opsy -ostomy, -stomy 6. 6. 7. -otomy, -tomy Blephar/o Arthr/o 7. 7. 7. Carcin/o, carcin- Chondr/o, chondri/o Eu- 7. 7. 7. Ascites Ecchymosis Edema, -edema 7. 7. 7. Iatr/o Idio- Mal- -ostomy, -stomy -opia, -opsia, -opsy -ist To furnish with a mouth; an artificial or surgical opening 1. condition of vision (-opia and –opsia) 2. process of viewing, to view (-opsy) One who specializes in Examples: Gastrostomy – establishing an artificial opening into the stomach Colostomy – surgical operation in which a part of the colon is brought through the abdominal wall and opened in order to drain or decompress the intestine; may be temporary or Permanent Examples: Hyperopia – farsightedness Autopsy – post-mortem examination of a body to determine cause of death or to study pathological changes present at death Arthr/o Blephar/o -otomy, -tomy A joint or articulation Eyelid An incision or cutting into Example: Arthritis – inflammation of one or more joints, or a state characterized by such inflammation Examples: Blepharoptosis – drooping of the upper eyelid Blepharedema – edema of the eyelids, causing swelling and an often baggy appearance Examples: Enterotomy – incision into the intestine Laparotomy – also celiotomy; a transabdominal incision into the peritoneal cavity Eu- Chondr/o, chondri/o Carcin/o, carcin- Good, well, normal, well-being 1. cartilage or cartilaginous 2. granular or gritty substance Cancer Example: Pharmacist – individual who is licensed to prepare and dispense drugs and has extensive knowledge of their properties Examples: Eukinesia – normal movement Euphoria – exaggerated feeling of well-being; elation Example: Chondrocyte – a cartilage cell, found in the lacunae of the matrix of cartilage Examples: Carcinogen – an agent that causes cancer Carcinogenesis – the production, development, or origin of cancer Edema, -edema Ecchymosis Ascites An accumulation of an excessive amount of fluid in cells, tissues, or serous cavities A purplish patch caused by hemorrhage under the skin from injury or spontaneous leaking from blood vessels; ecchymoses are the same as petechiae, except they are larger Also abdominal dropsy or hydroperitoneum; an abnormal accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity, causing abdominal swelling Mal- Idio- Iatr/o Bad, a disorder 1. unknown 2. peculiar, distinctive, individual Treatment Examples: Malformation – defective or abnormal formation or development Malaise – vague feeling of bodily discomfort Examples: Idiopathic – denotes a disease or condition which arises spontaneously , or of which the cause is unknown Idiosyncracy – an abnormal/unexpected effect of a drug that is peculiar to an individual Examples: Iatrogenic – unexpected side effects resulting from treatment by a physician Podiatry – the branch of medicine concerned with the treatment of diseases and injuries of the feet 7. 7. 7. Necr-, necr/o Neo- Onco-, oncho- 7. 7. 7. Splanchn/o, splanchni- Pariet/o Ped/o 7. 7. 7. Pre- Post- Pod/o, -pod 7. 7. 7. Petechiae Purpura Pruritus 7. 7. 7. Stom-, stomat/o, stoma Uresis, -uresis Urticaria Onco-, oncho- Neo- Necr-, necr/o A tumor, bulk, mass New or recent Death, dead Examples: Oncology – branch of medicine dealing with tumors Oncolytic – pertaining to, characterized by, or causing the destruction of a tumor or neoplasm Example: Neoplasm – tissue that grows more rapidly than normal and continues to grow even after the stimuli that initiated the growth cease, and that serves no useful function Examples: Necrosis – pathologic death of one or more cells, usually in a localized area Necrology – the science of the collection, classification, and interpretation of mortality statistics Ped/o Pariet/o Splanchn/o, splanchni- 1. Child (from Greek: pais, paid) 2. Foot (from Latin: pes, pedis) 1. a wall 2. a parietal bone The viscera (internal organs) Example: Parietal – relating to the wall of any cavity or to the parietal bone of the skull Example: Splanchnic – also visceral; pertaining to or supplying the viscera (as in the splanchnic nerves) Pod/o, -pod Post- Pre- Foot or foot-shaped (from Greek: pous, podos) Behind, after Before (in time or space), in front of Examples: Postsynaptic – situated beyond or distal to a synapse (after the synapse is crossed) Postprandial – following a meal Example: Presynaptic – situated before or proximal to a synapse (before a synapse is crossed) Pruritus Purpura Petechiae Itching A condition characterized by multiple pinpoint hemorrhages and accumulation of blood under the skin, producing purplish discoloration of the skin; merging ecchymoses and petechiae over any part of the body Pinpoint to pinhead-sized hemorrhagic spots under the skin; smaller versions of ecchymoses Urticaria Uresis, -uresis Stom-, stomat/o, stoma Also hives; an acute allergic reaction in which round wheals (welts) develop on the skin, usually accompanied by intense itching Excretion in urine (-uresis) Urination (uresis) Mouth, opening; an artificial opening between two cavities or canals or between such and the surface of the body Example: Pediatrics – medical specialty concerned with the study and treatment of children, from birth through adolescence Pedal – relating to the feet Example: Podiatrist – medical doctor concerned with the diagnosis and/or treatment of disorders of the feet Example: Natriuresis – Excretion of sodium in the urine; although this is normal, this term usually applies to greater than normal sodium excretion. Example: Stomatitis – inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the mouth 7. 7. 7. Viscer/o, viscera Phor-, phor/o, -phoria -oma 8. 8. 8. Angi-, angi/o Arteri/o Athero- 8. 