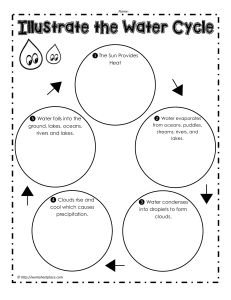
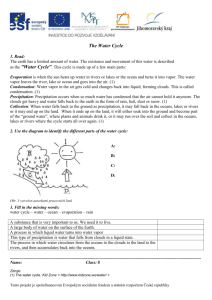
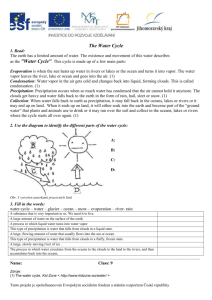
Evaporation: The ______ (temperature) is the energy force that
advertisement

Evaporation: The __________ (temperature) is the energy force that powers the water cycle It _____________ oceans, lakes, rivers and causes water to ____________ from the liquid state to the gaseous state The oceans contribute to about 80-90% of the water vapor in the _______________________. During ____________________, the impurities (for example, ________________) are left behind. This is important because about ________% of the water on Earth is salt water (oceans) and only 3% is freshwater (rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, and in the ground). Condensation: When atmospheric temperature __________________, the water vapor (gas) changes back into a liquid. Condensation is the _________________________ of evaporation. Small water droplets are formed in the atmosphere. Collections of water droplets form clouds in the sky or fog at ground level. You can see condensation on drinks in the summertime or leaves in the morning Precipitation: Tiny water droplets bounce around in a cloud and as they hit each other, they ______________ together and become ______________. The clouds get ________________ and eventually water falls back to the Earth. Precipitation can occur in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail. Most precipitation falls back into the oceans or onto land. If ______________________ falls in the form of snow it can accumulate in the form of ice caps or glaciers. Most of the ____________________ water in clouds does not actually fall as precipitation. Surface Run Off: About _________________ of the water that returns to the Earth as precipitation runs off the surface of the land, downhill, into streams, rivers, lakes, and oceans. The other 2/3 of precipitation is evaporated, transpired, or is infiltrated into __________________ water. Surface Runoff is a very important part of the water cycle because it returns water once again to the bodies of water, where evaporation occurs. For example, when snow ________________ Infiltration: Not all surface ____________________ water flows back into streams, rivers, lakes, and oceans. Some of it soaks into the ground. Infiltration is the _________________ movement of water from the land surface into soil or underlying rock layers This water can replenish ________________, which store large amounts of freshwater that can be removed from the ground using a water well. Some infiltration stays close to the land surface and can seep back into ________________water bodies (and the ocean) as groundwater discharge. Some groundwater finds openings in the land surface and comes out as _______________ springs. Transpiration: Water is returned to the _________________ by plants. Water is ______________ by plants (usually through the roots) from water that is in the soil. The water travels up through the plant and then is evaporated back into the atmosphere from the plant surface (usually the leaves). Sublimation Sublimation is the conversion between the ___________ and gaseous form of water, with no intermediate liquid stage. This occurs when there is _________ atmospheric pressure. An example of this is when ____________ and ice change into water vapor in the air without first melting into water.