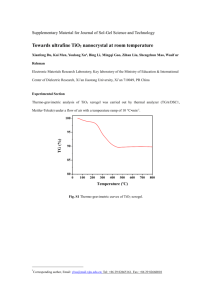
photolysis and photocatalysis of aqueous methylene blue under
advertisement

PHOTOLYSIS AND PHOTOCATALYSIS OF AQUEOUS METHYLENE BLUE UNDER UVC RADIATION VEYET Jonathan, THIVEL Pierre-Xavier, DELPEH Françoise LEPMI, 1130 rue de la piscine, Domaine universitaire, BP75, 38402 SAINT- MARTIN-D’HERES pierre-xavier.thivel@ujf-grenoble.fr, francoise.delpech@ujf-grenoble.fr Abstract k (min-1) Methylene blue (MB) is a standard model of dye used in order to study various treatment processes for textile wastewater. It is an organic compound, which could be directly decomposed by photolysis under UV and visible light. Among the colored wastewater treatment processes (adsorption, biodegradation, oxydative method as ozonation), photocatalysis using titanium dioxide (TiO2) is an emerging and interesting way leading to the mineralisation of organics compounds. Photolysis is a chemical reaction involving direct photons (h) absorption by the organic compounds : Organic compound + h subproducts Photocatalysis is a very interesting process for organic compound removal in aqueous or gaseous effluents. In this case, photons are absorbed by a semi-conductor (TiO2) leading to the production of hydroxyl radicals and then leading to the radical oxidation of the organic compound. TiO2 + h e- + h+ VOC + OH (ou h+) subproducts + CO2 + H2O In this study, we use a 254 nm light source, classified as UVC radiation and used for bacteriological decontamination of water. Photolysis and the photolysis/photocatalysis with TiO2 of methylene blue were performed. The influences of pH, TiO2 concentration and temperature are evaluated. The figure below shows a comparison of apparent constants k of photolysis and of photolysis/photocatalysis. 0,12 0,1 0,08 photolysis photolysis/photocatalysis 0,06 0,04 0,02 0 15°C 30°C 42°C The presence of TiO2 enhances the methylene blue degradation but the increase of temperature limits this phenomemon. At high temperature (40-45°C), the association of photolysis and photocatalysis becomes not interesting enough. The originality of this work lies in the use of the UVC radiation instead of UVB for photolysis and photocatalysis in aqueous phase and in the good results obtained.