Chemical Bonding
advertisement

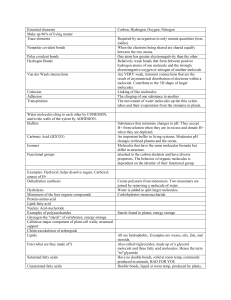
Chemical Bonding Chemical compounds are formed by the joining of two or more atoms. A stable compound occurs when the total energy of the combination has lower energy than the separated atoms. The bound state implies a net attractive force between the atoms ... a chemical bond. The two extreme cases of chemical bonds are: Covalent bond: bond in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms. Index Ionic bond: bond in which one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom, resulting in positive and negative ions which attract each other. Other types of bonds include metallic bonds and hydrogen bonding. The attractive forces between molecules in a liquid can be characterized as van der Waals bonds. Bond concepts Bond data Chemical concepts Sodium chloride Ionic Hydrogen molecule Covalent HyperPhysics***** Quantum Physics ***** Chemistry R Nave Go Back Covalent Bonds Covalent chemical bonds involve the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms, in contrast to the transfer of electrons in ionic bonds. Such bonds lead to stable molecules if they share electrons in such a way as to create a noble gas configuration for each atom. Hydrogen gas forms the simplest covalent bond in the diatomic hydrogen molecule. The halogens such as chlorine also exist as diatomic gases by forming covalent bonds. The nitrogen and oxygen which makes up the bulk of the atmosphere also exhibits covalent bonding in forming diatomic molecules. Index Bond concepts Chemical concepts Covalent bonding can be visualized with the aid of Lewis diagrams. Comparison of ionic and covalent materials. HyperPhysics***** Chemistry R Nave Go Back Polar Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal, with the electrons spending more time around the more nonmetallic atom, are called polar covalent bonds. In such a bond there is a charge separation with one atom being slightly more positive and the other more negative, i.e., the bond will produce a dipole moment. The ability of an atom to attract electrons in the presense of another atom is a measurable property called electronegativity. HyperPhysics***** Chemistry R Nave Index Bond concepts Go Back Ionic Bonds In chemical bonds, atoms can either transfer or share their valence electrons. In the extreme case where one or more atoms lose electrons and other atoms gain them in order to produce a noble gas electron configuration, the bond is called an ionic bond. Typical of ionic bonds are those in the alkali halides such as sodium chloride, NaCl. Index Bond concepts Ionic bonding can be visualized with the aid of Lewis diagrams. Comparison of ionic and covalent materials. Energy contributions to ionic bonds Table of ionic diatomic bonds HyperPhysics***** Chemistry R Nave Go Back Metallic Bonds Index The properties of metals suggest that their atoms possess strong bonds, yet the Bond ease of conduction of heat and electricity suggest that electrons can move concepts freely in all directions in a metal. The general observations give rise to a picture of "positive ions in a sea of electrons" to describe metallic bonding. HyperPhysics***** Chemistry R Nave Go Back Metal Properties The general properties of metals include malleability and ductility and most Index are strong and durable. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. Their strength indicates that the atoms are difficult to separate, but Bond malleability and ductility suggest that the atoms are relatively easy to move in concepts various directions. The electrical conductivity suggests that it is easy to move electrons in any direction in these materials. The thermal conductivity also involves the motion of electrons. All of these properties suggest the nature of the metallic bonds between atoms. HyperPhysics***** Chemistry R Nave Go Back Hydrogen Bonding Hydrogen bonding differs from other uses of the word "bond" since it is a force of attraction between a hydrogen atom in one molecule and a small atom of high electronegativity in another molecule. That is, it is an intermolecular force, not an intramolecular force as in the common use of the word bond. When hydrogen atoms are joined in a polar covalent bond with a small atom of high electronegativity such as O, F or N, the partial positive charge on the hydrogen is highly concentrated because of its small size. If the hydrogen is close to another oxygen, fluorine or nitrogen in another molecule, then there is a force of attraction termed a dipole-dipole interaction. This attraction or "hydrogen bond" can have about 5% to 10% of the strength of a covalent bond. Index Bond concepts Hydrogen bonding has a very important effect on the properties of water and ice. Hydrogen bonding is also very important in proteins and nucleic acids and therefore in life processes. The "unzipping" of DNA is a breaking of hydrogen bonds which help hold the two strands of the double helix together. Van der Waals Forces It is important to remember that van der Waals' forces are forces that exist between MOLECULES of the same substance. They are quite different from