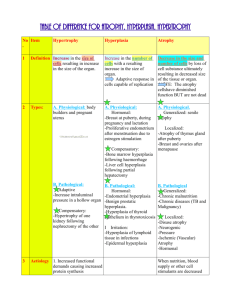
Cloudy swelling, hydropic degeneration and vacuolar degeneration
advertisement

Cloudy swelling, hydropic degeneration and vacuolar degeneration are all examples of..... morphologic expression of reversible cell injury post mortem artefact early neoplastic change morphologic hallmarks of cell death hyaline change Dystrophic calcification is.... associated with an elevated serum calcium level commonly observed in the lungs, stomach and small intestine frequently associated with renal impairment generally seen in foci of degeneration and necrosis observed in tissues which normally secrete acid Concerning autophagy, which statement is incorrect? The three types of autophagy are macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy. Is commonly associated with lipofuscin, the residue of auto-oxidized lipid from membrane remnants. Eukaryotic cells primarily use two distinct mechanisms for large-scale degradation, the proteasome and autophagy; but only autophagy has the capacity to degrade entire organelles. Appears to be a significant element of the aging process Autophagy occurs at basal levels in all cell types and contributes to the routine turnover of cytoplasmic components. Of the following which is the most likely site for metastatic calcification ? Lung Tuberculous granuloma Liver Atheroma Inflammed bursa With regard to thromboemboli, which statement is incorrect? Commomnly originates in arteries Occurs most frequently in the coronary arteries Are not lethal unless there is extensive infarction Prolonged bedrest is one of the most common predisposing conditions Focal fat necrosis is most often associated with which of the following clinical conditions? Fibrinous pericarditis Chronic salpingitis Acute pancreatitis Hepatitis Acute gastritis Effects of carbon tetrachloride on the liver includes.. fatty change damage to cell membranes by free radicals both neither The cells of a xanthoma are actually.... adipocytes macrophages muscle cells necrotic pericytes Atrophy of a cell, tissue or organ is LEAST likely to be the result of... prolonged pressure lack of appropriate hormonal stimulation lack of innervation congenital malformation deficient blood supply The principal storage form of lipid for energy production in man is... triglycerides cholesterol cholesterol esters phospholipids fatty acids The presence of squamous epithelium in the lower trachea of a 42-year-old female with a history of smoking is called..... Dysplasia Aplasia Anaplasia Hyperplasia Metaplasia Following tissue injury, parenchymal cells may be replaced by regeneration (hyperplasia of remaining parenchymal cells) or by fibrous tissue. The incorrect statement concerning the above is: In the central nervous system, fibrous repair predominates over regeneration. The capacity of the liver to regenerate is greater than that of the skeletal muscle. In the kidney, regeneration of the tubules but not of the glomeruli is observed. After Cesarean section, muscle regeneration exceeds fibroplasia. (fibroplasia=the formation of fibrous tissue) The following diseases are classified as inborn errors of metabolism EXCEPT... Tay-Sachs disease Wernicke's encephalopathy metachromatic leukodystrophy Niemann-Pick disease A person who is hemizygous for a recessive trait will most likely be.... a carrier phenotypically normal male a hermaphrodite In the condition called "brown atrophy of the heart", the brownish discoloration is produced by an increase in perinuclear, membrane-bound particles containing the pigment.... hematin cytochrome hematoidin lipofuscin hemosiderin In apoptosis, the caspase serves to..... crosslink the proteins dissolve the cytoskeleton puncture the cell membrane recognize a virally-infected cell tear up the DNA at every 110 base pairs Each of the following changes is associated with reversible cell injury EXCEPT... fatty change cellular swelling pyknosis glycogen storage hyaline droplets Which statement is correct Ducts in breast hyperplasia (black arrows) Prostate hyperplasia Lung bronchi (black arrows) Fatty infiltration Hyperplasia of the seminiferous tubules of the testis Epididymis and ductuli efferentes (black arrows) Seminal vesicle consists of a pair of tubes (black arrows) Brain abscess is a complication of each of the following EXCEPT... bacterial endocarditis bacterial pneumonia middle ear infection meningitis Herpes simplex infection Lipofuscin pigment present in myocardial cells: Indicates that these cells have sustained a critical injury Represents indigestible residues within autophagic vacuoles Represents an insoluble form of cardiolipin Is found in the hearts of patients with Alzheimer"s disease A term birth results in liveborn twins. The babies are both male. One weighs 2100gm and the other 2700gm. The larger baby is plethoric and the smaller baby exhibits pallor. No congenital anomalies are noted. Over the next year, the babies develop to become approximately the same size. How are the differences between these twins best explained? The mother had an elevated hemoglobin A1C A chromosomal abnormality is present in one baby The placenta was monochorionic One baby was infected with Herpes simplex virus There was a maternal dietary deficiency of iron At autopsy the patient's myocardium with H&E stain showed no evidence of ischemic changes, but there was diffuse intersitital fibrosis. Iron stain of the myocardium (see attached histopathology) suggests that he most likley had each of the following EXCEPT.... decreased liver function decreased serum ferritin diabetes mellitus increased brown pigment in the heart muscle fibers increased pressure in the portal vein Disuse atrophy might result from: Decreased secretion of trophic hormones Ductular obstruction in an exocrine gland Circulatory disturbances Stopping of exercise in sportsmen Glycogen storage diseases include which of the following, except ? hexoseaminidase A deficiency (Tay-Sachs disease) glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) deficiency (Von Gierke's disease) muscle phosphorylase deficiency (McArdle's disease) acid maltase deficiency (Pompe's disease) debrancher enzyme deficiency, Cori disease Hemosiderin: Stored primarily in the brain Accumulates in atrophic organs in old people Hemoglobin derived pigment devoid of iron Brownish pigment A 21-year-old woman has bilaterally diminished hearing . Audiometry confirms a conduction hearing loss. She has had several rib fractures, a right femoral fracture, and a left humeral fracture, as well as a left wrist fracture over the past 8 years. Her dentist notes deformities of multiple teeth, but no caries. The sclerae of her eyes demonstrate a faint slate-blue colour. A biochemical defect in formation of which of the following is most likely to produce these findings? Fibronectin Keratin Fibrinogen Hyaluronic acid Collagen Elastin Dermatan sulfate A patient with chronic hemolytic anemia is found to have pigmented stones in his gallbladder. The stones were formed due to excessive excretion of... hemosiderin hematin bilirubin melanin A cranial epidural abscess is usually mirrored in the cerebrospinal fluid by... increased cells elevated protein decreased protein elevated glucose no change in cells, protein or glucose Failure of an organ to reach full size is... hypoplasia atrophy both neithe In which of the following situations is metaplasia most likely to have occurred? Tanning of the skin following sunlight exposure Lactation following pregnancy Vitamin A deficiency Acute myocardial infarction Urinary obstruction from an enlarged prostate