8. 8. Arrhythmia Brady- Tachy-, tacho- 8. 8. 8. Aneurysm/o, aneurysm Auscultate Coronary 8. 8. 8. Cost/o Chron/o Ino- -oma Phor-, phor/o, -phoria Viscer/o, viscera A tumor or neoplasm Carrying, bearing, feeling Internal organs Examples: Sarcoma – a connective tissue tumor, usu. highly malignant, formed by proliferation of embryonic mesodermal cells Carcinoma – a malignant neoplasm derived from epithelial tissue Examples: Dysphoria – a feeling of unpleasantness or discomfort; feeling ill at ease Exophoria – tendency for one eye to deviate outward when fusion (the blending of slightly different images from each eye into a single perception) is suspended Example: Visceromotor – relating to or controlling movement in the internal organs, esp. the intestines Athero- Arteri/o Angi-, angi/o Deposit of soft, pasty material; porridge Artery 1. Blood or lymph vessels 2. A covering/enclosure Example: Atherosclerosis – a common form of arteriosclerosis characterized by irregularly distributed lipid deposits in the tunica intima/interna of large and medium-sized arteries, that will eventually lead to blockage of blood flow Example: Arteriosclerosis – collection of several pathological conditions in which the walls of blood vessels, esp. arteries, become thickened and hardened, losing their elasticity Examples: Angiogram – an x-ray of blood vessels following injection with radio-opaque material Angioscopy – insertion of a fiberoptic catheter through a peripheral artery to view the interior of blood vessels, esp. pulmonary arteries Tachy- Brady- Arrhythmia Rapid, quick Slow Example: Tachycardia – abnormally rapid heartbeat (usually applied to heart rates faster than 100 bpm) Example: Bradycardia – abnormally slow heartbeat (usually applied to heart rates slower than 60 bpm) Loss/lack of rhythm; any deviation from the normal (sinus) rhythm of the heart; an irregularity of the heartbeat Coronary Auscultate Aneurysm/o, aneurysm Relating to or resembling a crown; term is usually applied to the arteries that encircle and supply blood to the myocardium (the coronary arteries) To examine, by listening (usually with the aid of a stethoscope), to sounds produced by the movement of gases or liquids within the body, as a means of diagnosis A localized, balloon-like dilation or swelling in the wall of an artery or cardiac chamber Ino- Chrono- Cost/o, costa An obsolete prefix for fiber or fibrous; replaced in most terms by fibro- Time Rib or ribs Example: Chronic – relating to a health-related state or condition persisting over a long period of time (3 months or longer); may also refer to longterm or prolonged exposure Examples: Costa – the ribs Costochondral – also chondrocostal; pertaining to cartilage that is attached to the ribs Example: Inotropic – influencing the contractility of muscle cells (fibers) 8. 8. 8. Veno-, veni-, vene-, Phleb/o Vas/o, vasculo- Varico- 8. 8. 8. Coro-, core-, coreo- Sphygm/o Sten/o 8. 8. 8. Top/o Ortho- Isch/o 8. 8. 8. -tropic -malacia Infarct 8. 8. 8. Vascular Paroxysm Syncope Varico- Vas/o, vasculo- Veno-, veni-, vene-, Phleb/o 1. A dilated vein 2. An enlarged and tortuous (twisted) vein, artery, or lymphatic vessel Blood vessel Veins Example: Vasomotor – Causing dilation or constriction of the blood vessels, or denoting nerves with such action Examples: Venous – pertaining to a vein or the veins Venesection – also venipuncture and phlebotomy; the puncture of a vein, usually to withdraw blood or inject a solution Sten/o Sphygm/o Coro-, core-, coreo- Narrowness, constriction Pulse The pupil of the eye Example: Stenosis – the abnormal narrowing of a passage or opening, such as a blood vessel or heart valve Example: Sphygmomanometer – an instrument for measuring arterial blood pressure Example: Corestenoma – A narrowing or partial occlusion of the pupil Isch/o Ortho- Top/o To restrain, hold back, or repress 1. straight, correct 2. normal Place, location, position Example: Ischemia – Local and temporary lack of blood flow due to the mechanical obstruction of the circulation to a part of the body; may result in infarct if the circulation is withheld too long Example: Orthostatic – pertaining to the upright position of the body: used when describing this posture or a condition caused by it, such as Orthostatic Hypotension (a drop in blood pressure upon standing) Examples: Ectopic – in an abnormal location; out of place Topical – pertaining to a definite place or locality: used to describe the route of administration of a drug that is applied directly to the surface of the part being treated Infarct -malacia -tropic An area of necrosis (tissue death) due to sudden, localized ischemia Softening Changing, a turning forward, having an affinity for Example: Varicose – pertaining to varices – abnormally distended, tortuous vessels, especially veins Syncope A sudden, and generally temporary, loss of consciousness and postural tone, due to inadequate flow of oxygenated blood to the brain (Fainting) Examples: Malacia – a softening or loss of consistency and contiguity in any organ or tissue Osteomalacia – a disease characterized by a gradual softening and bending of the bones, accompanied by varying severity of pain Examples: Chronotropic – affecting the rate of rhythmic movements, such as the heartbeat Chronotropism – modification of the rate of a periodic movement, such as the heartbeat, via some external influence Paroxysm Vascular 1. 2. A sudden, violent attack, esp. a spasm or convulsion The abrupt onset or worsening of symptoms or recurrence of a disease Pertaining to or containing blood vessels; indicative of a copious blood supply