FC air pollution
advertisement
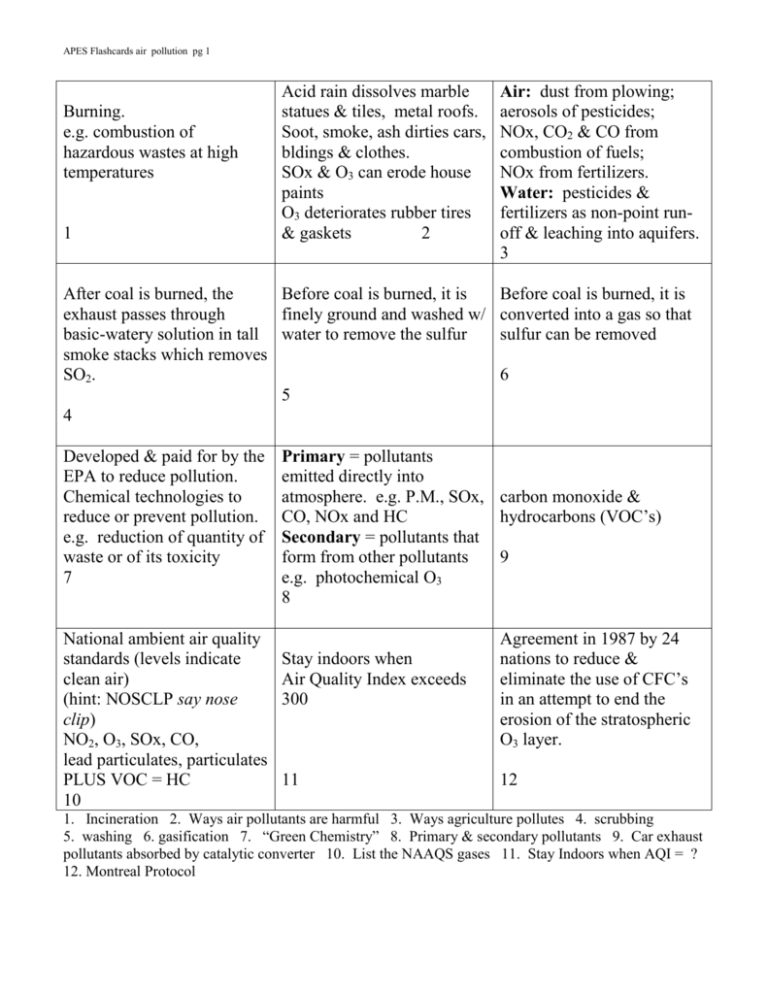
APES Flashcards air pollution pg 1 Burning. e.g. combustion of hazardous wastes at high temperatures 1 Acid rain dissolves marble statues & tiles, metal roofs. Soot, smoke, ash dirties cars, bldings & clothes. SOx & O3 can erode house paints O3 deteriorates rubber tires & gaskets 2 After coal is burned, the Before coal is burned, it is exhaust passes through finely ground and washed w/ basic-watery solution in tall water to remove the sulfur smoke stacks which removes SO2. 5 4 Developed & paid for by the EPA to reduce pollution. Chemical technologies to reduce or prevent pollution. e.g. reduction of quantity of waste or of its toxicity 7 National ambient air quality standards (levels indicate clean air) (hint: NOSCLP say nose clip) NO2, O3, SOx, CO, lead particulates, particulates PLUS VOC = HC 10 Air: dust from plowing; aerosols of pesticides; NOx, CO2 & CO from combustion of fuels; NOx from fertilizers. Water: pesticides & fertilizers as non-point runoff & leaching into aquifers. 3 Before coal is burned, it is converted into a gas so that sulfur can be removed 6 Primary = pollutants emitted directly into atmosphere. e.g. P.M., SOx, carbon monoxide & CO, NOx and HC hydrocarbons (VOC’s) Secondary = pollutants that form from other pollutants 9 e.g. photochemical O3 8 Stay indoors when Air Quality Index exceeds 300 11 Agreement in 1987 by 24 nations to reduce & eliminate the use of CFC’s in an attempt to end the erosion of the stratospheric O3 layer. 12 1. Incineration 2. Ways air pollutants are harmful 3. Ways agriculture pollutes 4. scrubbing 5. washing 6. gasification 7. “Green Chemistry” 8. Primary & secondary pollutants 9. Car exhaust pollutants absorbed by catalytic converter 10. List the NAAQS gases 11. Stay Indoors when AQI = ? 12. Montreal Protocol APES Flashcards air pollution pg 2 NOx + H.C. + O2 + sunlight tropospheric O3 O2 + UV stratospheric O3 13 No such thing!! However, there is a thinning of the O3 layer in stratosphere to less than 200 ppb. Thinning occurs during Antarctic winter Strong winds that form during cold Antarctic winter, circling tornado-like. The vortex isolates ice-crystal clouds which promote the CFC-O3 reactions. 15 14 UV-A longest wavelength & not absorbed by O3, so all UV-A reaches E’s surface UV-B is absorbed by stratospheric O3. UV-C shortest wavelength & is absorbed by E’s atmosphere including O3 16 Condition when at least 25% of workers inside a building complain of physical ailments. When outside, the ailment goes away. Usually no one knows exactly what causes SBS. 19 Also called L.A. smog or photochemical smog. On hot summer days where car engines burn gasoline. N2 NO2 + VOC + sunlight O3 Nitrogen gives brownish color. 