11_4 RUSH US as a World Power Reading 2008_09
advertisement

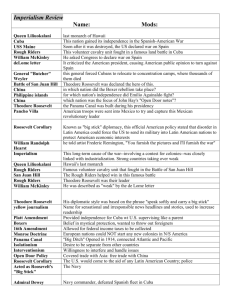
11.4 Students trace the rise of the United States to its role as a world power in the twentieth century. RUSH Reading Ch. 10 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire Pages 340-369 Chapter 10 Section 1 “Imperialism and America” Pages 342-345 1. Do you think Imperialism was an appropriate desire on the part of the US at the turn of the century (1900)? 2. Global competition, why did American want to control foreign lands? 3. Do you think Admiral Alfred T. Mahan’s ideas about Naval power are still valid today? Explain. 4. How did Hawaii become a part of the United States? 5. According to the text what was the main purpose for Imperialism? 6. What should we know about Alaska? 7. Identify three topics that you would like to discuss from the section you’ve read. What do you find interesting about them? Chapter 10 Section 2 “The Spanish American War” Pages 346-351 1. Read this section and outline the important aspects of the Spanish American War. 2. Identify three discussion topics regarding the Spanish American War. Why are these topics particularly important to discuss? 3. Debate over the Treaty of Paris, why did some people not want the Annexation of the Philippines? 4. Summarize the Cartoon on page 351. Chapter 10 Section 3 “Acquiring New Lands” Pages 352-358 1. Summarize issues regarding Puerto Rico including the Foraker Act. 2. Are people in Puerto Rico American Citizens? 3. Did the United States have any role in Cuba after the war? 4. Outline the story of the Filipino Rebels. 5. Outline the Boxer Rebellion. Chapter 10 Section 4 “America As a World Power” Pages 359-365 1. How was the creation of the country of Panama suspicious that the US “stole” the land? 2. How did Teddy Roosevelt win a Nobel Prize? 3. Many people in Latin America claim that the United States has a history of interfering in the affairs of Latin countries. Is this true? Use details from the reading to prove your point. 4. Do you think Roosevelt was correct in creating the “Big Stick Policy” and the Roosevelt Corollary? 5. Was President Wilson justified in sending troops to fight Pancho Villa? Explain. 6. Economic Imperialism is the use of economic power to control foreign countries. Elements of economic imperialism include the use of: loans, business investments, buying lands, bribery, opening businesses and factories. This was also called “Dollar Diplomacy.”? Do you think economic imperialism causes countries to follow US instructions and implement American interests? Key Terms To Know and Memorize Early American Imperialism US and China American Diplomacy TR, Taft, 1. Americans Want Hawaii 38. Open Door Policy Wilson 2. Sanford Dole 1899-1900 55. The Monroe Doctrine 3. Pearl Harbor Purposes 56. The Roosevelt Corollary 4. Queen LiliuokalaniEffects 57. “Speak softly and carry a 5. Annexation 39. China at the End of 19th big stick” 6. Social Darwinism Century 58. Big Stick Policy 7. Secretary of State William 40. Spheres of Influence 59. Central America, Seward 41. President William Caribbean, 8. Seward’s Folly McKinley 60. President William Howard 9. Admiral Alfred T. Mahan42. Secretary of State John Taft 1908-1912 Imperialism Hay 61. Dollar Diplomacy 10. President William McKinley 43. Boxer Rebellion 1900 62. President Woodrow 44. “Society of Devine Wilson 1912-1920 Spanish American War 11. Jose MartiFists” 63. Moral 12. Yellow JournalismDiplomacy/Missionary Panama and the US 13. William Randolph Hearst45. 1901 President Diplomacy14. Joseph PulitzerTheodore Roosevelt 64. Mexican Revolution 15. De Lome Letter takes office 65. Porfirio Díaz 16. USS Maine 46. Russo-Japanese War 66. Francisco Madero 191117. “Remember the Maine” 1904-06 67. 1912 General Victoriano 18. US Attacks Philippines 47. Treaty of Portsmouth Huerta – 19. Commodore George Dewey 1906 68. US Intervention in Mexico 20. US Invades Cuba 48. Nobel Peace Prize 69. Occupation of Vera Cruz 21. Theodore Roosevelt49. Gentlemen’s 70. Venustiano Carranza 191522. “Rough Riders”, Agreement (link) Wilson recognized this 23. “San Juan Hill” 50. Panama Canalgovernment 24. Treaty of Paris: 51. Philippe Bunau-Varilla 71. Francisco “Pancho” Villa 25. Puerto Rico 52. Colombia 72. Emiliano Zapata 26. Guam 53. Panamanian 73. General John J. Pershing 27. Philippines “Revolution” 28. Teller Amendment (pre-war) 54. Roosevelt and the 29. Platt AmendmentPanama Canal30. Protectorate 31. Anti-Imperialist League 32. Grover Cleveland 33. Mark Twain 34. Andrew Carnegie 35. Jane Addams 36. Philippine Insurgency 37. Emilio Aguinaldo Background Ideas: America is growing power militarily and economically Industrial Power- producing large amounts of goods in factories Most leading countries in the world have colonies that support trade and economic development example: Great Britain, France, Netherlands, Germany, Italy, Russia, Japan Imperialism (one country controlling another) is considered a very appropriate and popular use of power Beginning in the late 19th Century 1880s United States is late in the competition for colonies and the focus is the Pacific American Business leaders support trade and acquiring territory in order to sell more American goods Politicians in the US support trade and acquiring territory US gains territory in the Pacific Hawaii, and Samoa are acquired first Philippines and Guam are acquired from Spanish American War Notes: Americans Want Hawaii Hawaii- American business interests Sanford Dole- plantation owner, sugar and pineapple Pearl Harbor Good for stopping point of American Ships on way to China Queen Liliuokalani- Queen