seasons oceans
advertisement
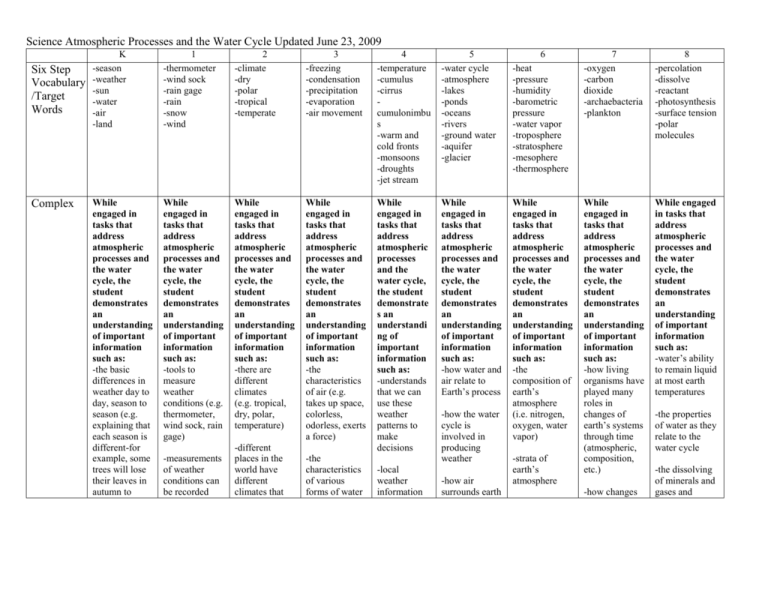
Science Atmospheric Processes and the Water Cycle Updated June 23, 2009 Six Step Vocabulary /Target Words Complex K -season -weather -sun -water -air -land 1 -thermometer -wind sock -rain gage -rain -snow -wind 2 -climate -dry -polar -tropical -temperate 3 -freezing -condensation -precipitation -evaporation -air movement 4 -temperature -cumulus -cirrus cumulonimbu s -warm and cold fronts -monsoons -droughts -jet stream 5 -water cycle -atmosphere -lakes -ponds -oceans -rivers -ground water -aquifer -glacier While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrates an understanding of important information such as: -the basic differences in weather day to day, season to season (e.g. explaining that each season is different-for example, some trees will lose their leaves in autumn to While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrates an understanding of important information such as: -tools to measure weather conditions (e.g. thermometer, wind sock, rain gage) While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrates an understanding of important information such as: -there are different climates (e.g. tropical, dry, polar, temperature) While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrates an understanding of important information such as: -the characteristics of air (e.g. takes up space, colorless, odorless, exerts a force) While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrate s an understandi ng of important information such as: -understands that we can use these weather patterns to make decisions While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrates an understanding of important information such as: -how water and air relate to Earth’s process -measurements of weather conditions can be recorded -different places in the world have different climates that -the characteristics of various forms of water -local weather information -how the water cycle is involved in producing weather -how air surrounds earth 6 -heat -pressure -humidity -barometric pressure -water vapor -troposphere -stratosphere -mesophere -thermosphere While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrates an understanding of important information such as: -the composition of earth’s atmosphere (i.e. nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor) -strata of earth’s atmosphere 7 -oxygen -carbon dioxide -archaebacteria -plankton 8 -percolation -dissolve -reactant -photosynthesis -surface tension -polar molecules While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrates an understanding of important information such as: -how living organisms have played many roles in changes of earth’s systems through time (atmospheric, composition, etc.) While engaged in tasks that address atmospheric processes and the water cycle, the student demonstrates an understanding of important information such as: -water’s ability to remain liquid at most earth temperatures -how changes -the properties of water as they relate to the water cycle -the dissolving of minerals and gases and Science Atmospheric Processes and the Water Cycle Updated June 23, 2009 prepare for the freezing temperatures of winter) -the sun warms the land and water and they warm the air Simple (Recall and Recognize) Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -season -weather -sun -water -air -land from day to day and longterm may or may not include seasons -the characteristics of seasons (types of weather) (e.g. explaining general information known about seasons - for example leaves change colors during autumn) Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -thermometer -wind sock -rain gage -rain -snow -wind in air (e.g. clouds, fog, rain, snow, hail) -water changes from one form to another through various processes (e.g. freezing, evaporation, melting, condensation) Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -climate -dry -polar -tropical -temperate Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -freezing -condensation -precipitation -evaporation -air movement to describe patterns of change over a period of time (e.g. temperature, precipitation, cloud types and formation, wind speed/directi on) Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -temperature -cumulus -cirrus cumulonimbu s -warm and cold fronts -monsoons -droughts -jet stream and as it moves temperature fluctuations and other factors produce wind currents -how most of earth’s surface is covered by water (e.g. oceans, freshwater sources) -how the earth’s motion around the sun and tilt of the earth’s axis of rotation causes seasons Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -water cycle -atmosphere -lakes -ponds -oceans -rivers -ground water -aquifer -glacier -differences between the atmosphere of earth and those of other planets -understand factors that create and influence weather in the atmospheric composition may decrease the capacity of the environment to support some life forms transport to the oceans Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -oxygen -carbon dioxide -archaebacteria -plankton Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -percolation -dissolve -reactant -photosynthesis -surface tension -polar molecules -water as a reactant to photosynthesis -understand how to use weather maps and data to predict weather Recognizing and recalling specific terminology such as: -heat -pressure -humidity -barometric pressure -water vapor -troposphere -stratosphere -mesophere -thermosphere Science Atmospheric Processes and the Water Cycle Updated June 23, 2009 Recognizing and recalling isolated details such as: -there are four seasons on earth -the sun is very important to earth Recognizing and recalling isolated details such as: -each season is different -changes occur in the sky as day changes into night -the sun is a star Recognizing and recalling isolated details such as: -air is a substance that surrounds us and takes up space -rain and drizzle are types of precipitation Recognizing and recalling isolated details such as: -weather patterns move east to west in the United States Recognizing and recalling isolated details such as: -sources of water -air is substance, wind is moving air -the processes in the water cycle Recognizing and recalling isolated details such as: -heat, air movement, pressure, humidity, oceans -how weather patterns are related to atmospheric pressure -global patterns of atmospheric movement (e.g. El Nino, trade winds, easterlies and westerlies) -factors that affect earth’s climate (e.g. volcanic eruptions, impacts of asteroids, glaciers) - Recognizing and recalling isolated details such as: -water moderates temperature -plants use CO2 and produce O2 and food during photosynthesis Recognizing and recalling isolated details such as: -how color and temperature are related in stars