The Water Cycle
advertisement

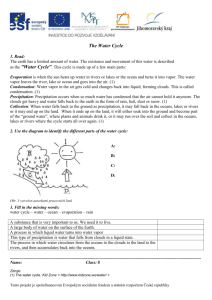
The Water Cycle On the sheet of paper provided work to create a visual representation of the water cycle using the steps given below. 1. The sun’s energy is the driving force behind the water cycle. 5. The water vapor cools and in a process called condensation forms droplets in the atmosphere. 2. The sun heats up water on land and in the oceans, lakes, and seas. 6. These droplets become clouds. 3. The water changes from liquid to vapor (From the ocean or ground surface) in a process called evaporation. 7. The droplets (or ice crystals if it’s cold enough) gather and then fall from the sky in a process called precipitation. 4. The water in plants changes from liquid to vapor and is released from the stomata of the plant in a process called transpiration. 8. This precipitation gathers in streams and rivers and flows and becomes run off, flowing back down to the oceans, seas, and lakes. Define these words and explain how they apply to the water cycle – 1. Transpiration 2. Precipitation 3. Condensation 4. Evaporation 5. Sunlight The Water Cycle On the sheet of paper provided work to create a visual representation of the water cycle using the steps given below. 1. The sun’s energy is the driving force behind the water cycle. 5. The water vapor cools and in a process called condensation forms droplets in the atmosphere. 2. The sun heats up water on land and in the oceans, lakes, and seas. 6. These droplets become clouds. 3. The water changes from liquid to vapor (From the ocean or ground surface) in a process called evaporation. 7. The droplets (or ice crystals if it’s cold enough) gather and then fall from the sky in a process called precipitation. 4. The water in plants changes from liquid to vapor and is released from the stomata of the plant in a process called transpiration. 8. This precipitation gathers in streams and rivers and flows and becomes run off, flowing back down to the oceans, seas, and lakes. Define these words and explain how they apply to the water cycle – 1. Transpiration 2. Precipitation 3. Condensation 4. Evaporation 5. Sunlight