Valid Pointer Operations
advertisement
POINTER OPERATIONS
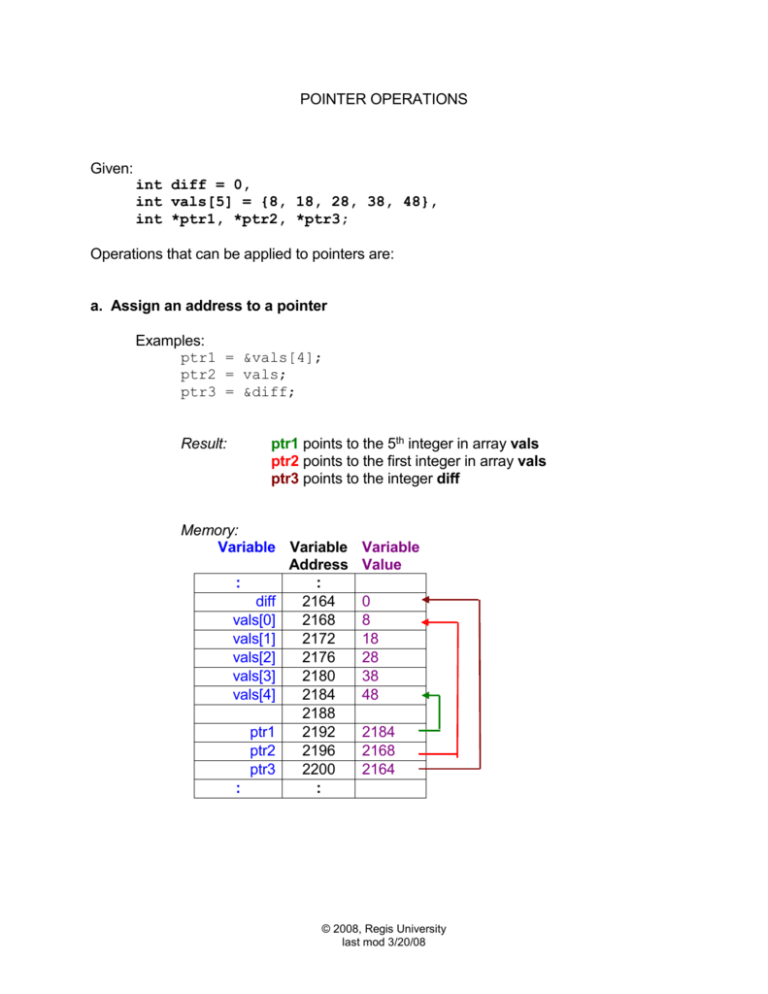
Given:
int diff = 0,
int vals[5] = {8, 18, 28, 38, 48},
int *ptr1, *ptr2, *ptr3;
Operations that can be applied to pointers are:
a. Assign an address to a pointer
Examples:
ptr1 = &vals[4];
ptr2 = vals;
ptr3 = &diff;
Result:
ptr1 points to the 5th integer in array vals
ptr2 points to the first integer in array vals
ptr3 points to the integer diff
Memory:
Variable Variable
Address
:
:
diff
2164
vals[0]
2168
vals[1]
2172
vals[2]
2176
vals[3]
2180
vals[4]
2184
2188
ptr1
2192
ptr2
2196
ptr3
2200
:
:
Variable
Value
0
8
18
28
38
48
2184
2168
2164
© 2008, Regis University
last mod 3/20/08
b. Increment a pointer (if it points to an array)
Example:
ptr2 += 2;
Result: Moves ptr2 down 2 indices, to point to the 3rd item in array vals
Variable Variable
Address
:
:
diff
2164
vals[0]
2168
vals[1]
2172
vals[2]
2176
vals[3]
2180
vals[4]
2184
2188
ptr1
2192
ptr2
2196
ptr3
2200
:
:
Variable
Value
0
8
18
28
38
48
2184
2176
2164
c. Decrement a pointer (if it points to an array)
Example:
ptr1 -= 3;
Result: Moves ptr1 up 3 indices to point to the 2nd item in array vals
Variable Variable
Address
:
:
diff
2164
vals[0]
2168
vals[1]
2172
vals[2]
2176
vals[3]
2180
vals[4]
2184
2188
ptr1
2192
ptr2
2196
ptr3
2200
:
:
Variable
Value
0
8
18
28
38
48
2172
2176
2164
© 2008, Regis University
last mod 3/20/08
NOTE:
Remember that all pointer calculations are performed on the pointer type,
not on the physical address. Therefore, if a pointer to an integer is
incremented, it is adjusted to point to the next integer (i.e. the address stored
in the pointer is incremented by the size of an integer).
The next two operations only make sense if the two pointers are pointing to data within
the same array, as in our example:
Variable Variable Variable
Address Value
:
:
diff
2164
0
vals[0]
2168
8
vals[1]
2172
18
vals[2]
2176
28
vals[3]
2180
38
vals[4]
2184
48
2188
ptr1
2192
2172
ptr2
2196
2176
ptr3
2200
2164
:
:
d. Subtract two pointers (to find distance between them)
Example:
diff = ptr2 – ptr1;
Result:
Since ptr1 points to the 2nd item, and ptr2 points to the 3rd
item, they are ONE integer apart. So diff gets the value 1.
NOTE: The result is computed in units of the data type pointed to, not in actual
addresses.
e. Compare the pointers (to see if one is ahead of the other)
Example:
while (ptr1 < ptr2)
ptr1++;
Result: Increments ptr1 until it points to the same integer address as ptr2.
NOTE: You CANNOT add, multiply or divide two pointers.
© 2008, Regis University
last mod 3/20/08











