NS440 Exam 3 - WordPress.com
advertisement

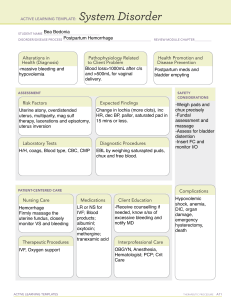
Postpartum nursing assessment- BUBBLE-PLEB B- breast/chest U-uterus B-bladder B-bowels L-lochia (COCA) E- episiotomy/laceration/incision (REEDA) P-pain L-legs/extremities E-emotional status B-bonding/attachment *REEDA- Redness, Edema, Ecchymosis, Drainage, Approximation; COCA- Color, Odor, Consistency, Amount Early discharge criteria for mom and infant- mom recovered & prepared to care for self & infant, at least 2 successful feedings >10mins, f/u care Postpartum Physiologic Changes: -uterus- involution- return of uterus to pre-preg state; autolysis of tissue w/o excess hormones of preg; @2-3cm under umbilicus after delivery, @ or 1cm above at 12hr, then dec’s 1cm/24h); placental site does not scar; locia (rubra- 13days, bright red; serosa- 10-22days, pinkish brownish; albaup to 6wks, whitish) -cervix- begins to regenerate 2-3days pp; normal by 1wk -vagina- muscle tone never completely returns, but back to normal size 6-10wks -ovarian fxn & menstruation- return of fxn varies w/ breastfeeding; w/ bf may not ovulate but still need birth control; nonbf ovulation returns 4-8wks, takes 3-4 cycles before normal, need birth control -breasts- colostrums first few days milk; engorgement 3-4 days -GI- hungry after delivery, have food avail; may take 3-4 days for b.m. -VS- temp slightly inc’d, brady 1st wk, BP may be inc’d if there was pre-eclampsia (continue MgSO4 24-48hr after), dec’d w/ blood loss -Cardiac- CO inc’d first 48hrs, returns ~3wks; WBC inc’d, hypercoag; excess fluid dec’d thru urine & sweat w/in 6mos -muscoloskeletal- ligaments tighten, joints stabilize by 68wks -integumentary- chloasma (mask) diasappears @ end of prego; hyperpigmentation of areolae & linea nigra may not completely regress; stretch marks fade but usually do not disappear; vascular abnormalities (ie: spider angiomas) diminish; hair growth slows (may experience hair loss); profuse diaphoresis -immune- no significant change; if not immune or equivocal to rubella, recheck & give immunization if neede\ -Urinary- can take hrs after epidural to be able to feel fullness; encourage frequent voiding; void before assessing fundus; w/in 12 hr begin losing excess fluid (profuse diaphoresis @ night for 2-3days pp); may have proteinuria 12 days pp in ~50% -Endocrine- estrogen & progesterone significantly dec after expulsion of placenta reaching lowest 1wk pp breast engorgement, dieresis of excess fluid; nonlactating women estrogen begins to inc by 2 wks pp; pituitary & ovarian hormones remain high in breastfeeding suppress ovulation~ 6mos, nonbreastfeeding ovulation as early as 27 days, mean 70-75 days, resume menstruation ~3mos Subinvolution- failure of uterus to return to nonpregnant state; 2o infection, retained placental parts, excessive vigorous massage of uterus Self care Education- SIDS/safety, pacifier use, when sex is ok (generally 6wks), contraception, pp blues/depression, f/u appts After birth pains- inc’s w/ # of preg & breastfeeding, Methergine; tx- ibuprofen Perineal discomfort- stretching, bruising; tx- ice q20min first 24hr, sitz baths after 24hrs Episiotomy/tears- preicare w/ warm water bottle, pat dry, wipe front to back Breast discomfort-non breastfeeding mom- good bra, do not massage, avoid hot shower/bath -breastfeeding- early & frequent feedings (q2-3hr; wash breast daily w/ warm water, avoid soap (dries out); for cracked nipples break seal before removing baby, proper latching, air-dry nipples (15-20min after feed), rotate positions, Lanolin or milk for sore nipples Nutrition- dec’d peristalsis, need inc fluids & fiber; cont prenatal vit & possibly need irion; healthy eating; +500cal for breastfeeding To assess breasfeeding: LATCH-L (latching on) A (audible swallowing) T (type of nipple- erect, flat, inverted) C (comfort) H (help) Medications- consult w/ provider before taking any OTC or Rx meds Post Partum Psychological Disorders Mood disorders -postpartum blues- adjustment rx w/ depressed moodoccurs 2-3days pp, disappears 1-2wks, still in touch w/ reality, able to fxn, crying/lonliness/anxiety/confusion -pp depression- w/in 6mos of birth, lasts >2wks, interferes w/ ADL’s, anorexia/wt loss/ insomnia/hygiene neglect/hypochondria/psychomotor agitation/disorientation; requires intervention (antidepressants, anxiolytics, ECT, therapy); prior h/o depression inc’s risk -pp psychosis- break in reality/delusions/panic; inc’d risk of suicide or harm to baby; psych emergency, may require hospitalization, tx w/ antipsychotics & mood stabilizers (lithium) PP onset panic disorder- 3-5% of pp pts Adaptation to Parenthood and Parent-Infant Interactions -taking in- pt focuses on her needs (food, comfort), letting others care for infant -taking hold- pt regains control of bodily fxns, active in her/baby cares, best time to teach -letting go- loss over separation of baby from body *adolescents need extra attention Attachement behaviors- eye contact, maternal gazing, finger grasping, rooting/seeking, comfort from mom/dad’s voice -factors affecting- pain, fatigue, knowledge, support system, expectations of newborn, previous experience, maternal temperament, infant characteristics, others (c-section, preterm/ill infant, multiple births) Postpartum hemorrhage-nursing process Definition- >1000ml w/ c section, >500ml vag; the most common & most serious type of excessive obstetric blood loss Predisposing factors- previous hemorrhage, previa, MgSO, clotting disorders, multiple gestations, abruption, uterine atony (most frequent cause), polyhydramnios, macrosomic baby, poor uterine tone, rapid/prolonged/precipitous labor, induction/augmentation, chorioamnionitis, anesthesia, over massage Causes- early: retained placental fragments, tears/lacerations, hematoma, inversion of uterus, DIC (seen in PIH, HELLP, & stillbirths); late: subinvolution from infection, retained placental parts, excessive vigorous massage of uterus s/s- inc’d lochia, >1pad/hr; boggy uterus (tx fundal massage, notify PCP if not corrected), u/a to locate fundus (sign of atony); tachycardia, dec BP classification- early/acute/primary (w/in first 24hr of delivery); late/secondary (after 24hr to 6wks) interventions- may need to cath to empty bladder & monitor I/O, fundal massage, inc Pitocin, Metergine (do not give if HTN), Hemabate (not ok for asthmatics); VS & SpO2, O2, labs (H/H, pt, ptt, fibrinogen), surgery (vessel repair, hysterectomy) herbal remedies- witch hazel & lady’s mantle (homeostatic), blue cohosh & cotton root bark (oxytocic), motherwort & sheperd’s purse (promotes uterine contraction), alfalfa leaf & nettle (inc avail of vit K, inc Hgb), red raspberry (homeostatic, promotes uterine contraction) Hemorrhagic Shock- perfusion of body organs may become severely compromised, leading to significant morbidity or mortality of mom; emergency situation -s/s- persisten significant bleeding (pad soaked in <15min); dec BP, pale, cool/clammy, tachycardia, anxiety, air hunger -interventions- notify PCP, fundal massage for atony, O2 810via mask, I/O, VS, lung sounds, maintain IV site, determine cause, fluid mngmnt (blood, IV crystalloids 3ml/L loss) Medications utilized in caring for the patient with postpartum hemorrhage- Pitocin inc to promote uterine contractions, Metergine (do not give if HTN), Hemabate (not ok for asthmatics) Postpartum (Puerperal) Infections-any inf w/in 28 days of delivery; strep most common s/s- temp >38 (100.4) on 2 or more occasions after 24h pp; in pain, malaise, dysuria, subinvolution, foul odor -prevention most effective & inexpensive tx; strict aseptic technique; standard precautions Endometritis- lining of uterus; *most common pp inf; seen more in c-sections; s/s- inc’d tenderness; fever (>38), inc HR, chills, anorexia, Nausea, fatigue,foul smelling profuse lochia; tx- ABX, encourage fluids, analgesics, fowler’s to promote drainage Wound/lacerations- s/s REEDA; tx- ABX, analgesics, sitz bath, hot/cold UTI’s- esp w/ freq caths, pelvic exams & w/ epidurals; s/sdysuria, frequency, urgency, lowgrade fever, retention, hematuria, pyuria, plank pain tx- fluids, hygiene (front to back), ABX Mastitis- staph from infants mouth 2o to improper latching, missed feeding, improper fitting bra; usually 5-6wks pp, s/sunilateral, reddened tender area, flu-like symptoms; prevention- handwashing, proper breast care & feeding, good/clean bra; tx-ice pack after feeding, cont feeding (start on unaffected side), ABX; assess for abscess- if found, no feeding on this breast, pump & dump until healed (ABX, drained, heat); Thromboembolic Disorders-nursing process Risk factors- pp immobility/inactivity, prolonged sitting/standing, c section, varicose veins or varicosities, DM, smoking, multiparity, h/o venous thrombosis, obesity, mom>35yr dx- venography, US, CT, MRI; screen w/ Homan’s sign, assess for hard vessels & pain w/ edema interventions- *prevention*- early ambulation/ROM, avoid long sit/stand/immobile, avoid crossing legs, elevate while sitting, quit smoking, fluids, stockings -SVT- analgesics (NSAIDS), rest w/ legs elevated, heat -DVT- @ risk for PE; anticoag (IV heparin 5-7 days, f/b oral Coumadin up to 3 mo), have protamine sulfate avail (antidote to heparin), teach s/s of med problems, take as ordered, do NOT stop abruptly -PE- assess: dyspnea, cough, pleuritic CP, VS, temp, resp status/sounds, pain, mental status, neck vein distention Interventions- semi fowlers w HOB up, O2, con’t heparin, analgesics Loss and Grief Maternal or fetal/neonate death, loss of what was hoped for (natural birth, girl/boy, etc), perception of loss of control during birthing (more common in Bradley pts), birth of child w/ handicap Plan of care- actualize loss, provide time to grieve, interpret normal feelings, allow for individual differences, cultural & spiritual needs, physical comfort, options for parents (seeing/holding, bathing/dressing, privacy, visitations, religious rituals/funeral arrangements, special memories, pictures) Maternal death- rare; families at risk for developing complicated bereavement & altered parenting, referral to social services