Definitions, Characterization, Bioavailability, and Drug Interactions
advertisement

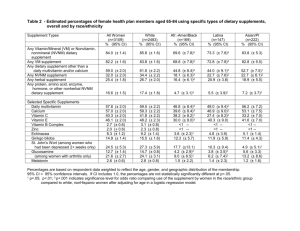
F&N 1-7 03/08 Abstract Multivitamin-Multimineral Supplements: Definitions, Characterization, Bioavailability, and Drug Interactions Prepared by: Janice Hermann, Ph.D., R.D./L.D. Nutrition Education Specialist 301 HES/NSCI Cooperative Extension Service Stillwater, OK 74078-6111 (405) 744-4601 Sources: Yetley, EA. J Am Clin Nutr. 2007;1(suppl):269S-276S. IMPLICATIONS FOR COOPERATIVE EXTENSION. Dietary supplement use is becoming increasingly common in the United States. Although information on potential drug interactions with multivitamin/multimineral supplements is scarce. Multivitamin/multimineral supplements may interfere with or enhance drug effects in unexpected ways. Because information is limited the ability to generalize drug interactions to multivitamin/multimineral supplements is problematic. Drug-nutrient interactions can interfere with a drug’s action, enhance a drug’s actions, or cause unexpected side effects. Certain drugs have also been reported to decrease the effectiveness of vitamins and minerals. However, limited information is available on possible or actual drugvitamin/mineral interactions. Some reported dietary supplement/drug interactions include vitamin E and aspirin, causing a risk of an additive antithrombotic effect and between vitamin E and warfarin resulting in an increased risk of bleeding. In a controlled clinical trial of patients with coronary heart disease, an antioxidant supplement containing vitamins C and E, β-carotene, and selenium blocked the beneficial response of HDL to niacin therapy. Multivitamin/multimineral supplement manufacturers have not been required to evaluate the possibility of drug interactions, but legislation is currently under consideration to mandate reporting of serious adverse dietary supplement/drug effects. Reports of suspected or documented serious adverse effects may be voluntarily submitted to the Food and Drug Administration's MedWatch program or other organizations, such as poison control centers. If multivitamin/multimineral supplement – drug interactions are documented, information regarding this would more likely be required for drug labeling than for supplement labeling. However, manufacturers and retailers may voluntarily place warning statements on mutltivitamin/multimineral supplements. These statements do not require review or approval by the Food and Drug Administration.