of Hawaii Leading American Imperialist: William Seward Secretary of State for President Lincoln late President Johnson Purchased Alaska 1867 from Russians for 7.2 Million Seward’s Folly Admiral Alfred T, Mahan- advocate the creation of strong Navy to support Imperialism President William McKinley supports annexation of Hawaii President during the Spanish American War Assassinated by anarchist in 1901 Spanish American War Chapter 10 Section 2 “The Spanish American War” Pages 346-351 Basics: Jose MartiCuban nationalist wanted Cuba to be independent from Spain Was afraid of United States control of Cuba Yellow JournalismWilliam Randolph HearstPublisher of newspapers, supported war with Spain New York Journal Joseph PulitzerPublisher of newspapers, supported war with Spain De Lome Letter- Spanish minister to US wrote a letter criticizing McKinley Published in Yellow Press Angers Americans and more support for war USS Maine Explodes- US blames Spain, really an accident, “Remember the Maine” US Declares War US Attacks Philippines Commodore George Dewey US Invades Cuba Theodore RooseveltVolunteers, creates his own cavalry unit the “Rough Riders”, fights in Cuba, becomes a hero charging up “San Juan Hill” Treaty of Paris: Americans Win, take Puerto Rico, Guam, Platt Amendment- to the Cuban Constitution Limits the independence of Cuba Making Treaties with other countries Allowing the right of the US to intervene in Cuba Limiting Cuba’s ability to go into Debt Allowing US to create naval bases in Cuba (Guantanamo) ProtectorateUS takes the responsibility of maintaining Cuba’s independence and has some control in Cuba Philippines Filipinos Rebel against the US control US does not allow Philippines Independence US controls Philippines as a colonyTo be given independence when the Filipinos are ready for independence Insurgency war is fought 20,000 Filipinos killed, 4,000 Americans Emilio Aguinaldo- Filipino Rebel Leader Anti-Imperialist League Some Americans are against Imperialism: William Jennings Bryan Democrat, presidential candidate Grover Cleveland Former president Mark Twain Author and commentator Andrew Carnegie Industrialist, capitalist, Philanthropist Jane Addams Progressive Social Worker, Activity: Nationalist Voice: Puerto Rico To the people of the USA: "You, citizens of a free fatherland, with its own laws, its own institutions, and its own flag, can appreciate the unhappiness of the small and solitary people that must await its laws from your authority…. When you acquire the certainty that you can found in Puerto Rico a republic like that founded in Cuba and Panama… give us our independence and you will stand before humanity as…. A great creator of new nationalities and a great liberator of oppressed peoples." From: Luis Munoz Rivera (Puerto Rican Businessman and Patriot) Write a letter as an American Voter. What would you say to this person to either criticize or justify American foreign policy toward weak countries? Chapter 10 Section 3 “Acquiring New Lands” (pg 356-357) Open Door Policy 1899-1900 Purposes Effects China 19th Century Weak Divided Trade is important for China- lots of Natural Resources Spheres of Influence European powers and Japan control areas both politically and for trade purposes Germany France England Japanese Americans Americans want to strengthen and improve their holdings American don’t want to be excluded from all parts of China William McKinley President John Hay is the Secretary of State creates the Open Door Policy Open Door Policy says: Starts as Open Door Notes There should be free trade in China No power should be excluded from trade in all parts of China Boxer Rebellion 1900 “Society of Devine Fists” Chinese nationalists respond to foreign influence by attacking foreigners Results of Open Door Not much change China still weak US is becoming stronger nation 11. 4.3 Discuss America’s role in the Panama Revolution and the building of the Panama Canal. Chapter 10 Sec 4 “America as a World Power” pages 359-365 1901 President Theodore Roosevelt takes office when McKinley was assassinated Russo-Japanese War 1904-06 Treaty of Portsmouth 1906 Nobel Peace Prize Gentlemen’s Agreement (link) Panama Canal- French planned to shorten route to Asia from Europe and the East of America… Philippe Bunau-Varilla French engineer and part of a company convinced TR to support the idea of a Canal in Panama. Colombia – resisted America’s desire to create a canal in Panama Panamanian “Revolution” US sends Warships to support a US backed independence movement against Colombia. Roosevelt and the Panama Canal- decides to Build the Canal- 1904-1914, $380 million dollars, 43,000 workers 5,600 people died. 11.4.4 Explain Theodore Roosevelt's Big Stick diplomacy, William Taft's Dollar Diplomacy, and Woodrow Wilson's Moral Diplomacy, drawing on relevant speeches. Chapter 10 Sec 4 America as a World Power The Monroe Doctrine The Roosevelt Corollary “Speak softly and carry a big stick” Big Stick Policy Central America, Caribbean, President William Howard Taft 1908-1912 Dollar Diplomacy President Woodrow Wilson 1912-1920 Moral Diplomacy/Missionary Diplomacy- Wilson pressured Latin American governments to create democratic countries, by not offering recognition to immoral governments Mexican Revolution Porfirio Díaz Francisco Madero 1911- deposed Diaz 1912 General Victoriano Huerta – took over from and kills Madero and Wilson refused to recognize the new government. US Intervention in Mexico Occupation of Vera Cruz- causes the Huerta regime to fal Venustiano Carranza 1915- Wilson recognized this government Francisco “Pancho” Villa Emiliano Zapata General John J. Pershing