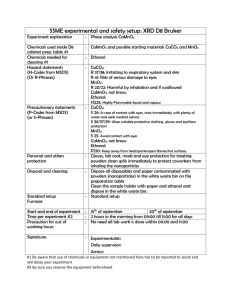
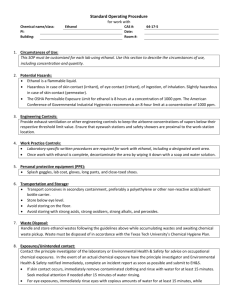
Alcohol Knowledge Quiz: Test Your Understanding
advertisement

So ya think you know everything there is to know about alcohol? Test yourself by doing the following exercise, then see where you rate on this informal, yet empirically validated, alcohol knowledge scale: 35 or more correct: you are an alcohol guru 30-34 correct: you are an apprentice guru 24-29 correct: not shabby at all, dude or dudette 18-23 correct: don’t mix any drinks for anyone; consider not drinking…ever below 18: please don’t drink, even socially THE ALCOHOL QUIZ 1. What is the chemical substance that makes alcoholic beverages intoxicating? carbonation alcohol ethanol sulfurous oxide 2. Ethanol and ether have similar effects. Are they classified as depressants, stimulants or neither? depressants stimulants neither 3. True or false? All distilled spirits are about 100 percent ethanol. true false 4. The proof stated on the bottle is equal to twice the amount of ethanol it contains. What percentage of ethanol is contained in 90-proof whiskey? 90 % 180 100 45 5. About how much ethanol does 1 ounce of distilled spirits contain? 1 ounce ½ ounce ¼ ounce minimal 6. An average serving of most alcoholic beverages contains about the same amount of ethanol. About how much ethanol is contained in a 4-ounce glass of table wine? ______________________________ 7. About how much ethanol is contained in a 12-ounce can of beer? ______________________________ 8. True or false? Alcohol is not digested like other foods. 9. About 20 percent of the alcohol you consume is absorbed through your stomach. From where is the other 80 percent absorbed? ______________________________ 10. Alcohol is a psychoactive substance because it changes brain neurochemistry and mood. True False 11. How does alcohol get to the brain? through the bloodstream through the blood-brain barrier usually starts its journey through the mouth all of the above none of the above 12. Ninety percent of the ethanol in one’s body is oxidized. This means the body produces heat and energy by combining alcohol with oxygen and ultimately converts the mixture to water and carbon dioxide. Will taking a cold shower or drinking hot coffee speed up oxidation? yes no sometimes 13. It is by means of oxidation that the body gets rid of most of the ethanol. Name a way, besides oxidation and urination, through which ethanol is eliminated from the body. fluoridation drinking lots of water drinking lots of caffeine expellation exhalation 14. Name one accurate way to measure the amount of ethanol in a person’s body. breath samples urine samples blood samples tissue samples observing the person ___________________________ 15. What results when a person drinks alcohol at a faster rate than his or her body can oxidize it? alcoholism alcohol dependence intoxication tolerance 16. What is one primary factor that affects the absorption rate of alcohol in the body?. ______________________________ 17. How do the nonalcoholic substances (such as water, sugar, salts, and other carbohydrates found in beer) affect the rate of alcohol absorption in the body? they do not affect rate quickens, increases rate slows, decreases rate 18. Does food in the stomach increase or decrease the speed of alcohol absorption? ______________________________ 19. A 4-ounce glass of table wine and a 12-ounce can of beer each contain about ½ ounce ethanol. Which beverage contains the higher concentration of ethanol? 20. Are champagne and other sparkling wines absorbed faster or slower than non-carbonated wines? 21. True or false? There is approximately the same amount of ethanol in a 1-ounce shot of 100proof distilled spirits, a 4-ounce glass of table wine, and a 12-ounce can of beer. 22. Generally speaking, a larger person must drink more than a smaller person to become intoxicated. What specific factor influences intoxication once alcohol has been absorbed in the bloodstream? 23. An average person needs an hour to oxidize ½ ounce ethanol. If you wish to drink, but avoid intoxication, how far apart should you space your drinks? 24. Are all of the following impaired by intoxication: judgment, memory, coordination, auditory and visual perception? yes no sometimes 25. True or false? Two people of the same weight and physical condition will have the same physical and psychological reactions to an equal amount of alcohol. ______________________________ 26. True or false? One person will have the same physical and psychological reactions to alcohol every time he or she drinks the same amount. ______________________________ 27. Ethanol provides heat and energy through oxidation. Because of this chemical property, can ethanol be classified as both a drug and a food? 28. What is the condition in which a person requires increasing amounts of alcohol in order to achieve the same effect as formerly was achieved