Ch23
advertisement

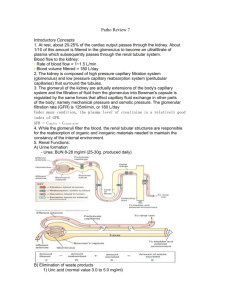
Guided Lecture Notes Chapter 23: Control of Kidney Function Learning Objective 1. Describe the location and gross structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomy and physiology of the structures of the renal system (refer to PowerPoint Slide 2 and Figs. 23-1 and 23-2). Learning Objective 2. Explain the physiology of renal blood flow. Trace the path of blood flow to and from the kidneys (refer to Fig. 23-3). Explain how renal blood flow is redistributed during SNS stimulation. Learning Objective 3. Explain the structure and function of the glomerulus and tubular components of the nephron (refer to PowerPoint Slide 4). Describe the anatomy and physiology of the nephron (the functional unit of the kidney), and identify the two capillary beds with which it is associated (refer to PowerPoint Slide 3 and Fig. 23-4). Describe the anatomy and physiology of the glomerulus (refer to PowerPoint Slides 5–6 and Fig. 23-5). Identify the tubular components of the kidney—proximal and distal tubules, loop of Henle, and collecting tubule—and explain the function of each (refer to Fig. 23-6). Learning Objective 4. Explain the function of sodium in terms of tubular transport mechanisms. Describe the loop of Henle’s cotransport system (Na+/K+/Cl-), and state its purpose (refer to PowerPoint Slides 15–16 and Fig. 23-9). Learning Objective 5. Describe how the kidney produces a concentrated or dilute urine. Explain the mechanisms by which urine concentration is regulated (refer to PowerPoint Slides 19–20). Learning Objective 6. Describe the elimination functions of the kidney. Identify the functions of the kidney, including elimination of water, waste excess electrolytes, and drugs/toxins. Explain what happens as a consequence of diminished renal function. Learning Objective 7. Characterize the function of the juxtaglomerular complex. Explain how neural, humoral, and autoregulatory control mechanisms maintain constant blood flow and GFR. Describe the location of the juxtaglomerular complex, and explain its function (refer to PowerPoint Slide 11 and Figure 23-10). Learning Objective 8. Explain the endocrine functions of the kidney. List the endocrine functions performed by the kidney, including the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system, erythropoietin, and vitamin D (refer to PowerPoint Slides 12, 13, and 26). Learning Objective 9. Describe the characteristics of normal urine. Describe the anatomy and physiology of urine. List laboratory tests that are used to evaluate renal function (refer to PowerPoint Slide 32 and Table 23-1). Learning Objective 10. Explain the significance of casts in the urine. Explain what a urine cast is. Identify causes of casts in a urine specimen. Learning Objective 11. Explain the value of urine specific gravity in evaluating renal function. Explain how the specific gravity/osmolality of urine reflects hydration status and renal function. List causes of increased and decreased specific gravity levels. Learning Objective 12. Explain the concept of GFR and how creatinine reflects its efficiency. Explain GFR, and list causes of increased and decreased GFR (refer to PowerPoint Slides 29–31 and Fig. 23-11). State normal values for GFR and urine output (UO) (refer to PowerPoint Slides 7–8). Explain how creatinine levels reflect GFR/renal function.