Global History Vocabulary List
advertisement

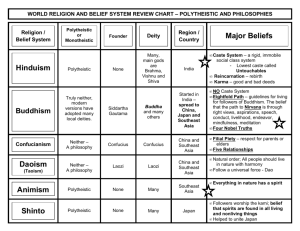
Global History I Vocabulary List GENERAL GEOGRAPHY Cultural Diffusion : The spreading outward of ideas from one culture to another. It is done through war, trade or missionary activity. 7 Factors that influence Climate: Land-Water relationship, Storms, Semi-permanent High and Low Pressure areas, Mountain Barriers, Ocean Currents, Latitude, Altitude Archaeologist: A scientist that studies the material remains of man's past sociologist: A social scientist that studies modern man; usually in groups economist : The social scientist that studies money and its relationship to human activities historian : Studies man's written past nationalism: Strong feeling for your country Geographic Isolation: When a culture is cut off from other cultures by natural barriers; little or no cultural diffusion takes place and the culture within develops uniquely. nonaligned: When a nation does not sign agreements with either communist or noncommunist nations, but takes aid from both sides leftists: People who believe in Marxian or communist ideas aligned : Countries that sign agreements with certain nations and not others capitalism: An economic theory based on the profit motive Socialism: a political and economic theory based on government ownership of some important industries imperialism: A stronger nation taking over a weaker one subsistence: Producing just enough for yourself and your family; nothing is left over for sale literacy: The ability to read & write nomadic: People who travel from place to place Traditional Village: Society is based in the tribal system, families are usually extended in nature, agriculture is subsistence Crusades: A series of "Holy Wars" to take the middle East from the Turks, waged by the Christian European nations, They were a failure but the brought on the AGE OF EXPLORATION Social Mobility: Ability in a society to change social class; generally through education, effort, wealth, etc. Melting Pot: The blending together of more than one culture; found in the same geographic area Age of Exploration: Result of the Crusades and the demand for spices in Europe. Began in the 1400's and carried European culture to the rest of the world Cultural Unity: When a society shares common elements like religion, history, traditions, etc. Return to the Top of the Page HUMAN BEGINNINGS Paleolithic: The "Old Stone Age", the time before the Agricultural Revolution Hunter-gatherer: People who travel from place to place hunting and gathering the food they need. Neolithic Revolution: "New Stone Age", the time period of and after the Agricultural Revolution when people settled in one place and domesticated plants and animals, people become food producers, as food production increases; population increases "Lucy": Early human remains found in the Great Rift Valley of Africa, She is the oldest, most complete best-preserved skeleton of any erect-walking human ancestor that has ever been found Where humans began: It is believed they began in the Great Rift Valley area of Eastern Africa Donald Johanson: In 1974, he discovered a 3.5 million-year-old fossil; nicknamed, "Lucy" What did humans master first?: It is believed they mastered fire first Specialization of labor: The development of skill in one area of work to such an extent that the person can use his skill to support himself [ indicates the beginning of the Urban Revolution- people living in communities] domestication : The taming of plants & animals for human use Return to the Top of the Page EARLY CIVILIZATIONS Fertile Crescent: The land between the Tigris & Euphrates Rivers where early Mesopotamian civilizations began, located where the modern nations of Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, & Iraq are found. the "Cradle of Civilization" The oldest continuous civilization : China Code of Hammurabi: Code of law, "an eye for an eye" ; let the punishment fit the crime Pyramids of Egypt: built as tombs for the pharaohs Barriers in Egypt: The Sahara Desert created geographic isolation Theocracy: rule by a religious group Ra: Important Egyptian god Isis: important Egyptian goddess pharaoh: priest-king, ruler of Egypt Nile: Egypt is called the "Gift of the Nile" because of the predictable flooding. Zhou Dynasty: China, feudal period, the time of the great philosophers [ ex. Confucius] Shang Dynasty: China, developed the use of silk Xia kingdom: 1st dynasty of China; exists in legend, little material evidence, [ founder Emperor Yu] feudalism: a social, political, &economic system based on land and protection form the upper classes and service and obedience from the lower classes Babylon: capital city of Babylonia, famous for its hanging gardens Sumer: earliest civilization in the Tigris-Euphrates Valley Mohenjo-Daro: earliest city ever found, located on the Indus River of modern day Pakistan, built on a grid pattern with sewers Mandate of Heaven: Chinese political philosophy; Stated if a ruler fails to meet the needs of the people then the people may remove him Divine Right of Kings: European political philosophy, Kings rule because God choose them to rule and NO ONE may question them. Return to the Top of the Page EMPIRES OF THE MIDDLE EAST Phoenicians: lived on the coast of the Med. Sea near Lebanon, "carriers of civilization"; because of their trade they carried on a lot of cultural diffusion, also gave us our alphabet Diaspora : Scattering of the Jews ; they were pushed out of the Middle East by the Romans Torah: Holy book for the Jews polytheistic: belief in more than one god. animism, Shintoism, Hinduism, Buddhism etc. monotheism: Belief in one god: Judaism, Christianity, Islam Judaism: found in the Middle East, 1st monotheistic religion, Moses is one of the prophets, Torah is the holy book Christianity: Founder Jesus; area the Middle East, 2nd monotheistic religion, holy book the Bible Islam: founder was Mohammed, 3rd monotheistic religion, literally means "submission to God's will" ; based on the 5 Pillars dynasty: rule by a family Mesopotamia: early civilization of the Fertile Crescent or Tigris-Euphrates Valley Babylonia: known for the hanging gardens Sumer : early city state Why were the first governments formed ? So people could work together so they could build things a single person could not do, example the irrigation systems of the T-E Valley [city state] Aryans: Invaders from central Asia that entered South Asia [Indian subcontinent] They brought the caste system and Hinduism, also the ancient language of Sanskrit Hittites: The most warlike group in the Middle East area Persians: settled in the area of modern day Iran Egyptians: civilization formed along the Nile River Castes of India: Top are the priests & teachers [ Brahmans]; next are the warriors, then the farmers and small businessmen, next the servant class and then the lowest [ so low they are outside the system are the untouchables. A person is born to a caste and can never change Siddhartha Gautauma: founded Buddhism, based on the 4 Noble Truths, 1. life is full of pain, 2. greed causes this pain 3. end greed then you end pain 4. there is a way to end greed called the Eightfold Path Jainism: polytheistic religion in India, don't kill any living thing Hinduism: polytheistic religion founded in India by the Aryans, based on caste and reincarnation, the cow is sacred Buddhism: polytheistic religion that began in India but died out there; it culturally diffused and became the predominate religion of Asia Confucius: famous teacher in China; set up an ethical system based on self-control, loyalty, and respect 5 Relationships: basis of Confucian teachings Man to Feudal Lord; Older brother to Younger brother, Husband to wife, Father to son, friend to friend . The first is responsible for the second and the second owes obedience to the first