by much smaller quantities of alcohol? ______________________________ 29. Frequent and heavy alcohol use can lead to what condition other than organic or mental disease? withdrawal tolerance dependence addiction all the above 30. What is the name of the disease most frequently associated with prolonged drinking that causes scar tissue to replace functioning liver cells? hematoma cirrhosis jaundice enlarged liver 31. True or false? In order to induce labor, physicians often administer small amounts of alcohol intravenously to pregnant women. ______________________________ 32. True or false? A person’s mood before drinking can influence the way alcohol affects him or her. 33. Name three beneficial changes in feeling caused by having alcohol in the bloodstream. depression, despair, and feelings of nothingness narcissistic enlightenment, nirvana, and detachment there are no beneficial changes or effects euphoria, less self-conscious, decreased tension 34. True or false? Whiskey was “discovered” and produced long before beer or wine. ______________________________ 35. True of false? Chronic drunkenness only affects the drinker. 36. Name two illnesses which are commonly contracted by the chronic drinker. intoxication and remorse alcohol hepatitis and cirrhosis cancer and diabetes 37. Which of the following may be considered a warning sign that a drinking problem may exist? preoccupation with alcohol constantly feeling uncomfortable when no alcoholic beverages are available drinking to deal with problems created by drinking all of the above Answers 1. Ethanol, or ethyl alcohol. Distilled spirits, wine, beer, all alcoholic beverages-contain ethanol. The concentration of ethanol is the primary intoxicant variable in alcoholic beverages. 2. Depressants (anesthetics/hypnotic-sedatives). Even though a little alcohol can release inhibitions and make a person forget his fatigue, alcohol is not a stimulant. Progressive amounts progressively deaden the central nervous system. 3. False. Distilled spirits can contain up to nearly 100 percent ethanol; but most American spirits contain 40 to 50 percent. The proof stated on the bottle is equal to twice the amount of ethanol it contains. For example, 100-proof whiskey contains 50 percent ethanol. 4. 45 percent. The next time you buy a bottle of whiskey or other distilled spirits, keep in mind that a shot of 80-proof vodka doesn’t “kick” the unwary drinker quite as hard as a shot of 100-proof bourbon. 5. ½ ounce. Remember, distilled spirits and ethanol aren’t the same. The amount or percentage of ethanol is equal to half the proof indicated on the bottle. 6. ½ ounce. Wine may be a connoisseur’s drink, but it packs more of a wallop than a lot of people think. Wine punch can be particularly deceiving if you drink enough of it. 7. ½ ounce. Despite its relatively mild alcoholic reputation, if you drink a lot of beer, you drink a lot. 8. True. That is why it acts on you so fast and why it seems to “go to your head.” 9. From the small intestine. Alcohol is absorbed faster from the small intestine than from the stomach. 10. True. Different behaviors are affected by the action of alcohol on different parts of the brain. 11. All of the above. It is carried to the brain through the bloodstream, easily passing the blood-brain barrier on the way. The higher the concentration of alcohol in the blood, the greater the effect on the functioning of the brain and nervous system. 12. No. Oxidation proceeds at a constant rate. That is why time is the important factor in eliminating alcohol from the body. Taking a cold shower or drinking coffee merely allows the passage of time; it does not create sobriety by increasing the rate of oxidation. What might happen when you give an intoxicated person lots of coffee? Just a more energetic, yet still drunk, person. 13. Exhaling. Since 90 percent of the alcohol one drinks is oxidized or burned up at a constant rate, breathing faster or running around the block will not significantly speed up the time it takes to get rid of the alcohol consumed. 14. Blood, urine, and breath samples can reveal the concentration of ethanol in a person’s system. Each of these procedures, particularly blood sampling, is quite accurate. Police usually use a breath-testing device on suspected intoxicated drivers because of the test’s convenience. 15. Intoxication if enough alcohol is accumulated. Remember, drinking doesn’t have to go hand in hand with intoxication. People can drink alcoholic beverages at rates or in amounts that do not necessarily cause drunkenness or intoxication. 16. False. Concentration of alcohol in beverage consumed; amount of alcohol consumed; rate of consumption; amount of food in stomach; nonalcoholic substances in beverage; emotions (i.e., stress, fear, anger); and carbonation in beverage are all factors to consider in regard to absorption. 