THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
advertisement

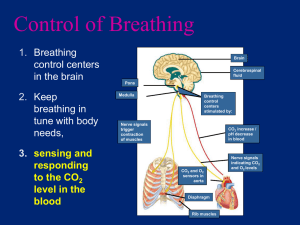
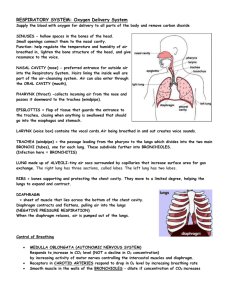
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM HEALTH TERMS: Respiration- The exchange of gasses between the body and one’s environment Diaphragm- The muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the chest cavity and is responsible for the act of breathing Pharynx- The Throat Trachea- The Wind Pipe Bronchi- An Extension of the trachea that forks/ branches off to deliver O2 to the lungs Larynx- The Voice Box Pleurisy- Inflammation of the membrane lining the lungs and the chest cavity Asthma- Inflammatory condition in which bronchioles become narrowed causing difficulty in breathing Exhalation- the act of breathing out CO2 Lobe- A section of the lung, the right has 3, the left has only 2 Bronchioles- A subdivision of Bronchi that forms a network of tubes that supply entire lung with Oxygen Alveoli- thin-walled air sacs that are covered by a vast number of capillaries Uvula- skin flap that hangs down in the back of the mouth that prevents food from traveling in the wrong direction. Epiglottis- The flap of skin that protects the body from choking FUNCTIONS of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: Responsible for Respiration o The exchange of gasses between the body and one’s environment o Two Kinds Internal- the exchange of gasses between blood and cells External- the exchange of gasses between blood and lungs STRUCTURE of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: Pharynx - Throat Epiglottiso Flap of skin that protects the body from choking o When swallowing, it closes over the trachea Larynx- Voice Box o Made of two fibrous sheets of tissue o Produces Sound as air passes over the cords o Tissues vibrate Trachea- Wind Pipe Lungs o Principle organs of the respiratory system o Responsible for inhalation/ exhalation o Gets their power from the Diaphragm o Each lung is divided into sections—lobes Right lung = three lobes Left lung = two lobes o Bronchus Connects Trachea to lungs splits into two bronchi o Bronchi Feeds air into lungs splits into many bronchioles o Bronchioles Subdivision of Bronchi Forms network of tubes that supply entire lung with Oxygen o Alveoli thin-walled air sacs covered by vast number of capillaries o Capillaries Responsible for CO2 / O2 exchange Diaphragm o Responsible for the act of breathing Contracts Inhale Diaphragm moves downward allowing extra room for lungs to pull air in Relaxes Exhale Diaphragm moves back up to original position and pushes air out of the lungs CARE of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: Avoid putting hands near face and mouth Wash Hands frequently Avoid Smoking & Second-hand smoke Workout Regularly to exercise lungs PROBLEMS of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: Colds/ Sore Throat o Considered Upper Respiratory Infection o Symptoms include Runny Nose, Post Nasal Drip, Cough, Sore Throat, Mild Fever o Due to easy access for germs to invade – nose and mouth Bronchitis o Inflammation of the Bronchi o Symptoms include wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing o More common in smokers o Can be acute (sudden onset) or Chronic (occurring over a period of time) Acute- clears up faster Chronic longer-lasting can be recurring can get progressively worse Asthma o Inflammatory condition in which bronchioles become narrowed causing difficulty in breathing o Mucous lining swells and secretions build up o Triggered by allergens, overexertion, emotion, infection, changes in weather o Treated with Bronchodilators/ nebulizers/ inhalers Pneumonia o Inflammation of the lungs o Not one specific single disease Two main types—Lobar and Bronchial Lobar- one lobe affected at first then spreads Bronchial- starts in the bronchi and spreads to the lung tissue o Symptoms include fever, chills, shortness of breath, severe cough, chest pain, Pleurisy (inflammation of the membrane lining the lungs and chest cavity) Tuberculosis o Infectious bacterial disease of the lungs o Symptoms include fever, chills, sweating, weakness, poor appetite, shortness of breath, severe coughing o Treatment includes Quarantine, and immediate Medical supervision Emphysema o Disease in which alveoli in the lungs burst and blend to form fewer, larger sacs with less surface area. o Normal exchange of O2 and CO2 is disrupted. o Symptoms include difficulty in breathing, chronic cough o Caused by breathing in foreign matter such as smoke and air pollutants over a long period of time o Condition can not be reversed Sinusitis o Inflammation of membrane lining the facial sinuses (air filled cavities in the bones that surround your nose) o Symptoms include fever, stuffy nose, throbbing ache in the affected area o Treatments include use of antibiotics/ decongestants/ and steam inhalants