Elodea Cell Transport Lab
advertisement

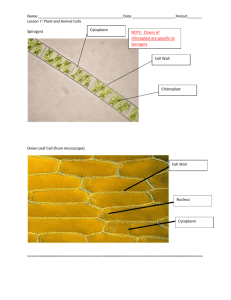
ELODEA MEMBRANE TRANSPORT LAB Background In order for cells to maintain the chemical reactions occurring inside themselves substances must move back and forth between a cell’s external and internal environments. More specifically, reactants need to be acquired by the cell while harmful products must be eliminated. For example, during respiration your cells must acquire oxygen and must eliminate carbon dioxide. Other products, like ATP (an energy molecule) are beneficial and are used by the cell. As you know, the cell membrane is a fluid structure composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, and various membrane proteins (adhesion, recognition, receptor, and transport). The precise location through which a substance travels is dependent on two important molecular characteristics; the molecule size and charge (polarity). In general, small uncharged (non-polar) substances move through the lipid portion of the membrane, while small charged (polar) and larger molecules must enter the cell through proteins. In most instances, the movement of substances requires the existence of a concentration gradient across the cell membrane and substances move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. In such situations, substances will move by osmosis, diffusion, or passive diffusion (facilitated diffusion). When substances require movement against their concentration gradient active transport is used. In the following laboratory exercise you will investigate the movement of substances into and/or out of the membrane of an elodea leaf in order to gain a greater understanding of processes of osmosis and diffusion. Objective 1. You should understand how and why water moves through a semi-permeable membrane in various liquid environments. Materials 1 Elodea Leaf soaked in Distilled Water 1 Elodea Lead soaked in Saltwater Compound Light Microscope 1 Microscope Slide 1 Cover Slip Procedure Elodea Exercise 1. While you are waiting for the eggs to sit, acquire a Compound Light Microscope, Microscope Slide, Cover Slip, and an Elodea Leaf that has been soaking in Distilled Water. 2. Place the Elodea Leaf on the Microscope Slide, use a dropper to transfer a single drop of water on top of the leaf, and then gently place the Cover Slip over the leaf. 3. Focus on the Elodea Leaf so that you can examine a number of individual cells, and complete the Elodea Exercise Questions on the worksheet provided. 4. Then, dispose of the current Elodea Leaf and acquire one that has been soaking in Saltwater. 5. Place the Elodea Leaf on the Microscope Slide, use a dropper to transfer a single drop of saltwater on top of the leaf, and then gently place the Cover Slip over the leaf. 3. Focus on the Elodea Leaf so that you can examine a number of individual cells, and complete the Elodea Exercise Questions on the worksheet provided. MEMBRANE TRANSPORT LAB QUESTIONS Name: __________________________ Elodea Exercise 1. In the space provide below make a sketch of the Elodea cell that you have observed, and using your book label the cell wall, chloroplasts, and cell membrane and central vacuole (hypothesize where it should be). 2. What is the function of the cellular structures and organelles labeled above? a. Cell Wall b. Chloroplast c. Central Vacuole 3. In the space provide below make a sketch of the Elodea cell that you have observed, and using your book label the cell wall, chloroplasts, and cell membrane and central vacuole (hypothesize where it should be). 4. How has the position of the Chloroplast changed between the Elodea Leaf in Distilled Water and Saltwater? To understand what is going on in these situations you need to read pages 118121 and answer the following questions. 5. Describe the motion of molecules in a fluid. 6. Define diffusion. 7. When does the diffusion of a molecule in solution stop? 8. How are cell membrane considered selectively permeable. 9. Contrast the movement of molecules by passive and facilitated transport. Based on our previous discussions, what are the contrasting characteristics of molecules that travel in these two manners? 10. Based on your knowledge of the terms hypertonic and hypotonic, label the two solutions diagramed below relative to each other. 11. Does water tend to move across a permeable membrane from a hypertonic to a hypotonic solution OR from a hypotonic to hypertonic solution? 12. Given that there are more solutes (things dissolved in water) outside the Elodea cell when it is immersed in saltwater, first identify if the surrounding solution is hypertonic or hypotonic. Then, identify using an arrow which direction water will tend to move in the cell below. Assuming that the cell membrane is located between the cell wall and chloroplasts, explain why the chloroplast become clumped when the Elodea is placed in saltwater. Cell 13. Given that there are more solutes (things dissolved in water) inside the Elodea cell when it is immersed in distilled water (more like its real environment), first identify if the surrounding solution is hypertonic or hypotonic. Then, identify using an arrow which direction water will tend to move in the cell below. Then, explain why the chloroplasts become are spread out in this situation and why it might be important that the cells have a cell wall. Cell 14. View the video link on the action of the freshwater paramecium’s contractile vacuole. Based on the knowledge you have gained regarding osmosis, hypothesize the function of the contractile vacuole. 15. Discuss issues associated with living saltwater that a saltwater fish would have to adapt to/overcome? 16. Explain how pouring salt on a slug kills it.