Protocol for DNA digestion by restriction enzyme
advertisement

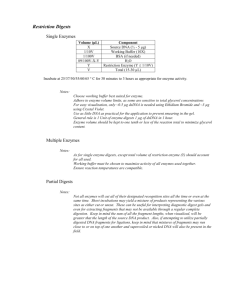
Experiment 3: DNA Digestion by Restriction Enzyme Theory: Restriction enzymes are enzymes isolated from bacteria that recognize specific sequences in DNA and then cut the DNA to produce fragments, called restriction fragments. Restriction enzymes play a very important role in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules as is done in gene cloning experiments. Another application of restriction enzymes is to map the locations of restriction sites in DNA. Materials required: Suitable restriction enzyme, 10 X buffer, PCR water, DNA sample, gel running buffer, agarose, weighing balance, gel electrophoresis apparatus. Bromophenol blue (BPB) loading dye. Procedure: 1. In order to digest plasmid DNA with one enzyme first of all make the following calculations: Plasmid DNA up to 1 µg Buffer (10X) 2 µl Enzyme (10U/µL) 1 µl H2O to 20 µl 2. After calculations, prepare the master mix with DNA, buffer and water, vortex the mixture and add the enzyme. 3. Thereafter, mix by pipetting and incubate at least 40 min at the temperature optimal for the enzyme. 4. Meanwhile the incubation is going on, make 0.8% agarose gel in 1X TAE buffer and make the plate ready for electrophoresis. 5. Now load DNA marker along with 5µL of digested product after mixing it with loading dye. 6. Run the gel for about 30 minutes and visualize the gel by transilluminator. Precautions: 1. Pipetting must be accurate and the sequence of reagent mixing must be followed strictly. 2. Incubation time should be monitored carefully. 3. Carefully load the sample in the wells. 4. DNA marker must be used.