the forces that make up the molecule. For example, a water molecule is made up of hydrogen and oxygen, which are bonded together by the sharing of electrons. These electrostatic forces that keep a molecule intact are existent in covalent and ionic bonding but they are NOT van der Waals' forces. The van der Waals' forces are the forces that exist between the millions of separate water molecules, and not between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in the case of water. Dipole-Dipole forces are one of van der Waals' three forces. Dipole Dipole forces occur in polar molecules, that is, molecules that have an unequal sharing of electrons. For example, HCl comprised of the atom Hydrogen and Chlorine is polar. The Chlorine atom has an extra electron, which came from the hydrogen atom. Because of this, the chlorine part of the molecule is negatively charged, and the hydrogen side of the molecule is positively charged. ie. H - Cl + So in a solution where there are thousands of these molecules around that are slightly charged on each side, the molecules naturally orient themselves the accommodate the charge. The positive part of one molecule will move until it is next to the negative part of a neighboring molecule. These forces between molecules tend to make them 'stick' together. Dispersion forces are another of van der Waals' three forces. They exist between nonpolar molecules. For example, chlorine gas is made up of two chlorine atoms. In this bond, the electrons are equally shared and are not dominant on one side of the molecule as is the case in HCl. The atom looks like this Cl - Cl no overall charge on either side but, it is important to remember that within a bond, electrons are constantly MOVING. They zoom around the atoms really quickly. As a result, there may be a tiny instant in time where the electrons happen to be dominant on one side, creating a situation like this, Cl - Cl + However, this temporary charge disappears as quickly as it appeared because the electrons are moving so fast. These temporary dipoles allow the temporarily negative side of one molecule to attract the temporarily positive side of another molecule, which is the intermolecular force. Hydrogen bonding is the third type of van der Waals' forces. It is exactly the same as dipole-dipole interaction, it just gets a special name. A hydrogen bond is a dipole dipole interaction that occurs between any molecule with a bond between a hydrogen atom and any of oxygen/fluorine/nitrogen. So, Hydrogen Fluoride (HF), Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3)....any kind of substance that has a hydrogen bonded to either an oxygen, fluorine or nitrogen atom, exhibits hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bond is just the dipole dipole force but it is extremely strong compared to either dipole dipole forces like HCl. It is extremely strong because F N and O are extremely good at attracting electrons and H is extremely good at losing them. So basically, the bond is EXTREMELY a one-sided affair, resulting in an extreme dipole situation, thus named, a hydrogen bond. The extremely positive side of the molecule will orient itself with the extremely negative side of another molecule. The van der Waals' forces are very weak. I said the hydrogen bond is extremely strong, but that is only compared to the other van der Waals' forces. Compared to say, a covalent bond, a hydrogen bond is approximately one tenth of that strength. The dipole-dipole bond is weaker still, and the dispersion forces are the weakest of Van De Waals' forces. That is demonstrated in the fact that, take for example, Cl2. Chlorine gas exhibits dispersion forces, the weakest of van der Waals' forces. Cl2 is a GASEOUS compound, because the dispersion forces are not strong enough to pull the molecules together as a solid. The dispersion forces can only suffice to keep the substance as a gas, because the forces between molecules are so weak that they can float about all over the place and exist as a gas. Now that we know what van der Waals' forces are we move on to the second part of the question. When you vaporize water, you need to turn it from a liquid to a gas. To do this, you need to overcome the forces between the molecules, to allow them to float about freely by themselves. You supply the substance with energy in the form of heat. The heat makes the molecules vibrate. If the vibrations are strong enough, the molecules break free of the van der Waals' forces that hold them together. In the case of water, these forces are hydrogen bonding. So you supply the system with enough energy, and it is able to overcome the forces between the molecules. This accounts for the fact that water has an unusually high boiling point. Because hydrogen bonds are stronger than the other van der Waals' forces, then water will take more energy to overcome these bonds than say, HCl as a liquid- which would need sufficiently less because it has weaker bonds between molecules to overcome. So, in a sentence, the role of energy in vaporizing water is that is needed to overcome the van der Waals' forces at work between the molecules.