22 Peroxyacetyl nitrates (PAN) = one of the chemicals formed during the photochemical reaction of NOx + VOC’s Threat: very damaging to plants 17 Rain, dew, particles or ash with a pH lower than 5.6 Usually sulfuric acid (burning coal) or nitric acid (car exhaust), but sometimes is hydrochloric acid (industrial processes) 18 Ventilation sys: make sure Radon emitted from rock. size matches volume of Gases migrate up through building, change filters often soils into basements. Can Source removal: smokers diffuse into groundwater, outside, replace old bedding into wells: drinking or Replace formaldehyde breathing in shower steam. materials. Even tho short ½ life, Cover over lead & asbestos. continual exposure can lead 20 to lung disease. 21 Also called London smog or In 1984 an accidental release industrial smog. of a pesticide killed 2000 During winter when burning people as they lay sleeping. coal for heat & industry. 15,000 were injured, many Sulfur in coal SOX + becoming blind. H2O H2SO4 These people should have Gray color comes from been wakened and warned to London fog. escape!!! 24 23 13. Formation of tropospheric O3 & stratospheric O3 14. Ozone hole 15. Polar vortex 16. Types of UV 17. PAN’s 18. Acid deposition 19. Sick Building Syndrome 20. Ways to reduce indoor air pollution 21. Ways radon can enter buildings 22. Brown smog 23. Gray smog 24. Bhopal, India incident APES Flashcards air pollution pg 3 Source: particle board, furniture, foam insulation Threat: irritant to eyes, throat, lungs, skin. Can cause nausea & dizziness. Source: pipe insulation, ceiling and floor tiles, asbestos shingles, brake linings Threat: lung disease, lung cancer 25 38 Colorless, odorless, radioactive gas that forms when uranium decays. Half-life = 3.8 days releasing alpha particle. Threat: longtime breathing of radon is linked to lung cancer. 40 Pollen, dust, ash, seasalt, sand, smoke, pet dander, rubber from tires, lead particles, Threat: blocks lung pathways, can be toxic Colorless, tasteless gas. Source: combustion 43 This lubricant was once added to gasoline to reduce the wear and tear on a car’s engine. Now it’s illegal. 46 Threat: combines w/ hemoglobin preventing the transport of O2 w/in the body. i.e. suffocation 41 Volatile organic = hydrocarbons natural gas, methane, butane, propane Source: cars 56%, industry 16%, solvent evaporatives 9% Threat: forms L.A. smog 44 Source: from agricultural fertilizers and burning of fossil fuels Source: pipes, house paint before 1970’s. Threat: causes learning disabilities, behavioral problems, ADD, seizures, comas, infertility, even death. Can lower IQ 39 chlorofluorocarbons. Sources: refrigerants (freon), propellants (in spray cans), solvents & cleaning agents. Threat: as rises into stratosphere, combines w/ O3 producing O2 (removal of strato. O3) 42 Sources: tobacco smoke, radon gas, CO, dust mites, mold, pollen, remodeling dust, pesticides, bacteria, formaldehyde, etc. Threat: headache, nausea, sick building syndrome 45 Source: from burning coal w/ high sulfur concentration Threat: one component of brown smog Threat: 47 48 37. Formaldehyde pollution 38. Asbestos 39. Lead 40. Radon 41. Carbon monoxide 42. CFC’s 43. Particulates 44. VOC = HC 45. Indoor air pollution 46. Lead 47. NOx 48. SOx