Bernstein Psychology Book Brain and Behavior
advertisement

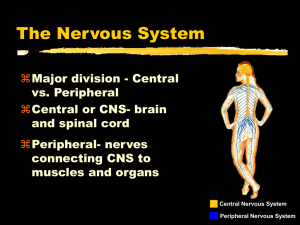
Bernstein Psychology Book Brain and Behavior Pg 59 Bio-Psychology Deals With: Brain Chemistry= RX Drugs to treat disorders Experience is rooted in Biological Processes Brain Cells, Hormones, genes o Are related to everything you think feel and do Chapter will describe Biological Factors related to behavior Bio-Psychology = the study of cells and organs of the body and physical and chemical changes involved in behavior and mental processes. Shows the relationship between Body and Mind Brain and Behavior Everything- thoughts, actions, feeling= are related to nervous system Experiences still play a role in biology Biological processes are influenced by the environment Experiences can change brain Chemistry + Brian Anatomy Behavioral Genetics= new approach Includes heredity + Environment= intelligence, personality, and mental disorders are impacted by both To Understand behavior + Mental Processes Need to combine information from different sources Biological is a major source of information Pg 60 Nervous System Billions of cells Brain + Spinal cord+ Nerve Fibers Detect info Executes responses Info is processedo It is combined with info about past experiences and current wants + needs o Then info is used to make decisions about how to respond Info Processing: (includes) Input Processing Output Capabilities Brain can also Anticipate on it’s own or unconsciously 1 Pg 61: Cells of the Nervous System: Brian Tissue Inter connecting Fibers Research of Ramon and Cajal - Found neurons Neurons respond to and send signals Missing Pages 61-67 (I’ll do it later) Peripheral Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Functions Somatic (body) Nervous System From body to CNS From CNS to Muscles Sensory Neurons = messages from body to brain Motor Neurons = messages from brain to body Autonomic Nervous System Relates to motivation Autonomous= outside conscious control o Digestion, perspiration Carries messages back and forth between CNS and the heart, lungs, organs, and glands Messages decrease or increase the activity of organs or glands o Example liver burning fat or storage of fat Pg 68 Sympathetic Mobilizes body for action Fight or Flight Sugar + blood pressure Parasympathetic Regular- body energy conserving functions Slows down body Parasympathetic Rebound= Heart slows down and heart attack occurs after a sudden increase of the Sympathetic system 2 Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Somatic Autonomic Sympathetic Parasympathetic 3 Neuromuscular Junction: 4 Pg. 69 Central Nervous System (Neural Network Theory= Pathways) Brain and Spinal Cord Input-Processing-Output Parallel Distributed Processing Sensation- Perception- Learning- Memory o Input simultaneously activates several paths in the network o Info is processed in various places at the same time Spinal Cord Receives Signals- from senses including pain Sends signals to the brain Carries signals down the spinal cord 5 6 Reflexes= Reflex Arc= Involuntary Impulse travels to spinal cord not to brain Then back to muscle o Afferent Neurons (going toward) Sensory neurons sense the pain o Efferent Neurons (going away) Motor neurons respond Acronym = SAME = Sensory + Afferent + Motor + Efferent 7 Brain’s Three Main Subdivisions: 1. Hindbrain 2. Midbrain 3. Forebrain I. Hind Brain: 1. Medulla Oblongata 2. Reticular Formation 3. Cerebellum Continuation of Spinal Cord Info from body reaches Hind Brain first Blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, Autonomic functions Reflexive actions: Vomiting, Sneezing, Swallowing 1. Medulla Oblongata Autonomic functions Heart rate, breathing, Blood Pressure 2. Reticular Formation (Netlike) Network of cells Involved Arousal, Attention Arouses the brain Heart rate + Blood Pressure Directing attention Linked to: depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, sleep problems, PTSD 3. Pons (Latin for Bridge) inferior to the Midbrain Carries sensory signals to the thalamus Inferior (below) to the mid brain 4. Cerebellum: Motor Control Coordination of fine movements Contains