17. Slow, decrease. Any food substance blocks absorption to some extent. However, this doesn’t mean the tomato juice in a Bloody Mary will offer a lot of protection. 18. Decrease. Food both dilutes the alcohol and cushions the wall of the stomach against absorption. Only foods and proteins such as milk are especially effective in slowing down absorption. 19. Wine. As indicated, a 12-ounce can of beer and a 4-ounce glass of table wine contain comparable amounts of ethanol. So, we may assume the wine is roughly three times as strong as beer. However, since few people stop at only 4 ounces of beer, an “average” serving of beer is as potent as an “average” glass of wine. 20. Faster. The carbon dioxide in carbonated beverages can cause the valve between the stomach and the small intestine to open. With the entrance to the small intestine open, one’s alcohol absorption rate is increased. 21. True. An average serving of each has about the same alcohol content and is almost equally intoxicating. 22. Body weight. Large people have more blood. Alcohol is diluted in proportion to the amount of blood a person has. This is not to say a larger person can drink more than a smaller person without feeling the effects of alcohol; other physical and psychological factors are involved. However, body weight and size are important factors in one’s rate of intoxication. 23. About 1 hour. In addition, you should “nurse” your drinks. 24. Any of the above. Different skills and behavior are affected as intoxication anesthetizes different parts of the brain. Most people show visible signs of intoxication at 0.10 percent to 0.15 percent BAC. Most people’s judgment and coordination, however, are impaired to some degree before they drink four or five drinks. 25. False. An individual’s reaction to alcohol involves too many different physical, social, and psychological factors to assume that any two people’s reaction will be the same. 26. False. The same person may react differently on different occasions. Each individual’s physical and psychological makeup, drinking experience, and condition and mood on any one occasion can affect the rate and intensity of reactions to an ounce of alcohol on every occasion. 27. True. Ethanol is classified as a simple, incomplete food with limited nutritional value: It lacks vitamins, amino acids, and minerals, yet is very high in calories. Those who make a habit of “drinking their meals” rather than maintaining a balanced diet may develop serious nutritional deficiencies. 28. Tolerance is the condition in which the body responds less and less to repeated use of the same drug - in this case the drug is alcohol so that a greater dose is required to achieve the former effect. 29. All of the answers. A person may become an alcohol addict just as one may become a heroin or nicotine addict. Physical addiction or dependence means that the body reacts markedly when deprived of the drug; this is called withdrawal. 30. Cirrhosis. A heavy drinker may be likely to develop cirrhosis, rarely otherwise contracted. Less commonly related to drinking, but a real danger for heavy drinkers, are heart disease, ulcers, and other physical, mental, and nervous disorders. 31. False. In some studies pregnant women were given small amounts of alcohol to successfully curb or reduce premature labor contractions. Precious growing time was gained for the premature infants who were born free of ill symptoms. 32. True. Although alcohol may not affect an individual in the same way every time it is consumed, its effect is influenced by a person’s mood. 33. Lessened feelings of tiredness and fatigue; lessened feelings of tension, anxiety, and pressure; lessened feelings of self-consciousness and increased feelings of well-being and maybe even “I’m a pretty good person, after all” types of self-statements; social relations may seem less difficult, more honest, healthy and open; release of inhibitions and transient mild to moderate euphoria. Any of these is correct. 34. False. Wine and beer are much “older” than distilled spirits such as whiskey as far as historians, archeologists, and anthropologists can tell. Beers were produced in Egypt as far back as 5000 B.C., while Europe apparently began making distilled alcohol like whiskey in the 8th or 9th century A.D. 35. False. Chronic and patterned drunkenness not only affects the drinker but also those around him or her. Spouse and family problems are likely to occur. Excessive drinking may affect an individual’s job performance. Even the general public may be affected because this type of drunkenness leads to a much higher risk of accidents, particularly auto accidents. 36. Alcohol hepatitis and cirrhosis. About 10-20% of alcoholics develop cirrhosis of the liver. 37. All of the above. The question to generally ask is “How much has drinking and drinking-related behavior affected one’s emotional, psychological, physical, occupational, financial, family and social life?