memory about movement Coordination of well rehearsed movements o Dancing o Playing Musical Instrument o Athletics Associated (Memory, impulse control, Emotion, language, and higher order cognitive processes) Problems with Cerebellum = problem with Equilibrium and posture 8 II Mid-Brain: (part of the brain stem) Located above hindbrain Integrates simple movements with Sensory input Seeing + holding eyes on a subject & moving head III The Forebrain: (Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Limbic System = Amygdala, Hippocampus Responsible for Complex Tasks Thalamus (Processes Sensory info) o Relays signals from spinal cord o Relays signals from eyes & other SENSE organs Hypothalamus (Hypo=under) o Lies under the thalamus o Regulating: Hunger Thirst Sex Drive o Connection to the Autonomic Nervous System o Destruction of one side of Hypothalamus -= overwhelming urge to eat o Damage to the other area = urge to not eat o Damage can also lead to Sex Organ degeneration/sex drive decreases o Supra-chiasmatic Nuclei Part of the Hypothalamus 24 hour clock= Bio Rhythm Lymbic System = Amygdala + Hippocampus o Regulates Memory o Regulates Emotion Amygdala: Associated with fear Emotion PTSD= Amygdala Hippocampus Formation of Memories Damage to hippocampus can result in Anterograde Amnesia Aneterograde Amnesia o Not able to remember new events (50 First Dates) Memory Ability is associated with size of the hippocampus o Small hippocampus = memory problems 9 Cerebral Cortex: Includes 2 halves = Cerebral Hemispheres = Left and Right Located on the outer most part of the Brain Associate with functions o Analysis of Sensory Info o Control of Voluntary Movements o Higher order thought Cortex is folded o Ridges are called Gyri = Ji-rye o Valleys are called Sulci = Sulk-eye Sulci divide the cortex into 4 Lobes o Frontal Lobe o Parietal Lobe o Occipital Lobe o Temporal Lobe P83 Sensory Cortex, Motor Cortex, and Association Cortex Sensory Cortex: located Parietal, Occipital, Temporal Part of Cerebral Cortex that receives information from senses Different senses affect different locations of cortex Visual info= Visual Cortex found in Occipital Lobe Auditory Cortex found in Temporal Lobe o Receives auditory info Somato-Sensory Cortex found in Parietal Lobe Info from Skin-touch, Pain, Temperature (P85) Sensory Homunculus- “The Little Man” Tells us places on the Cortex where sensory information is identified o This can change by experience o The Amount of Sensory Cortex that responds to a particular sensory input can be changed by experience o Example: Even practicing the violin can increase the number of neurons in Somatosensory Cortex that respond to finger touch Motor Cortex found in Frontal Lobe Voluntary movements in specific part of body, hand, foot, knee Motor Homunculus 10 Association Cortex Parts of Cerebral Cortex not directly involved with either receiving specific sensory information or creating movement Cognitive Tasks o Associating words + images Combining sensory and motor information Aphasia (Found in Auditory Cortex (processing spoken language) Difficulty in understanding speech Difficulty in producing speech (Motor Cortex produces speech) Visual Cortex includes processing written language Association Cortex and Language Broca’s Area 1861 (Left Frontal) Found damage to association cortex on left side of brain Frontal Lobe near Motor Area controls facial muscles Broca’s Area Damage = speech production is difficult Victims have difficulty speaking Paused speech Wernicke’s Area (left Temporal) Asspcoation cortex Temporal Lobe Area receives information from ears + eyes Interpretation of both speech and written words Damage to Wernicke’s the Person is able to speak but disrupts ability to understand meaning of words or speak understandably Speech is fluent without meaning Prefrontal Cortex Front of Brain Conscious controls of thought and actions that help us understand the world The Divided Brain in a Unified Self Each hemisphere may have special functions independent of the other. Lateralization= tasks that is specialized to one hemisphere Right Hemisphere: Left Side Left Hemisphere: 11